Abstract
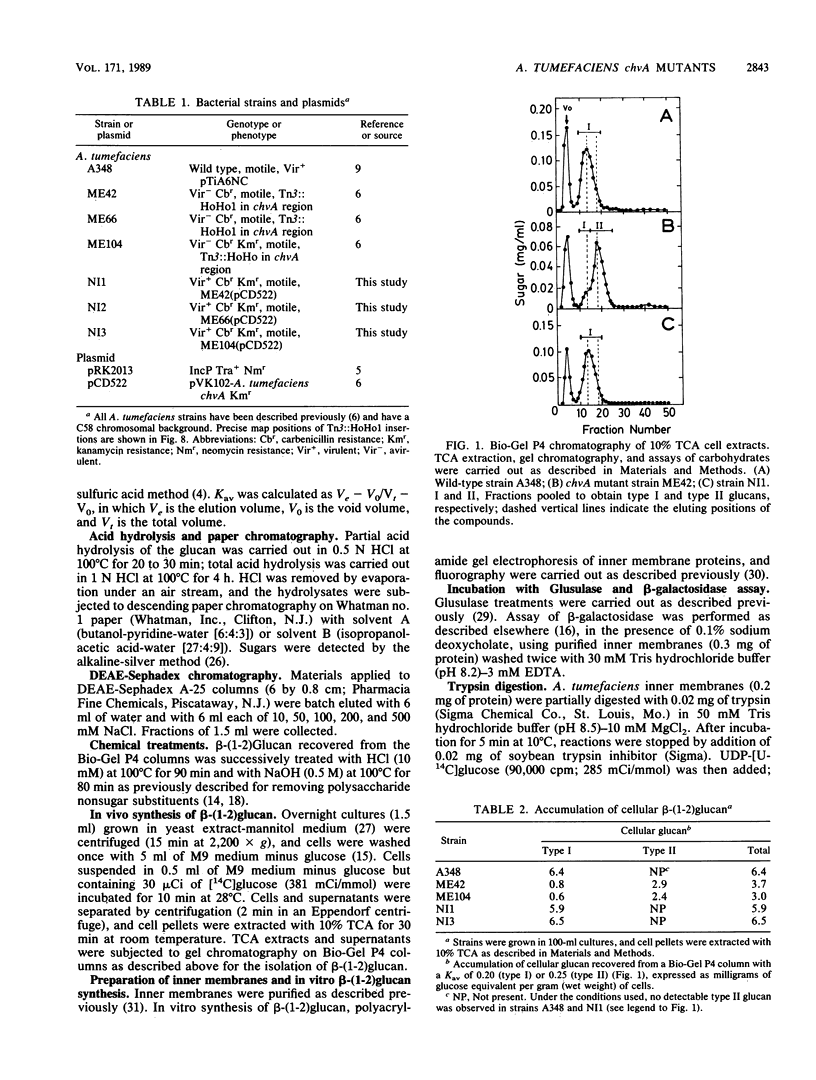
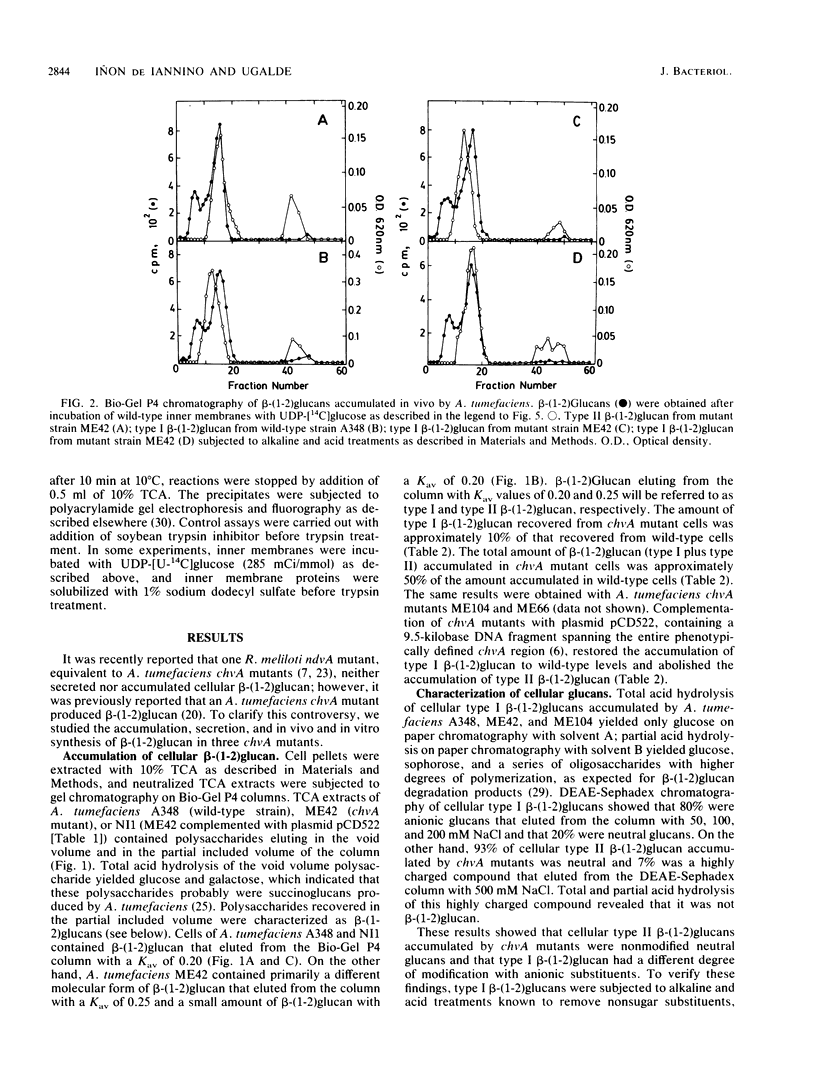
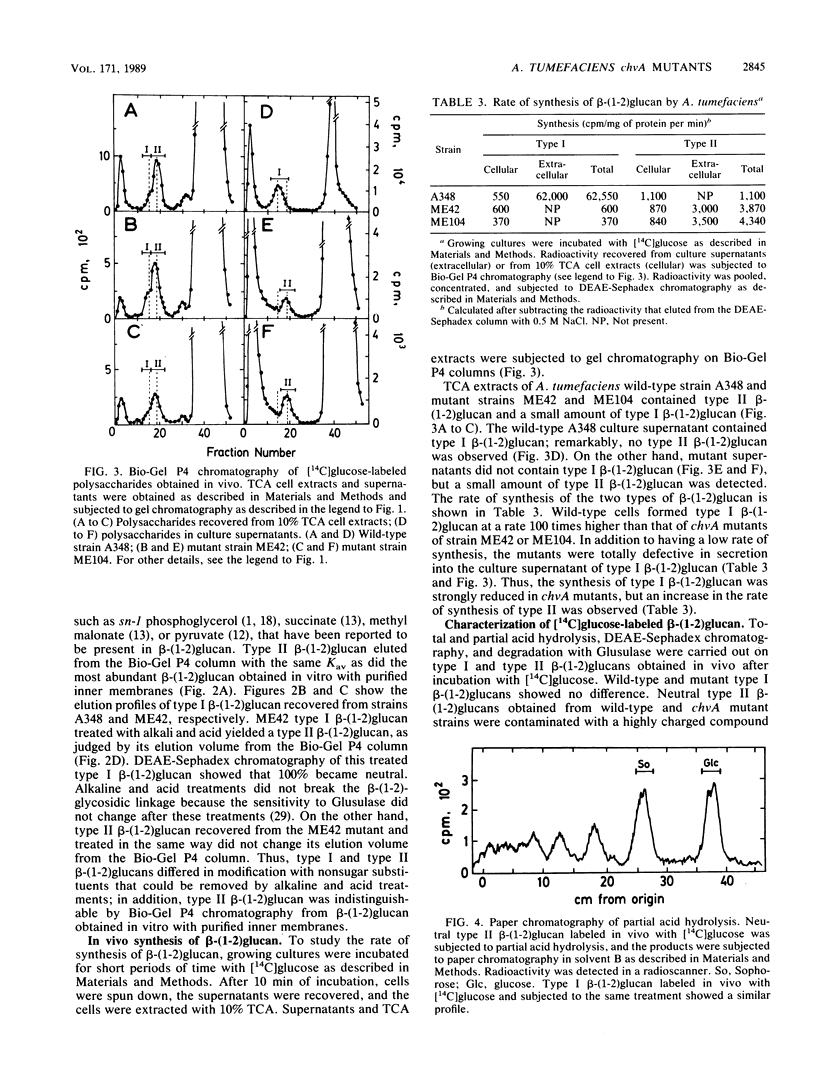
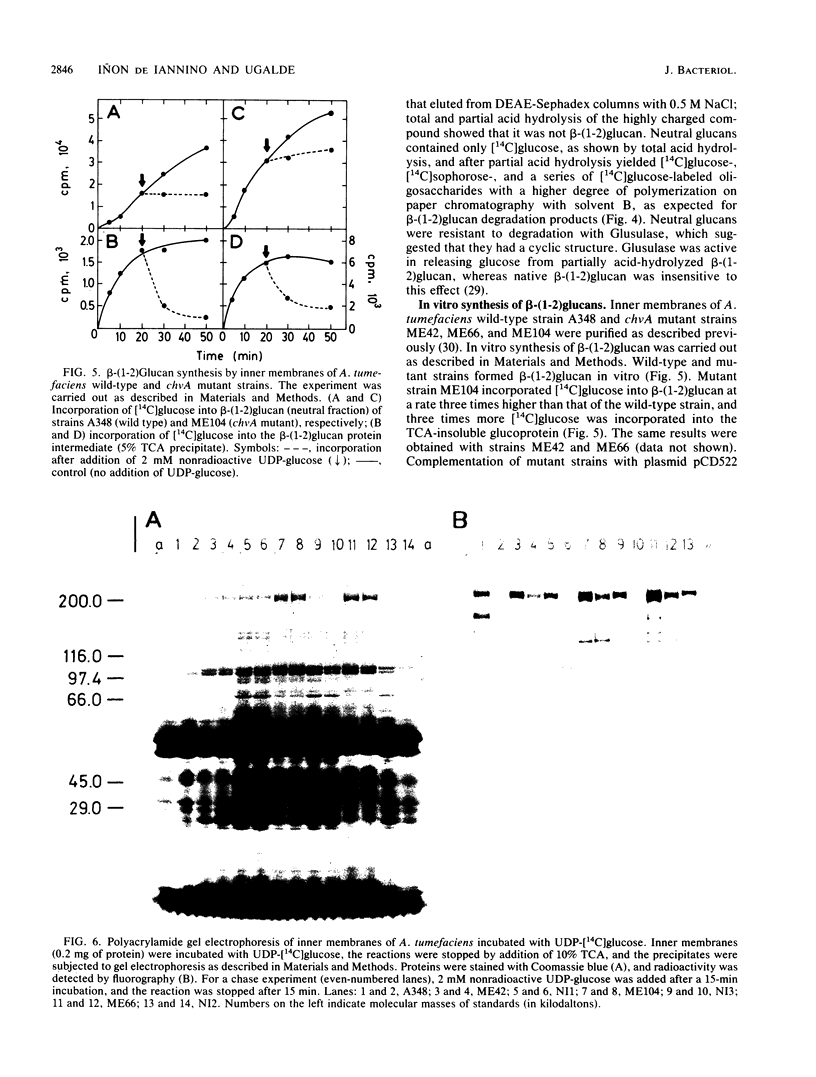
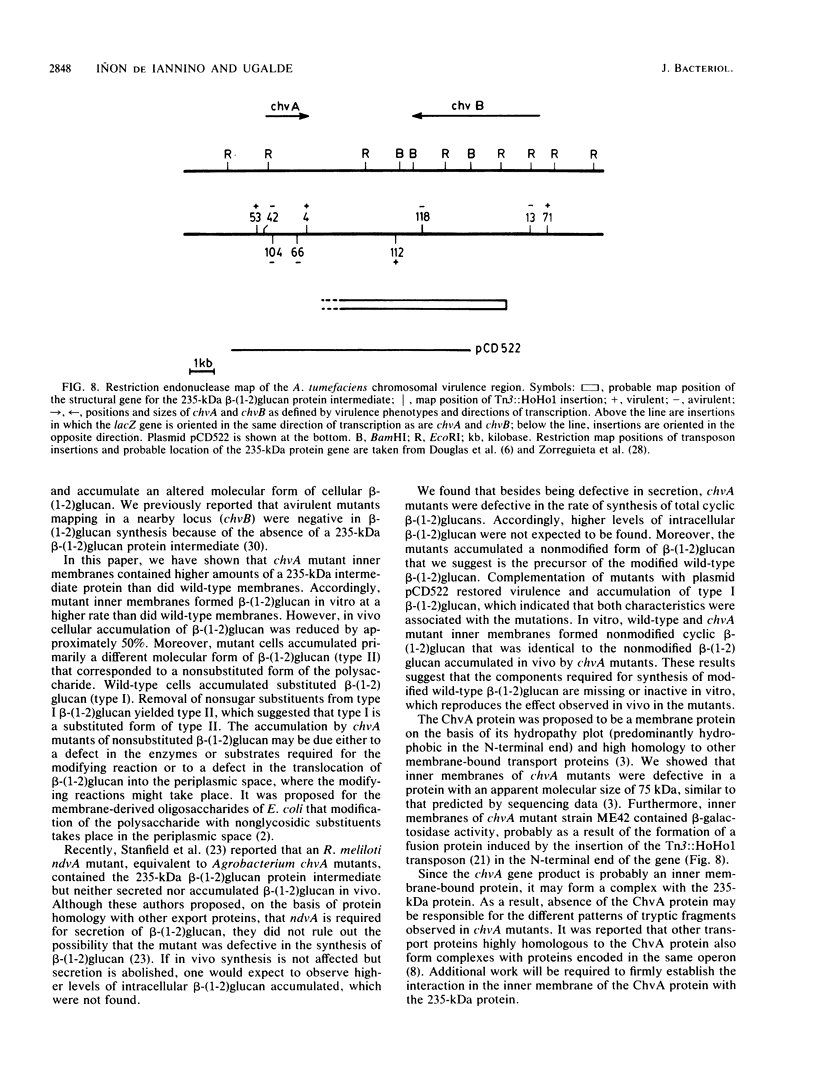
The chvA gene product of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is required for virulence and attachment of bacteria to plant cells. Three chvA mutants were studied. In vivo, they were defective in the synthesis, accumulation, and secretion of beta-(1-2)glucan; however, the 235-kilodalton (kDa) protein known to be involved in the synthesis of beta-(1-2)glucan (A. Zorreguieta and R. Ugalde, J. Bacteriol. 167:947-951, 1986) was present and active in vitro. was present and active in vitro. Two molecular forms of cyclic beta-(1-2)glucan, designated types I and II, were resolved by gel chromatography. Type I beta-(1-2)glucan was substituted with nonglycosidic residues, and type II beta-(1-2)glucan was nonsubstituted. Wild-type cells accumulated type I beta-(1-2)glucan, and chvA mutant cells accumulated mainly type II beta-(1-2)glucan and a small amount of type I beta-(1-2)glucan. Inner membranes of wild-type and chvA mutants formed in vitro type II nonsubstituted beta-(1-2)glucan. A 75-kDa inner membrane protein is proposed to be the chvA gene product. chvA mutant inner membranes had increased levels of 235-kDa protein; partial trypsin digestion patterns suggested that the 235-kDa protein (the gene product of the chvB region) and the gene product of the chvA region form a complex in the inner membrane that is involved in the synthesis, secretion, and modification of beta-(1-2)glucan. All of the defects assigned to the chvA mutation were restored after complementation with plasmid pCD522 containing the entire chvA region.