Abstract
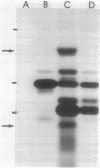
A 1,442-base-pair (bp) insertion sequence (IS861) was identified in the type III group B streptococcal (GBS) strain COH-1. It is flanked by 26-bp imperfect inverted repeats and contains two open reading frames, 1 and 2, encoding 141- and 277-amino-acid proteins, respectively. A 3-bp target sequence, ACA, is duplicated and flanks each inverted repeat. IS861 shares greater than 30% homology with IS3 and IS150 of Escherichia coli, primarily in the region of their putative transposases. Northern (RNA) analysis revealed that RNA is actively transcribed in vivo by IS861 and 17- and 36-kilodalton proteins were synthesized in E. coli maxicell assays. Multiple copies of IS861 were observed throughout the chromosome of COH-1, and one of the copies is located near genes involved in GBS capsule synthesis. IS861 is the first insertion sequence identified in GBS. Its role in GBS and the significance of its relationship to the phylogenetically similar insertion sequences typified by IS150 and IS3 of E. coli are unknown.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barberis-Maino L., Berger-Bächi B., Weber H., Beck W. D., Kayser F. H. IS431, a staphylococcal insertion sequence-like element related to IS26 from Proteus vulgaris. Gene. 1987;59(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. R., Rubens C. E., Wilson C. B. Lung antibacterial defense mechanisms in infant and adult rats: implications for the pathogenesis of group B streptococcal infections in the neonatal lung. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):91–100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rak B., Lusky M., Hable M. Expression of two proteins from overlapping and oppositely oriented genes on transposable DNA insertion element IS5. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):124–128. doi: 10.1038/297124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. C., Spanier J. G., Jones S. J., Simpson W. J., Cleary P. P. Streptococcus pyogenes type 12 M protein gene regulation by upstream sequences. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5633–5640. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5633-5640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronecker H. J., Rak B. Genetic organization of insertion element IS2 based on a revised nucleotide sequence. Gene. 1987;59(2-3):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Wessels M. R., Heggen L. M., Kasper D. L. Transposon mutagenesis of type III group B Streptococcus: correlation of capsule expression with virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7208–7212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E., Kröger M., Rak B. IS150: distribution, nucleotide sequence and phylogenetic relationships of a new E. coli insertion element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6789–6802. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmerman K. P., Tu C. P. Complete sequence of IS3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2127–2139. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinks K., Habermann P., Beyreuther K., Starlinger P., Ehring R. An IS4-encoded protein is synthesized in minicells. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):183–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00269656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]