Abstract
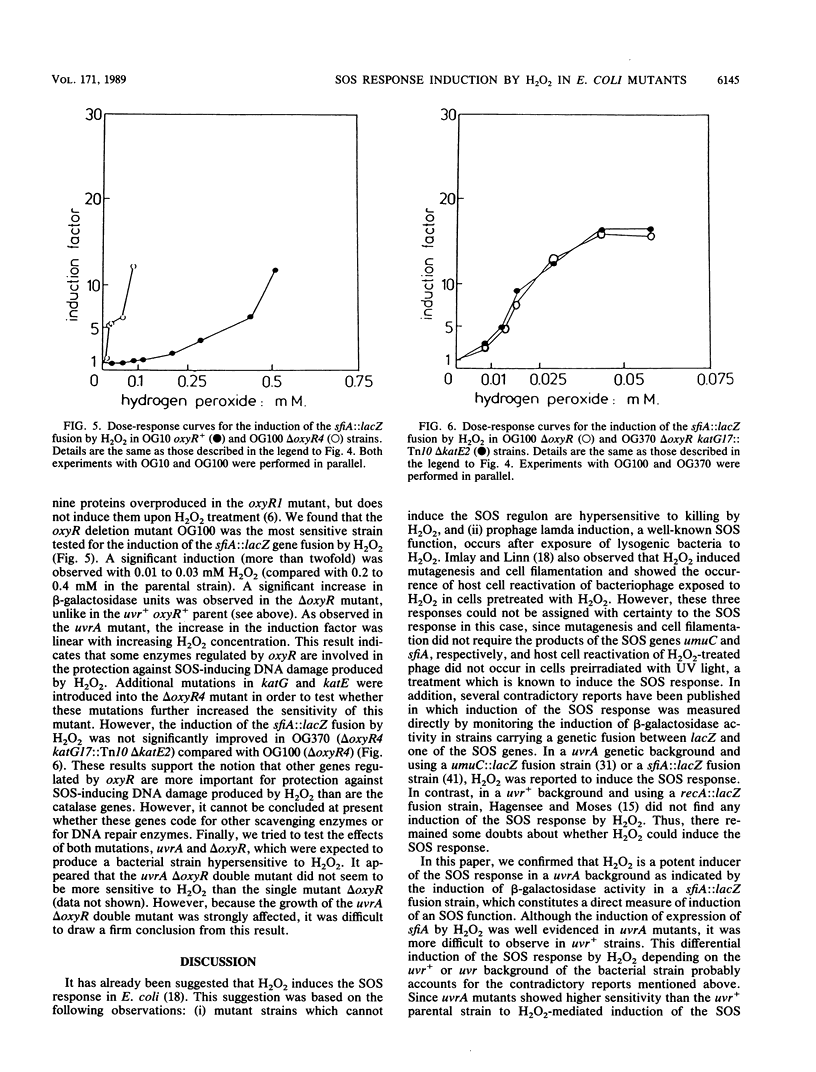
The induction of the SOS response by H2O2 was measured in Escherichia coli by means of a sfiA::lacZ operon fusion. The effects of mutations in genes involved in DNA repair or DNA metabolism on the SOS response were investigated. We found that in an uvrA mutant, H2O2 induced the SOS response at lower concentrations than in the uvr+ parent strain, indicating that some lesions induced by H2O2 may be repaired by the uvrABC-dependent excision repair system. A nth mutation, yielding deficiency in thymine glycol DNA glycosylase, had no detectable effect on SOS induction, indicating that thymine glycol, a DNA lesion expected to be induced by H2O2, does not participate detectably in the induction of the SOS response by this chemical under our conditions. H2O2 still induced the SOS response in a dnaC(Ts) uvrA double mutant under conditions in which no DNA replication proceeds, suggesting that this chemical induces DNA strand breaks. Induction of the SOS response by H2O2 was also assayed in various mutants affected in genes suspected to be important for protection against oxidative stress. Mutations in the catalase genes, katE and katG, had only minor effects. However, in an oxyR deletion mutant, in which the adaptative response to H2O2 does not occur, SOS induction occurred at much lower H2O2 concentrations than in the oxyR+ parent strain. These results indicate that some enzymes regulated by the oxyR gene are, under our conditions, more important than catalase for protection against the H2O2-induced DNA damages which trigger the SOS response.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ananthaswamy H. N., Eisenstark A. Repair of hydrogen peroxide-induced single-strand breaks in Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):187–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.187-191.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun A. G. Host DNA replication or excision repair requirement for ultraviolet induction of bacteriophage lambda lysogens. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):164–166. doi: 10.1038/261164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlioz A., Touati D. Isolation of superoxide dismutase mutants in Escherichia coli: is superoxide dismutase necessary for aerobic life? EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):623–630. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Carpenter V. S. The recA+ gene product is more important than catalase and superoxide dismutase in protecting Escherichia coli against hydrogen peroxide toxicity. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):319–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.319-321.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Morgan R. W., Jacobson F. S., Ames B. N. Positive control of a regulon for defenses against oxidative stress and some heat-shock proteins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Weiss B. Endonuclease III (nth) mutants of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):474–478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Halbrook J. Inducible repair of oxidative DNA damage in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):466–468. doi: 10.1038/304466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Halbrook J., Linn S. Escherichia coli xth mutants are hypersensitive to hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1079–1082. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1079-1082.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Linn S. 5,6-Saturated thymine lesions in DNA: production by ultraviolet light or hydrogen peroxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3781–3789. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. The biology of oxygen radicals. Science. 1978 Sep 8;201(4359):875–880. doi: 10.1126/science.210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Demple B. Overproduction of peroxide-scavenging enzymes in Escherichia coli suppresses spontaneous mutagenesis and sensitivity to redox-cycling agents in oxyR-mutants. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2611–2617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03111.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory E. M., Fridovich I. Induction of superoxide dismutase by molecular oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):543–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.543-548.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory E. M., Yost F. J., Jr, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutases of Escherichia coli: intracellular localization and functions. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):987–991. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.987-991.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagensee M. E., Moses R. E. Multiple pathways for repair of hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA damage in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):991–995. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.991-995.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R. An inducible DNA replication-cell division coupling mechanism in E. coli. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):797–799. doi: 10.1038/290797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. Bimodal pattern of killing of DNA-repair-defective or anoxically grown Escherichia coli by hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):519–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.519-527.