Abstract
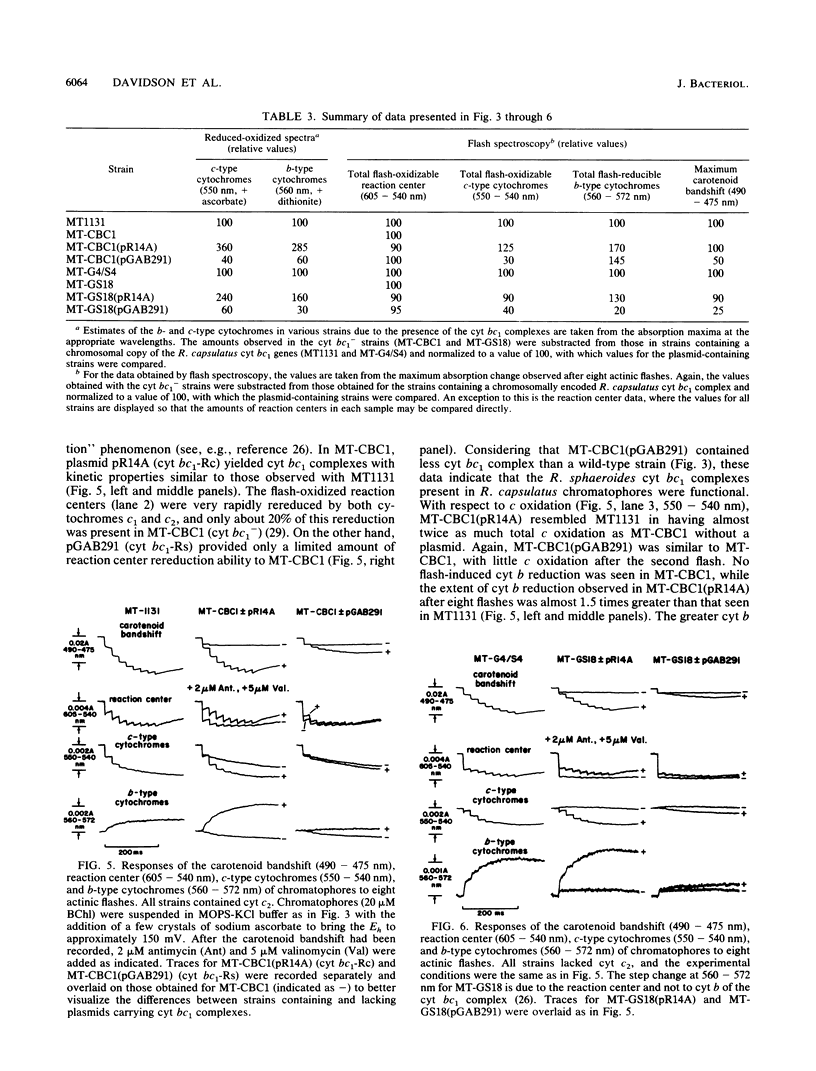
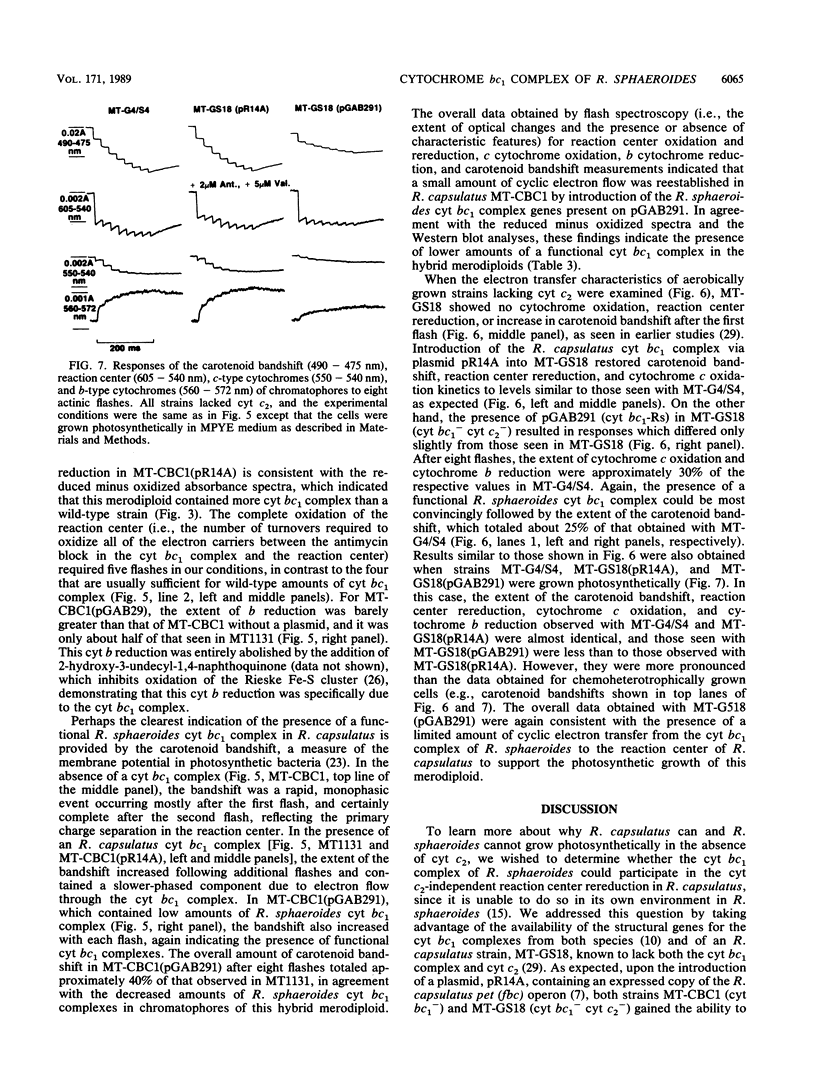
Plasmids encoding the structural genes for the Rhodobacter capsulatus and Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome (cyt) bc1 complexes were introduced into strains of R. capsulatus lacking the cyt bc1 complex, with and without cyt c2. The R. capsulatus merodiploids contained higher than wild-type levels of cyt bc1 complex, as evidenced by immunological and spectroscopic analyses. On the other hand, the R. sphaeroides-R. capsulatus hybrid merodiploids produced only barely detectable amounts of R. sphaeroides cyt bc1 complex in R. capsulatus. Nonetheless, when they contained cyt c2, they were capable of photosynthetic growth, as judged by the sensitivity of this growth to specific inhibitors of the photochemical reaction center and the cyt bc1 complex, such as atrazine, myxothiazol, and stigmatellin. Interestingly, in the absence of cyt c2, although the R. sphaeroides cyt bc1 complex was able to support the photosynthetic growth of a cyt bc1-less mutant of R. capsulatus in rich medium, it was unable to do so when C4 dicarboxylic acids, such as malate and succinate, were used as the sole carbon source. Even this conditional ability of R. sphaeroides cyt bc1 complex to replace that of R. capsulatus for photosynthetic growth suggests that in the latter species the cyt c2-independent rereduction of the reaction center is not due to a structural property unique to the R. capsulatus cyt bc1 complex. Similarly, the inability of R. sphaeroides to exhibit a similar pathway is not due to some inherent property of its cyt bc1 complex.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry E. A., Trumpower B. L. Isolation of ubiquinol oxidase from Paracoccus denitrificans and resolution into cytochrome bc1 and cytochrome c-aa3 complexes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2458–2467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J., Kaplan S. The in vitro transcription-translation of DNA and RNA templates by extracts of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Optimization and comparison of template specificity with Escherichia coli extracts and in vivo synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15110–15121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daldal F. Cytochrome c2-independent respiratory growth of Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2388–2391. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2388-2391.