Abstract
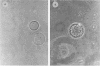
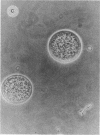
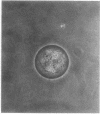
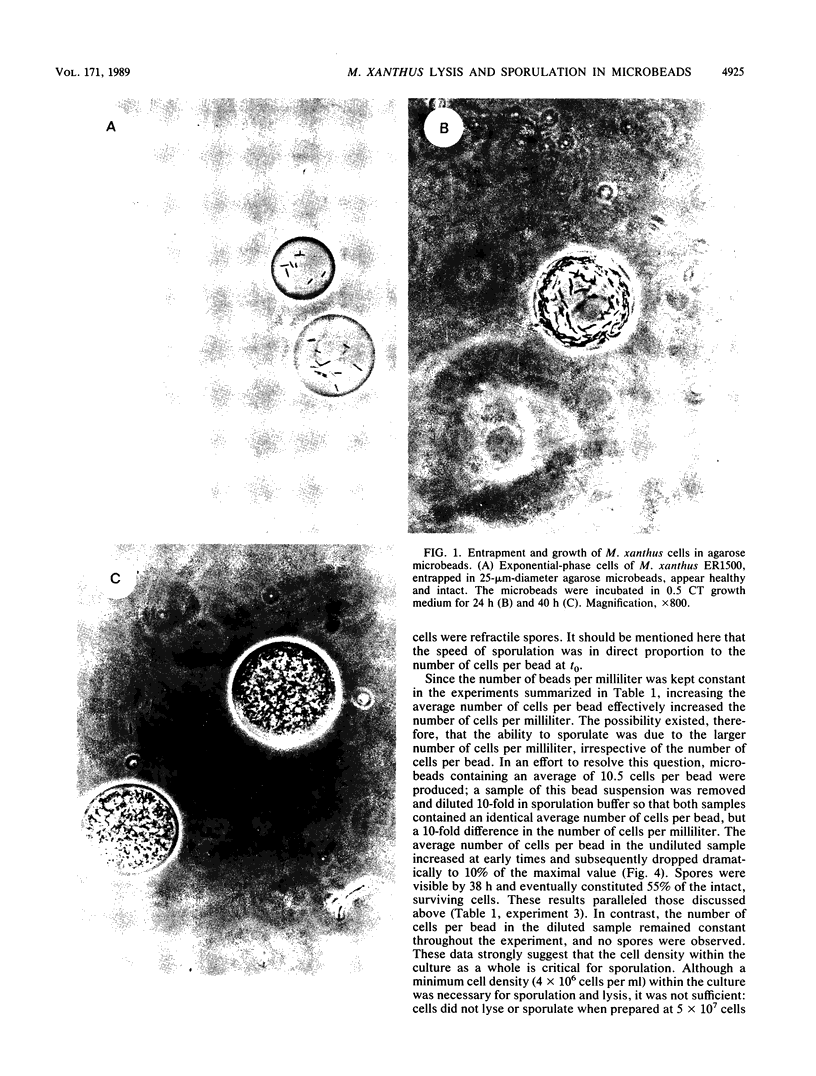
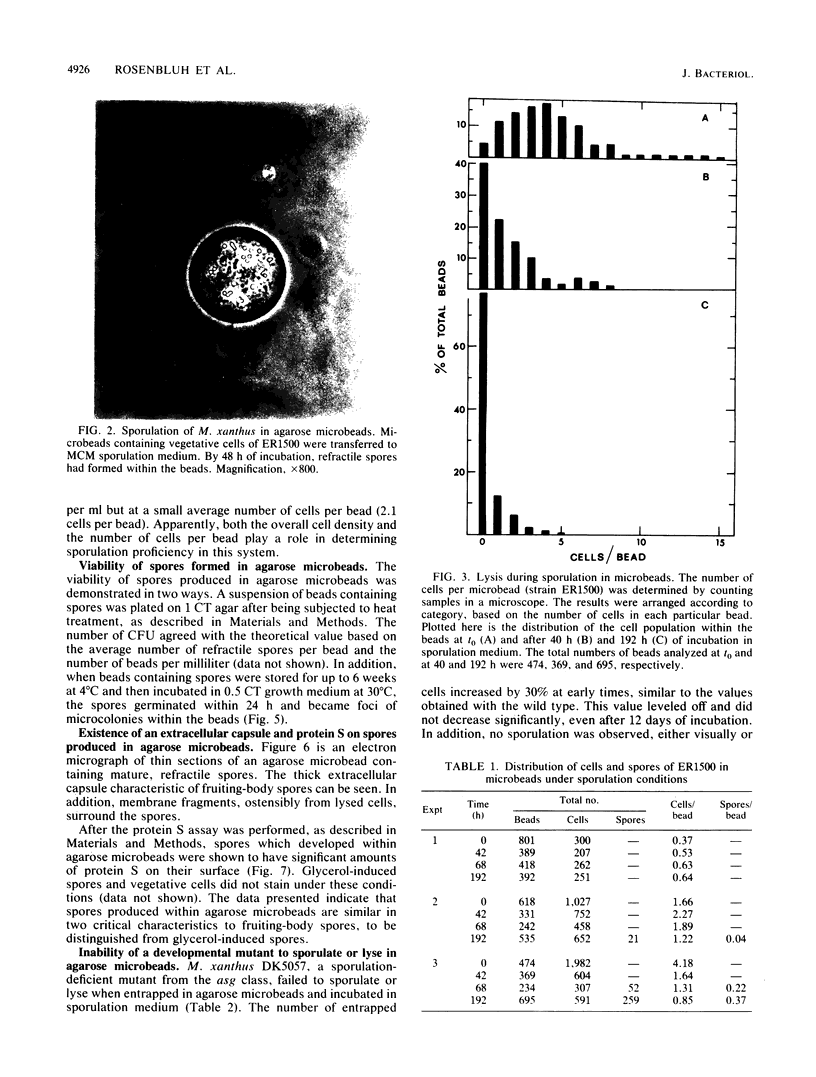
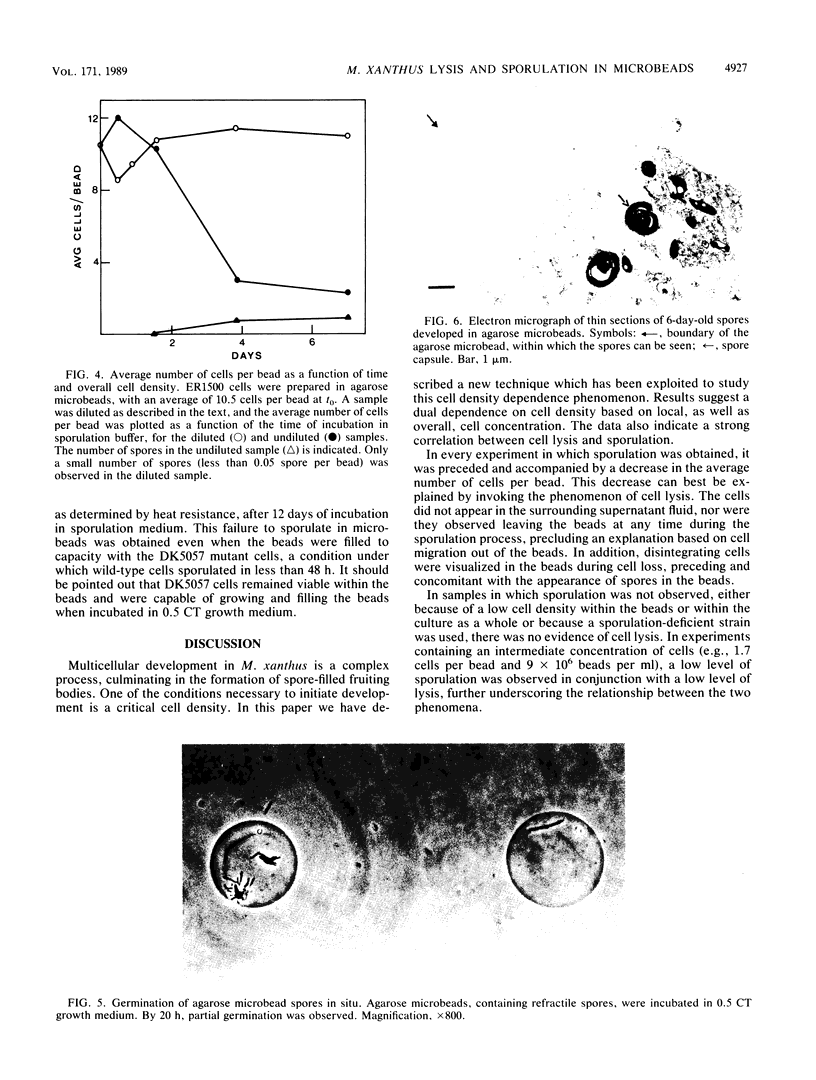
Vegetative cells of Myxococcus xanthus were immobilized in 25-microns-diameter agarose microbeads and incubated in either growth medium or sporulation buffer. In growth medium, the cells multiplied, glided to the periphery, and then filled the beads. In sporulation buffer, up to 90% of the cells lysed and ca. 50% of the surviving cells formed resistant spores. A strong correlation between sporulation and cell lysis was observed; both phenomena were cell density dependent. Sporulation proficiency was a function of the average number of cells within the bead at the time that sporulation conditions were imposed. A minimum of ca. 4 cells per microbead was necessary for efficient lysis and sporulation to proceed. Increasing this number accelerated the lysis and sporulation process. No lysis occurred when an average of 0.4 cell was entrapped per bead. Entrapping an average of 1.7 cells per bead resulted in 46% lysis and 3% sporulation of survivors, whereas entrapping an average of 4.2 cells per bead yielded 82% lysis and 44% sporulation of the surviving cells. Sporulation and lysis also depended upon the cell density in the culture as a whole. The existence of these two independent cell density parameters (cells per bead and cells per milliliter) suggests that at least two separate cell density signals play a role in controlling sporulation in M. xanthus.