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. Mutagenesis and stress responses induced in Escherichia coli by hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2967–2976. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2967-2976.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Reichardt K., Botstein D. Inversions and deletions of the Salmonella chromosome generated by the translocatable tetracycline resistance element Tn10. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 5;127(1):89–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90461-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesko S. A., Lorentzen R. J., Ts'o P. O. Role of superoxide in deoxyribonucleic acid strand scission. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):3023–3028. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Hollstein M., Christman M. F., Schwiers E. A., Ames B. N. A new Salmonella tester strain (TA102) with A X T base pairs at the site of mutation detects oxidative mutagens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7445–7449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C. Isolation of catalase-deficient Escherichia coli mutants and genetic mapping of katE, a locus that affects catalase activity. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):622–626. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.622-626.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Triggs B. L., George C. S., Hrabarchuk B. E. Genetic mapping of katG, a locus that affects synthesis of the bifunctional catalase-peroxidase hydroperoxidase I in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.661-667.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Nunn W. D. Selection for loss of tetracycline resistance by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1110–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1110-1111.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massie H. R., Samis H. V., Baird M. B. The kinetics of degradation of DNA and RNA by H 2 O 2 . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 31;272(4):539–548. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90509-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. P., Fischer J. R., Pachlatko J. P., Eisenstark A. Characterization of a cell-lethal product from the photooxidation of tryptophan: hydrogen peroxide. Science. 1976 Feb 6;191(4226):468–469. doi: 10.1126/science.1108203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody C. S., Hassan H. M. Mutagenicity of oxygen free radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2855–2859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. W., Christman M. F., Jacobson F. S., Storz G., Ames B. N. Hydrogen peroxide-inducible proteins in Salmonella typhimurium overlap with heat shock and other stress proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8059–8063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda Y., Nakamura S., Oki I., Kato T., Shinagawa H. Evaluation of the new system (umu-test) for the detection of environmental mutagens and carcinogens. Mutat Res. 1985 Oct;147(5):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(85)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quillardet P., Hofnung M. The SOS Chromotest, a colorimetric bacterial assay for genotoxins: procedures. Mutat Res. 1985 Jun;147(3):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(85)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quillardet P., Huisman O., D'Ari R., Hofnung M. SOS chromotest, a direct assay of induction of an SOS function in Escherichia coli K-12 to measure genotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5971–5975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorth M., Jensen P. K. Determination of catalase activity by means of the Clark oxygen electrode. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):171–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salles B., Defais M. Signal of induction of recA protein in E. coli. Mutat Res. 1984 Feb;131(2):53–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salles B., Germanier M., Defais M. A bacterial strain for detecting agents that produce free radical-mediated DNA strand breaks. Mutat Res. 1987 May;183(3):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(87)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg E. Reconstitution of an Escherichia coli repair endonuclease activity from the separated uvrA+ and uvrB+/uvrC+ gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2569–2573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Christman M. F., Sies H., Ames B. N. Spontaneous mutagenesis and oxidative damage to DNA in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8917–8921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell R. M. A common pathway for protection of bacteria against damage by solar UVA (334 nm, 365 nm) and an oxidising agent (H2O2). Mutat Res. 1985 May;145(3):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(85)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoakum G., Eisenstark A. Toxicity of L-Tryptophan photoproduct on recombinationless (rec) mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):653–655. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.653-655.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Hude W., Behm C., Gürtler R., Basler A. Evaluation of the SOS chromotest. Mutat Res. 1988 Apr;203(2):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(88)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



