Abstract
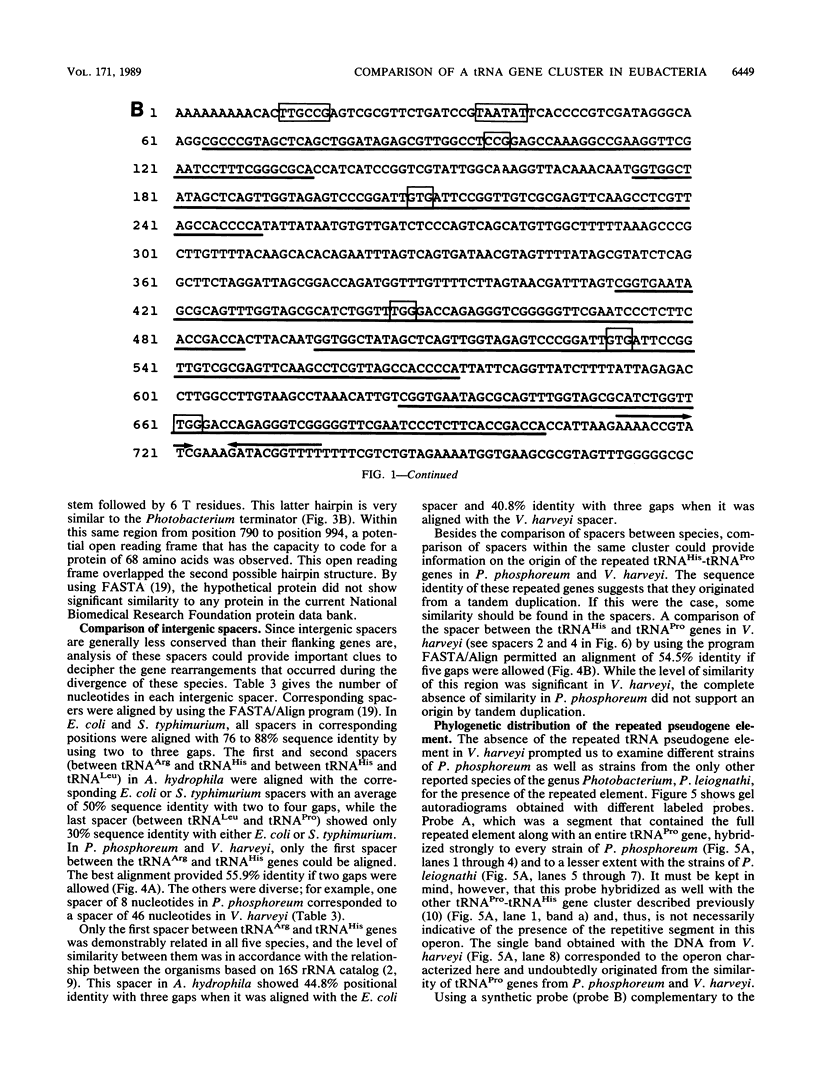
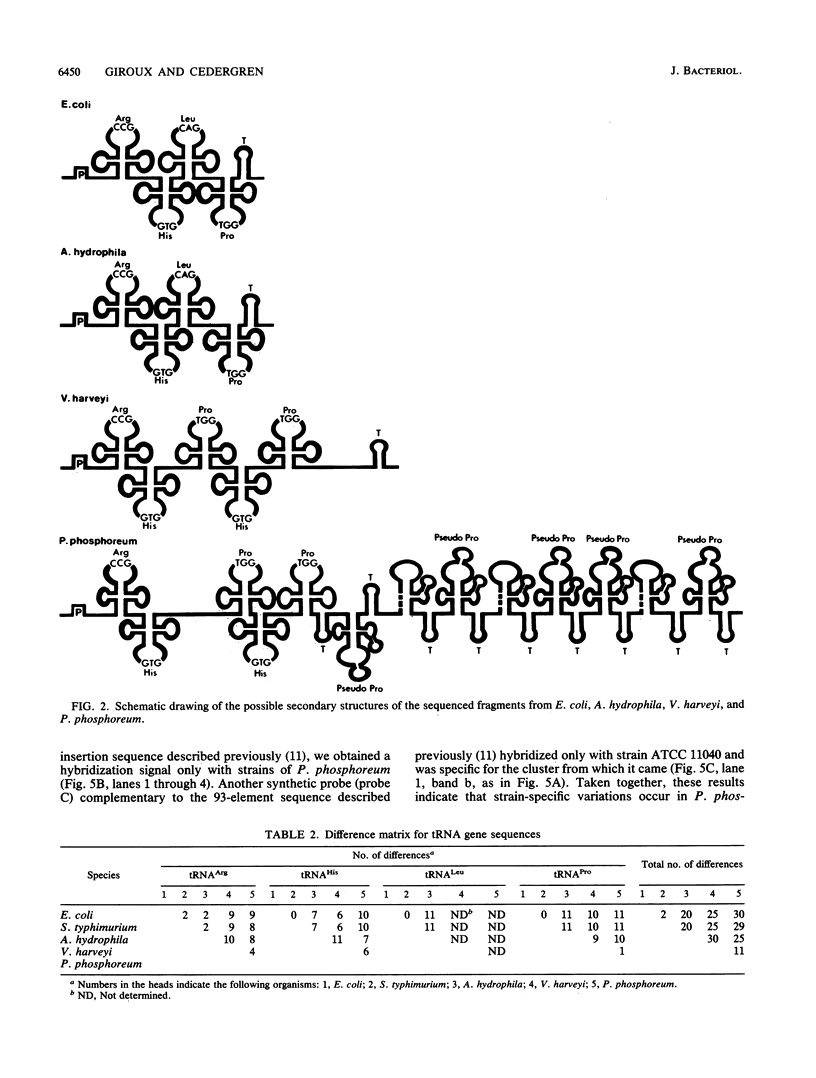
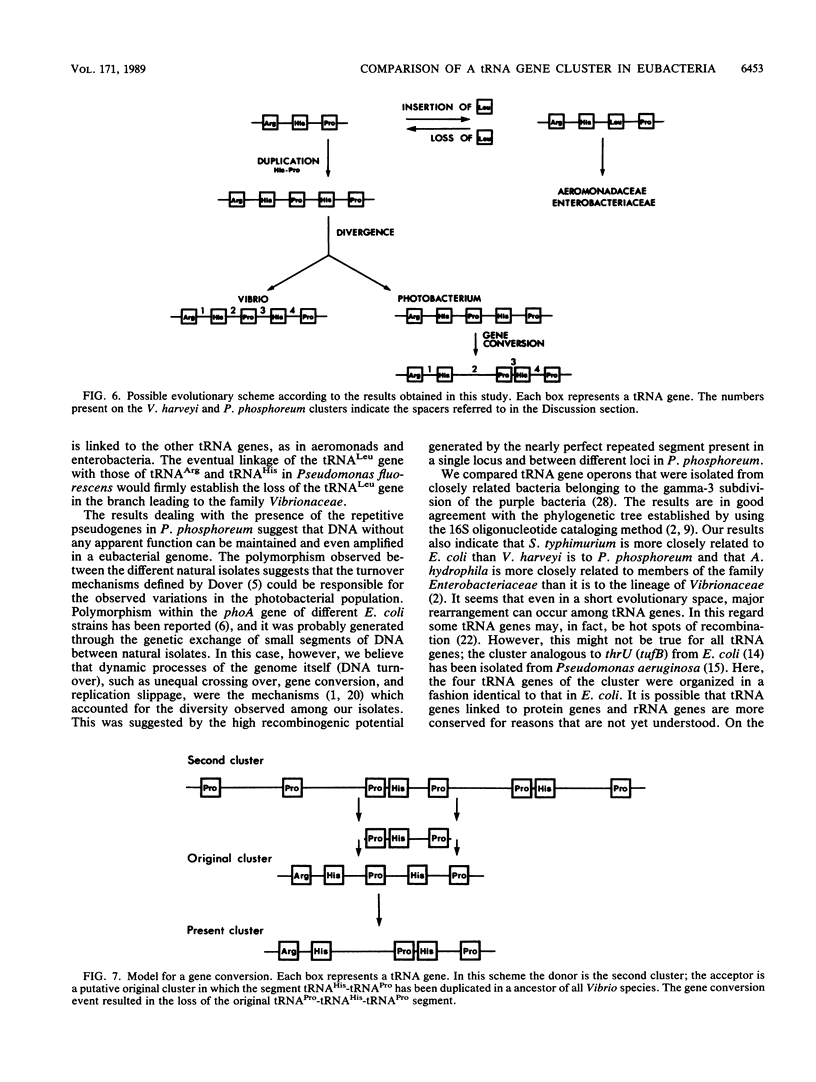
Genomic DNA from eubacteria belonging to the gamma-3 subdivision of purple bacteria, as classified by Woese (C.R. Woese, Microbiol. Rev. 51:221-271, 1987), were probed with the argT operon of Escherichia coli encoding 5'-tRNA(Arg)-tRNA(His)-tRNA(Leu)-tRNA(Pro)-3'. The homologous operon from Vibrio harveyi was isolated and sequenced. Comparison of the five available sequences of this tRNA cluster from members of the families Enterobacteriaceae, Aeromonadaceae, and Vibrionaceae led to the conclusion that variations in different versions of this operon arose not only by point mutations but also by duplication and addition-deletion of entire tRNA genes. This data base permitted the formulation of a proposal dealing with the evolutionary history of this operon and suggested that DNA regions containing tRNA genes are active centers (hot spots) of recombination. Finally, since the operon from V. harveyi was not highly repetitive and did not contain tRNA pseudogenes, as in the Photobacterium phosphoreum operon, hybridization of genomic DNAs from different photobacterial strains with probes specific for the repeated pseudogene element was performed. We conclude that the phylogenetic distribution of the repetitive DNA is restricted to strains of P. phosphoreum.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini A. M., Hofer M., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. On the formation of spontaneous deletions: the importance of short sequence homologies in the generation of large deletions. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Woolkalis M. J., Bang S. S. Evolutionary relationships in vibrio and Photobacterium: a basis for a natural classification. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:369–398. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L. The hisR locus of Salmonella: nucleotide sequence and expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;192(1-2):163–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00327662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedergren R., Gray M. W., Abel Y., Sankoff D. The evolutionary relationships among known life forms. J Mol Evol. 1988 Dec;28(1-2):98–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02143501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBose R. F., Dykhuizen D. E., Hartl D. L. Genetic exchange among natural isolates of bacteria: recombination within the phoA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7036–7040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap P. V., Steinman H. M. Strain variation in bacteriocuprein superoxide dismutase from symbiotic Photobacterium leiognathi. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):393–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.393-398.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier M. J., Ozeki H. Structure and organization of the transfer ribonucleic acid genes of Escherichia coli K-12. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):379–397. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.379-397.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroux S., Beaudet J., Cedergren R. Highly repetitive tRNA(Pro)-tRNA(His) gene cluster from Photobacterium phosphoreum. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5601–5606. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5601-5606.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroux S., Cedergren R. Tandemly repeated tRNA pseudogenes in photobacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9101–9105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu X. R., Giroux S., Cedergren R. The nucleotide sequence of the argT locus of Aeromonas hydrophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10936–10936. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. M., Klee H. J., Zagorski J., Fournier M. J. Structure of an Escherichia coli tRNA operon containing linked genes for arginine, histidine, leucine, and proline tRNAs. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):934–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.934-942.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L., Rossi J., Landy A. Dual function transcripts specifying tRNA and mRNA. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):422–427. doi: 10.1038/294422a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M. A., Jones D. S. A fragment of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa genome contains five tRNA genes, four of which are linked to an EF-Tu gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7193–7193. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Stringent control of bacterial transcription. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):6–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Ozeki H., Shimura Y. Organization and structure of an E. coli tRNA operon containing seven tRNA genes. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T. D., Hill C. W. Recombination between repeated genes in microorganisms. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:147–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Yeats S. Transfer RNA genes frequently serve as integration sites for prokaryotic genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1907–1914. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Hartmann T., Weber J., Blank J., Zeidler R. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17 (Suppl):r1–172. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich A. K., Parker J. Strains overproducing tRNA for histidine. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Dec;205(3):540–545. doi: 10.1007/BF00338095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vold B. S. Structure and organization of genes for transfer ribonucleic acid in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.71-80.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]