Abstract
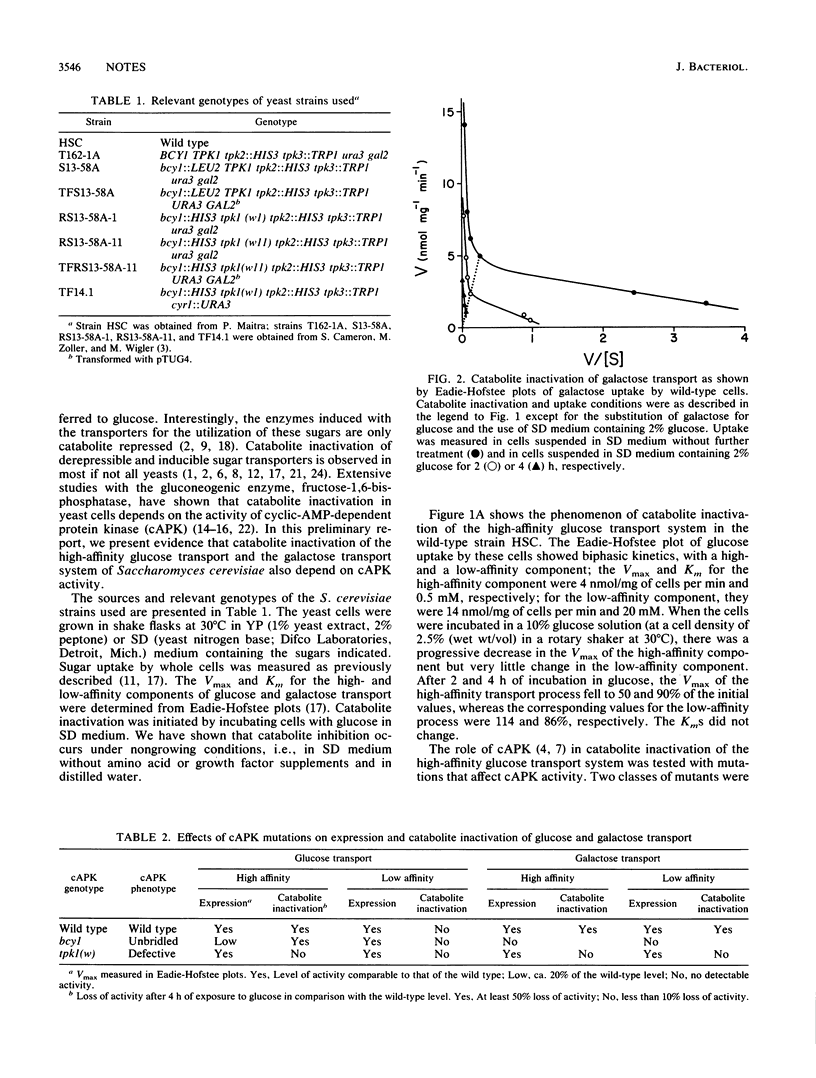
The derepressed high-affinity glucose transport system and the induced galactose transport system are catabolite inactivated when cells with these transport systems are incubated with glucose. The role of the cyclic AMP cascade in the catabolite inactivation of these transport systems was shown by using mutants affected in the activity of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase (cAPK). In tpk1(w) mutants with reduced cAPK activity, the sugar transport systems were expressed but were not catabolite inactivated. In bcy1 mutants with unbridled cAPK activity resulting from a defective regulatory subunit, the transport systems were absent or present at low levels.