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daldal F., Davidson E., Cheng S. Isolation of the structural genes for the Rieske Fe-S protein, cytochrome b and cytochrome c1 all components of the ubiquinol: cytochrome c2 oxidoreductase complex of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E., Daldal F. Primary structure of the bc1 complex of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Nucleotide sequence of the pet operon encoding the Rieske cytochrome b, and cytochrome c1 apoproteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E., Daldal F. fbc operon, encoding the Rieske Fe-S protein cytochrome b, and cytochrome c1 apoproteins previously described from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides, is from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue T. J., McEwan A. G., Kaplan S. Cloning, DNA sequence, and expression of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome c2 gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):962–972. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.962-972.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue T. J., McEwan A. G., Van Doren S., Crofts A. R., Kaplan S. Phenotypic and genetic characterization of cytochrome c2 deficient mutants of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1918–1925. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Jackson J. B. Thermodynamic and kinetic characterization of electron transfer components in situ in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides and Rhodospirillum rubrum. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Nov 7;30(3):495–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch J., Cannac V., Meyer T. E., Cusanovich M. A., Tollin G., Van Beeumen J., Rott M. A., Donohue T. J. Expression of a cytochrome c2 isozyme restores photosynthetic growth of Rhodobacter sphaeroides mutants lacking the wild-type cytochrome c2 gene. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jun;271(2):502–507. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90301-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabellini N., Harnisch U., McCarthy J. E., Hauska G., Sebald W. Cloning and expression of the fbc operon encoding the FeS protein, cytochrome b and cytochrome c1 from the Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides b/c1 complex. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):549–553. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabellini N., Sebald W. Nucleotide sequence and transcription of the fbc operon from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Evaluation of the deduced amino acid sequences of the FeS protein, cytochrome b and cytochrome c1. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):569–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley P. E., Yu L., Dong J. H., Keyser G. C., Sanborn M. R., Yu C. A. Immunological comparison of the b and c1 cytochromes from bovine heart mitochondria and the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14593–14599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. B., Dutton P. L. The kinetic and redox potentiometric resolution of the carotenoid shifts in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides chromatophores: their relationship to electric field alterations in electron transport and energy coupling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 