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Bacterial periplasmic transport systems: structure, mechanism, and evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:397–425. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohin J. P., Kennedy E. P. Regulation of the synthesis of membrane-derived oligosaccharides in Escherichia coli. Assay of phosphoglycerol transferase I in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8388–8393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangelosi G. A., Martinetti G., Leigh J. A., Lee C. C., Thienes C., Theines C., Nester E. W. Role for [corrected] Agrobacterium tumefaciens ChvA protein in export of beta-1,2-glucan. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1609–1615. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1609-1615.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. J., Staneloni R. J., Rubin R. A., Nester E. W. Identification and genetic analysis of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens chromosomal virulence region. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):850–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.850-860.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dylan T., Ielpi L., Stanfield S., Kashyap L., Douglas C., Yanofsky M., Nester E., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. Rhizobium meliloti genes required for nodule development are related to chromosomal virulence genes in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Nester E. W. Agrobacterium tumefaciens mutants affected in crown gall tumorigenesis and octopine catabolism. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):732–743. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.732-743.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geremia R. A., Cavaignac S., Zorreguieta A., Toro N., Olivares J., Ugalde R. A. A Rhizobium meliloti mutant that forms ineffective pseudonodules in alfalfa produces exopolysaccharide but fails to form beta-(1----2) glucan. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):880–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.880-884.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hiles I. D., Salmond G. P., Gill D. R., Downie J. A., Evans I. J., Holland I. B., Gray L., Buckel S. D., Bell A. W. A family of related ATP-binding subunits coupled to many distinct biological processes in bacteria. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):448–450. doi: 10.1038/323448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEPSELL H. J., SHARPE E. S. Micro-determination of pyruvic and alpha-keto-glutaric acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Jul;38:443–449. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. J., Kennedy E. P., Reinhold V. N. Osmotic adaptation by gram-negative bacteria: possible role for periplasmic oligosaccharides. Science. 