Full text
PDF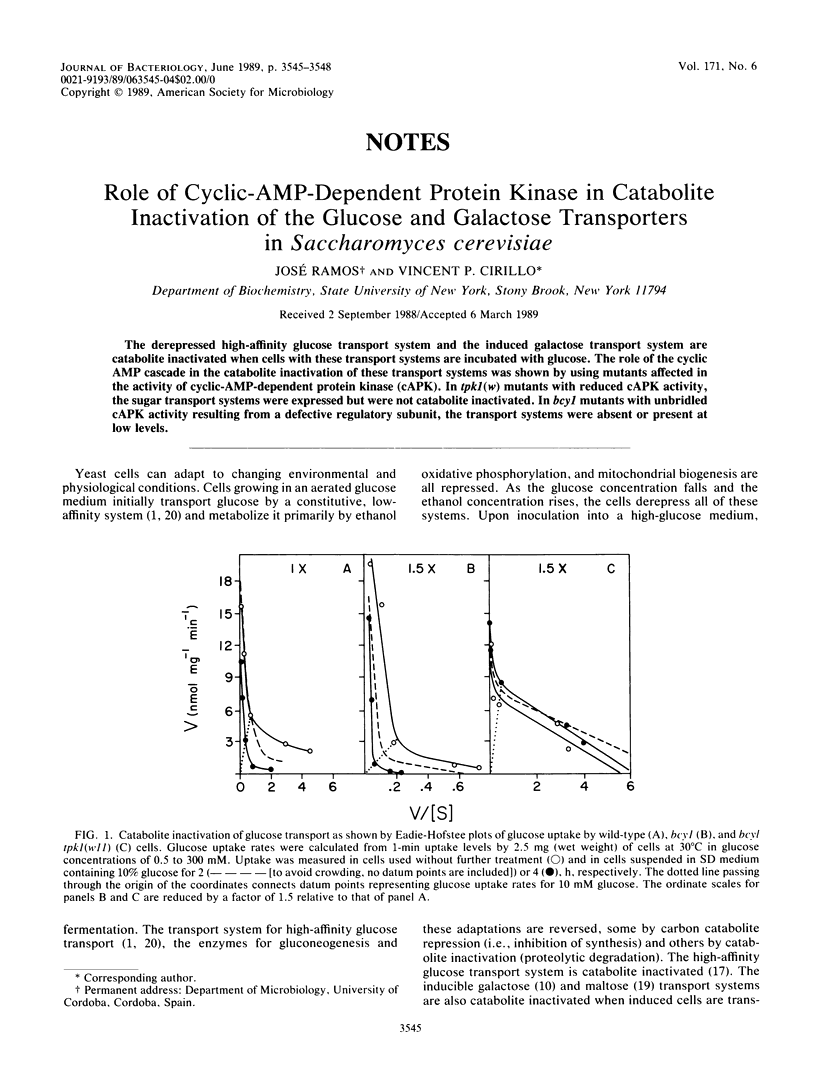


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bisson L. F., Fraenkel D. G. Expression of kinase-dependent glucose uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1013–1017. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1013-1017.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgouin C., Delécluse A., Ribier J., Klier A., Rapoport G. A Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis gene encoding a 125-kilodalton larvicidal polypeptide is associated with inverted repeat sequences. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3575–3583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3575-3583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron S., Levin L., Zoller M., Wigler M. cAMP-independent control of sporulation, glycogen metabolism, and heat shock resistance in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90572-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. F., Tatchell K. Characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes encoding subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2653–2663. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Marshall-Carlson L., Carlson M. The yeast SNF3 gene encodes a glucose transporter homologous to the mammalian protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruijne A. W., Schuddemat J., Van den Broek P. J., Van Steveninck J. Regulation of sugar transport systems of Kluyveromyces marxianus: the role of carbohydrates and their catabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 22;939(3):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasnier B. Characterization of low- and high-affinity glucose transports in the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 16;903(3):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görts C. P. Effect of glucose on the activity and the kinetics of the maltoseuptake system and of alpha-glucosidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(2):233–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. M., Cirillo V. P. Glucose transport in a kinaseless Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2932–2937. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2932-2937.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matern H., Holzer H. Catabolite inactivation of the galactose uptake system in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6399–6402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Genetic analysis of the role of cAMP in yeast. Yeast. 1985 Sep;1(1):15–24. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazón M. J., Gancedo J. M., Gancedo C. Inactivation of yeast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. In vivo phosphorylation of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1128–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlig G., Holzer H. Phosphorylation and inactivation of yeast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13818–13823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purwin C., Nicolay K., Scheffers W. A., Holzer H. Mechanism of control of adenylate cyclase activity in yeast by fermentable sugars and carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8744–8749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. J., HALVORSON H. O. The components of maltozymase in yeast, and their behavior during deadaptation. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):186–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.186-198.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Delafuente G. Regulatory properties of the constitutive hexose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biochem. 1974 Dec 20;5(3):161–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01731379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortora P., Burlini N., Leoni F., Guerritore A. Dependence on cyclic AMP of glucose-induced inactivation of yeast gluconeogenetic enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 2;155(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J. F., Emr S. D., Field C., Schekman R. GAL2 codes for a membrane-bound subunit of the galactose permease in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):313–318. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.313-318.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma R. S., Spencer-Martins I., Van Uden N. Role of de novo protein synthesis in the interconversion of glucose transport systems in the yeast Pichia ohmeri. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 12;900(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


