Abstract
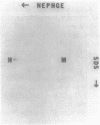
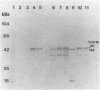
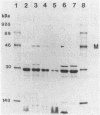
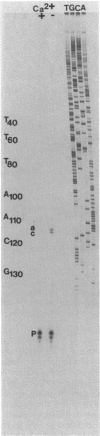
In Yersinia pestis KIM, there are 11 Yops (yersinial outer membrane proteins) encoded by the low-Ca2+ response virulence plasmid pCD1. Only Yops M and N are found in easily detectable amounts in the culture medium. In this study, we located and characterized the yopM gene to obtain clues about its role in the virulence of Y. pestis. Rabbit antibody was raised against Yops M and H, copurified from the supernatant of Y. pseudotuberculosis 43(pGW600, pCD1 yopE::Mu dI1[Apr lac]). This antiserum was adsorbed with an Escherichia coli clone that strongly expressed YopH. The resulting YopM-specific antibody was used to screen a HindIII library of pCD1. HindIII-F and several subclones from it expressed YopM in E. coli minicells. A DNA fragment of 1.39 kilobases from HindIII-F was sequenced and found to contain a 367-amino-acid open reading frame capable of encoding a protein with molecular mass (41,566 daltons) and isoelectric point (4.06) similar to those of YopM. The +1 site of the yopM gene was determined by primer extension. The DNA sequence contained repeating structures: 11 pairs of exact direct repeats, two exact inverted repeats, and three palindromes, ranging from 10 to 42 bases in size. One consensus 14-amino-acid sequence was repeated six times in the predicted protein sequence. The YopM sequence shares some significant homology with the von Willebrand factor- and thrombin-binding domain of the alpha chain of human platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. These findings suggested a testable hypothesis for the function of YopM.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R., Sample A. K., Yu D. Z., Zahorchak R. J., Hu P. C., Fowler J. M. Proteolysis of V antigen from Yersinia pestis. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jan;2(1):49–62. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H. Expression of the temperature-inducible outer membrane proteins of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.234-240.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. The plasmid-encoded Yop2b protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is a virulence determinant regulated by calcium and temperature at the level of transcription. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):237–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caen J. P., Nurden A. T., Jeanneau C., Michel H., Tobelem G., Levy-Toledano S., Sultan Y., Valensi F., Bernard J. Bernard-Soulier syndrome: a new platelet glycoprotein abnormality. Its relationship with platelet adhesion to subendothelium and with the factor VIII von Willebrand protein. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Apr;87(4):586–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Analysis of recombinant DNA using Escherichia coli minicells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:347–362. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., McClure M. A. Relationships of human protein sequences to those of other organisms. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):447–455. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg A., Wolf-Watz H. The virulence protein Yop5 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is regulated at transcriptional level by plasmid-plB1-encoded trans-acting elements controlled by temperature and calcium. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):121–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuster W., Bowie E. J., Lewis J. C., Fass D. N., Owen C. A., Jr, Brown A. L. Resistance to arteriosclerosis in pigs with von Willebrand's disease. Spontaneous and high cholesterol diet-induced arteriosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):722–730. doi: 10.1172/JCI108985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguen J. D., Yother J., Straley S. C. Genetic analysis of the low calcium response in Yersinia pestis mu d1(Ap lac) insertion mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):842–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.842-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy N., Beutin L., Achtman M., Skurray R., Rahmsdorf U., Herrlich P. Conjugation proteins encoded by the F sex factor. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):580–585. doi: 10.1038/270580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. H., Walker G. C. Mud(Ap, lac)-generated fusions in studies of gene expression. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:501–509. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesnaw J. A., Reichmann M. E. RNA synthesis by temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus, New Jersey serotype. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):492–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. A., Chung D. W., Fujikawa K., Hagen F. S., Papayannopoulou T., Roth G. J. Cloning of the alpha chain of human platelet glycoprotein Ib: a transmembrane protein with homology to leucine-rich alpha 2-glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5615–5619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. Protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:615–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Haddix P., Atkins E. B., Soughers T. K., Straley S. C. Regulation of expression of V antigen and outer membrane proteins in Yersinia pestis. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:173–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. Inhibition of phagocytosis in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: a virulence plasmid-encoded ability involving the Yop2b protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2139–2143. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2139-2143.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., De Marco L., Gatti L., Bader R., Montgomery R. R. Platelets have more than one binding site for von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):1–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI110946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample A. K., Brubaker R. R. Post-translational regulation of Lcr plasmid-mediated peptides in pesticinogenic Yersinia pestis. Microb Pathog. 1987 Oct;3(4):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodeinde O. A., Goguen J. D. Genetic analysis of the 9.5-kilobase virulence plasmid of Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2743–2748. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2743-2748.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodeinde O. A., Sample A. K., Brubaker R. R., Goguen J. D. Plasminogen activator/coagulase gene of Yersinia pestis is responsible for degradation of plasmid-encoded outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2749–2752. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2749-2752.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Bowmer W. S. Virulence genes regulated at the transcriptional level by Ca2+ in Yersinia pestis include structural genes for outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):445–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.445-454.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins of yersiniae cultivated under conditions simulating mammalian intracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C. The plasmid-encoded outer-membrane proteins of Yersinia pestis. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S323–S326. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Takio K., Handa M., Ruggeri Z. M. Amino acid sequence of the von Willebrand factor-binding domain of platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5610–5614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Tschopp T. B., Baumgartner H. R., Sussman I. I., Johnson M. M., Egan J. J. Decreased adhesion of giant (Bernard-Soulier) platelets to subendothelium. Further implications on the role of the von Willebrand factor in hemostasis. Am J Med. 1974 Dec;57(6):920–925. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Watz H., Portnoy D. A., Bölin I., Falkow S. Transfer of the virulence plasmid of Yersinia pestis to Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):241–243. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.241-243.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]