1986 Jan 3;231(4733):48–51. doi: 10.1126/science.3941890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. J., Reinhold V. N., Weissborn A. C., Kennedy E. P. Cyclic glucans produced by Agrobacterium tumefaciens are substituted with sn-1-phosphoglycerol residues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 10;901(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvanesarajah V., Schell F. M., Stacey G., Douglas C. J., Nester E. W. Role for 2-linked-beta-D-glucan in the virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):102–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.102-106.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., An G., Flores C., Nester E. W. A Tn3 lacZ transposon for the random generation of beta-galactosidase gene fusions: application to the analysis of gene expression in Agrobacterium. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):891–898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Zambryski P. C. Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the susceptible plant cell: a novel adaptation of extracellular recognition and DNA conjugation. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield S. W., Ielpi L., O'Brochta D., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. S. The ndvA gene product of Rhizobium meliloti is required for beta-(1----2)glucan production and has homology to the ATP-binding export protein HlyB. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3523–3530. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3523-3530.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W. Biosynthesis and composition of gram-negative bacterial extracellular and wall polysaccharides. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:243–270. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmasky M. E., Staneloni R. J., Leloir L. F. Lipid-bound saccharides in Rhizobium meliloti. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6751–6757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorreguieta A., Geremia R. A., Cavaignac S., Cangelosi G. A., Nester E. W., Ugalde R. A. Identification of the product of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens chromosomal virulence gene. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1988 Mar;1(3):121–127. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorreguieta A., Tolmasky M. E., Staneloni R. J. The enzymatic synthesis of beta 1-2 glucans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 May 1;238(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorreguieta A., Ugalde R. A. Formation in Rhizobium and Agrobacterium spp. of a 235-kilodalton protein intermediate in beta-D(1-2) glucan synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):947–951. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.947-951.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorreguieta A., Ugalde R. A., Leloir L. F. An intermediate in cyclic beta 1-2 glucan biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):352–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90613-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]