Full text
PDF

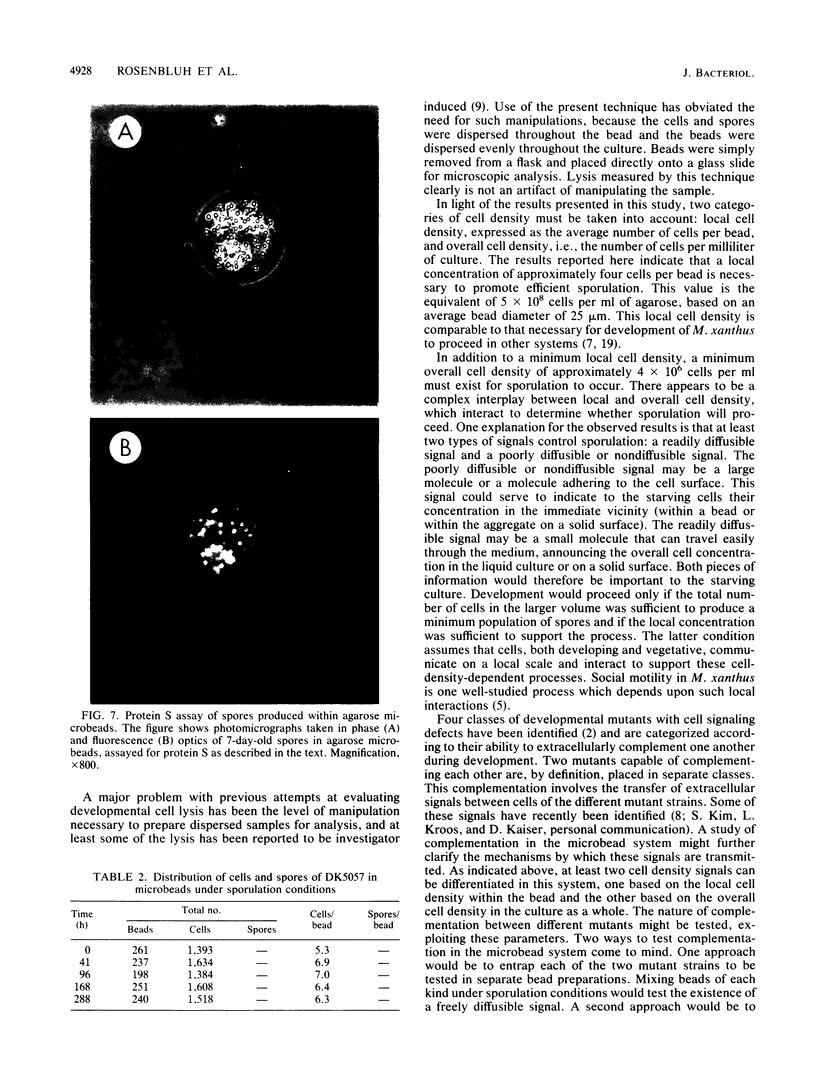

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen G. R., Dworkin M. Cell-cell interactions in developmental lysis of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1985 Nov;112(1):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. Social gliding is correlated with the presence of pili in Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5952–5956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Kaiser D. Fruiting body morphogenesis in submerged cultures of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):458–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.458-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Kroos L., Kaiser D. Intercellular signaling is required for developmental gene expression in Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. A., Zusman D. R. Reexamination of the role of autolysis in the development of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4103–4112. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4103-4112.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Rosenberg E. Autocide AMI rescues development in dsg mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1513–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1513-1518.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Rosenberg E. Sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus in liquid shake flask cultures. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4521–4524. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4521-4524.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Control of morphogenesis in myxobacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(3):195–227. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Gill R. E., Kaiser D. Developmental cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus and the spoC locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1406–1410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Kaiser D. Murein components rescue developmental sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):462–470. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.462-470.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Developmentally induced autolysis during fruiting body formation by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):798–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.798-802.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Morphogenesis and developmental interactions in myxobacteria. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):516–523. doi: 10.1126/science.806967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]