19;325(1):102–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl P. O., Pennoyer J. D., Robertson D. E., Trumpower B. L. Purification of highly active cytochrome bc1 complexes from phylogenetically diverse species by a single chromatographic procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 May 6;891(3):227–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(87)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs B. Mobilization of the genes for photosynthesis from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata by a promiscuous plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1003–1012. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1003-1012.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura K., Bowyer J. R., Ohnishi T., Dutton P. L. Inhibition of electron transfer by 3-alkyl-2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinones in the ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxidoreductases of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides and mammalian mitochondria. Interaction with a ubiquinone-binding site and the Rieske iron-sulfur cluster. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1571–1579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Baccarini-Melandri A., Hauska G. A., Melandri B. A., Crofts A. R. Asymmetry of an energy transducing membrane the location of cytochrome c2 in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides and Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 15;387(2):212–227. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Daldal F. Physiological electron donors to the photochemical reaction center of Rhodobacter capsulatus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 17;894(3):370–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(87)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone N., Sekimachi M., Kutoh E. Identification and properties of a quinol oxidase super-complex composed of a bc1 complex and cytochrome oxidase in the thermophilic bacterium PS3. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15386–15391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierbach G., Reichenbach H. Myxothiazol, a new inhibitor of the cytochrome b-c1 segment of th respiratory chain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 14;638(2):282–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver P. F., Wall J. D., Gest H. Characterization of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Nov 7;105(3):207–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00447139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannoni D., Melandri B. A., Baccarini-Melandri A. Energy transduction in photosynthetic bacteria. X. Composition and function of the branched oxidase system in wild type and respiration deficient mutants of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 12;423(3):413–430. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]