Abstract
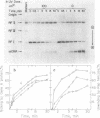
Cloning of the phi X174 viral origin of replication into phage M13mp8 produced an M13-phi X174 chimera, the DNA of which directed efficient replicative-form----single-strand rolling-circle replication in vitro. This replication assay was performed with purified phi X174-encoded gene A protein, Escherichia coli rep helicase, single-stranded DNA-binding protein, and DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. The nicking of replicative-form I (RFI) DNA by gene A protein was essentially unaffected by the presence of UV lesions in the DNA. However, unwinding of UV-irradiated DNA by the rep helicase was inhibited twofold as compared with unwinding of the unirradiated substrate. UV irradiation of the substrate DNA caused a strong inhibition in its ability to direct DNA synthesis. However, even DNA preparations that contained as many as 10 photodimers per molecule still supported the synthesis of progeny full-length single-stranded DNA. The appearance of full-length radiolabeled products implied at least two full rounds of replication, since the first round released the unlabeled plus viral strand of the duplex DNA. Pretreatment of the UV-irradiated DNA substrate with purified pyrimidine dimer endonuclease from Micrococcus luteus, which converted photodimer-containing supercoiled RFI DNA into relaxed, nicked RFII DNA and thus prevented its replication, reduced DNA synthesis by 70%. Analysis of radiolabeled replication products by agarose gel electrophoresis followed by autoradiography revealed that this decrease was due to a reduction in the synthesis of progeny full-length single-stranded DNA. This implies that 70 to 80% of the full-length DNA products produced in this system were synthesized on molecules that carried photodimers. Thus, similarly to its activity on UV-irradiated single-stranded DNA, DNA polymerase III holenzyme can bypass pyrimidine photodimers in the more complex replicative form --->single-strand replication, which involves, in addition to the polymerizing activity, the unwinding of the duplex by the rep helicase and the participation of a more complex multiprotein replisome.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baas P. D., Jansz H. S. Bacteriophage phiX174 DNA synthesis in a replication-deficient host: determination of the origin of phiX DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):633–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brotcorne-Lannoye A., Maenhaut-Michel G., Radman M. Involvement of DNA polymerase III in UV-induced mutagenesis of bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(1):64–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00327511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. Formation of dimers in ultraviolet-irradiated DNA. Basic Life Sci. 1975;5A:61–65. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2895-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Stasiak A., Koller T., Cozzarelli N. R. Duplex DNA knots produced by Escherichia coli topoisomerase I. Structure and requirements for formation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4975–4983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Griffith J., Kornberg A. phiX174 cistron A protein is a multifunctional enzyme in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Harbers B., Hours C., Denhardt D. T. The mechanism of replication of phiX174 DNA. XII. Non-random location of gaps in nascent phiX174 RF II DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 25;99(1):107–123. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Kornberg A. Purification and characterization of phiX174 gene A protein. A multifunctional enzyme of duplex DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5328–5332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Scott J. F., Kronberg A. Enzymatic replication of phiX174 duplex circles: continuous synthesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):295–302. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Walker G. C. Proteins required for ultraviolet light and chemical mutagenesis. Identification of the products of the umuC locus of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):175–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafstrom R. H., Park L., Grossman L. Enzymatic repair of pyrimidine dimer-containing DNA. A 5' dimer DNA glycosylase: 3'-apyrimidinic endonuclease mechanism from Micrococcus luteus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13465–13474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagensee M. E., Timme T. L., Bryan S. K., Moses R. E. DNA polymerase III of Escherichia coli is required for UV and ethyl methanesulfonate mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hevroni D., Livneh Z. Bypass and termination at apurinic sites during replication of single-stranded DNA in vitro: a model for apurinic site mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonczyk P., Fijalkowska I., Ciesla Z. Overproduction of the epsilon subunit of DNA polymerase III counteracts the SOS mutagenic response of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9124–9127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa Y., Akaboshi E., Shinagawa H., Horii T., Ogawa H., Kato T. Structural analysis of the umu operon required for inducible mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4336–4340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh Z. Directed mutagenesis method for analysis of mutagen specificity: application to ultraviolet-induced mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):237–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh Z., Lehman I. R. Recombinational bypass of pyrimidine dimers promoted by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3171–3175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh Z. Mechanism of replication of ultraviolet-irradiated single-stranded DNA by DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. Implications for SOS mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9526–9533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh Z. Replication of UV-irradiated single-stranded DNA by DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli: evidence for bypass of pyrimidine photodimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4599–4603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C., Scheuermann R. H., Echols H. Capacity of RecA protein to bind preferentially to UV lesions and inhibit the editing subunit (epsilon) of DNA polymerase III: a possible mechanism for SOS-induced targeted mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):619–623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry C. S. DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:519–550. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry C., Kornberg A. DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. Purification and resolution into subunits. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6478–6484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shwartz H., Livneh Z. Dynamics of termination during in vitro replication of ultraviolet-irradiated DNA with DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10518–10523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shwartz H., Shavitt O., Livneh Z. The role of exonucleolytic processing and polymerase-DNA association in bypass of lesions during replication in vitro. Significance for SOS-targeted mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18277–18285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessman I. UV-induced mutagenesis of phage S13 can occur in the absence of the RecA and UmuC proteins of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6614–6618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villani G., Boiteux S., Radman M. Mechanism of ultraviolet-induced mutagenesis: extent and fidelity of in vitro DNA synthesis on irradiated templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3037–3041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner J. H., Bertsch L. L., Kornberg A. The deoxyribonucleic acid unwinding protein of Escherichia coli. Properties and functions in replication. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):1972–1980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgate R., Bridges B. A., Herrera G., Blanco M. Mutagenic DNA repair in Escherichia coli. XIII. Proofreading exonuclease of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme is not operational during UV mutagenesis. Mutat Res. 1987 Jan;183(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(87)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarranton G. T., Gefter M. L. Enzyme-catalyzed DNA unwinding: studies on Escherichia coli rep protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1658–1662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]