Abstract
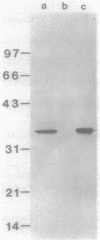
The phosphatidylinositol (PI)-specific phospholipase C (PLC) of Bacillus cereus was cloned into Escherichia coli by using monoclonal antibody probes raised against the purified protein. The enzyme is specific for hydrolysis of the membrane lipid PI and PI-glycan-containing membrane anchors, which are important structural components of one class of membrane proteins. The protein expressed in E. coli comigrated with B. cereus PI-PLC in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, as detected by immunoblotting, and conferred PI-PLC activity on the host. This enzyme activity was inhibited by PI-PLC-specific monoclonal antibodies. The nucleotide sequence of the PI-PLC gene suggests that this secreted bacterial protein is synthesized as a larger precursor with a 31-amino-acid N-terminal extension to the mature enzyme of 298 amino acids. From analysis of coding and flanking sequences of the gene, we conclude that the PI-PLC gene does not reside next to the gene cluster of the other two secreted phospholipases C on the bacterial chromosome. The deduced amino acid sequence of the B. cereus PI-PLC contains a stretch of significant similarity to the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific PLC of Trypanosoma brucei. The conserved peptide is proposed to play a role in the function of these enzymes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Trifonov E. N. A computer algorithm for testing potential prokaryotic terminators. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4411–4427. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffaud G., Inouye M. Signal peptidases recognize a structural feature at the cleavage site of secretory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10224–10228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A., Soliz N. M., Saltiel A. R. Purification of a phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase C from liver plasma membranes: a possible target of insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2663–2667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Yang M., Chen E., Hellmiss R., Rodriguez H., Low M. G. Sequence of the Bacillus thuringiensis phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase C. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10383–10383. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereld D., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. cDNA encoding the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Trypanosoma brucei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8914–8918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough E., Hansen L. K., Birknes B., Jynge K., Hansen S., Hordvik A., Little C., Dodson E., Derewenda Z. High-resolution (1.5 A) crystal structure of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):357–360. doi: 10.1038/338357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T., Holm T., Guddal P. H., Sletten K., Haugli F. B., Little C. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the phosphatidylcholine-preferring phospholipase C of Bacillus cereus. Gene. 1988 May 30;65(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90466-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M., Kriz R. W., Totty N., Philp R., Meldrum E., Aldape R. A., Knopf J. L., Parker P. J. Determination of the primary structure of PLC-154 demonstrates diversity of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activities. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90549-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami T., Miki A., Ikehara Y. Electrophoretic characterization of hepatic alkaline phosphatase released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. A comparison with liver membrane and serum-soluble forms. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):183–189. doi: 10.1042/bj2270183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Staphylococcus aureus. Methods Enzymol. 1981;71(Pt 100):741–746. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)71087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Stiernberg J., Waneck G. L., Flavell R. A., Kincade P. W. Cell-specific heterogeneity in sensitivity of phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane antigens to release by phospholipase C. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Oct 4;113(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Kelly K. L., Abler A., Jarett L. Identification of a novel insulin-sensitive glycophospholipid from H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2131–2137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin stimulates the generation from hepatic plasma membranes of modulators derived from an inositol glycolipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Fox J. A., Sherline P., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin-stimulated hydrolysis of a novel glycolipid generates modulators of cAMP phosphodiesterase. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):967–972. doi: 10.1126/science.3016898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Cloning and sequence of multiple forms of phospholipase C. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C: complete cDNA and protein sequences and sequence homology to tyrosine kinase-related oncogene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5419–5423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler R., Alberts A. W., Vagelos P. R. Enzymatic properties of phosphatidylinositol inositolphosphohydrolase from Bacillus cereus. Substrate dilution in detergent-phospholipid micelles and bilayer vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4175–4179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi R., Ikezawa H. Phosphatidyl inositol-specific phospholipase C from Clostridium novyi type A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Feb;186(1):196–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volwerk J. J., Wetherwax P. B., Evans L. M., Kuppe A., Griffith O. H. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus: improved purification, amino acid composition, and amino-terminal sequence. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Mar;39(3):315–325. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Tsukagoshi N., Udaka S., Sasaki T., Makino S., Nakamura S., Little C., Tomita M., Ikezawa H. Nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene coding for sphingomyelinase of Bacillus cereus. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Transcending the impenetrable: how proteins come to terms with membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 9;947(2):307–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]