Abstract
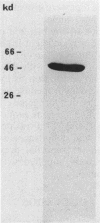
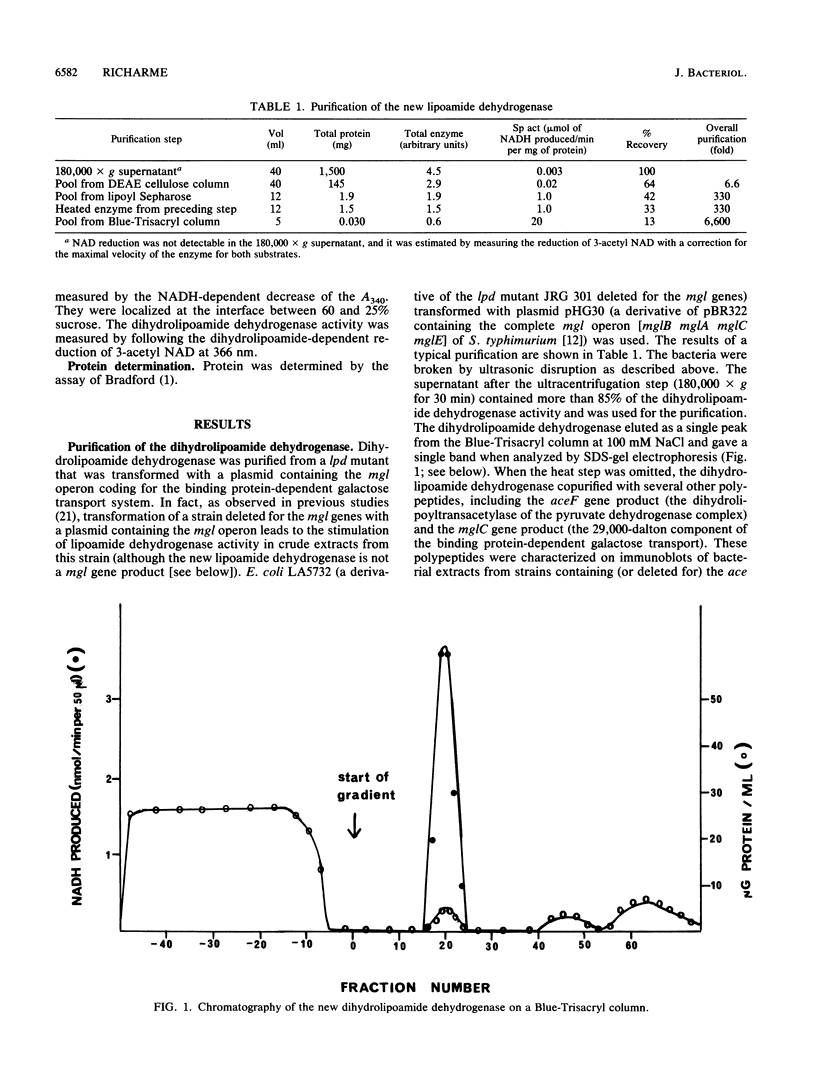
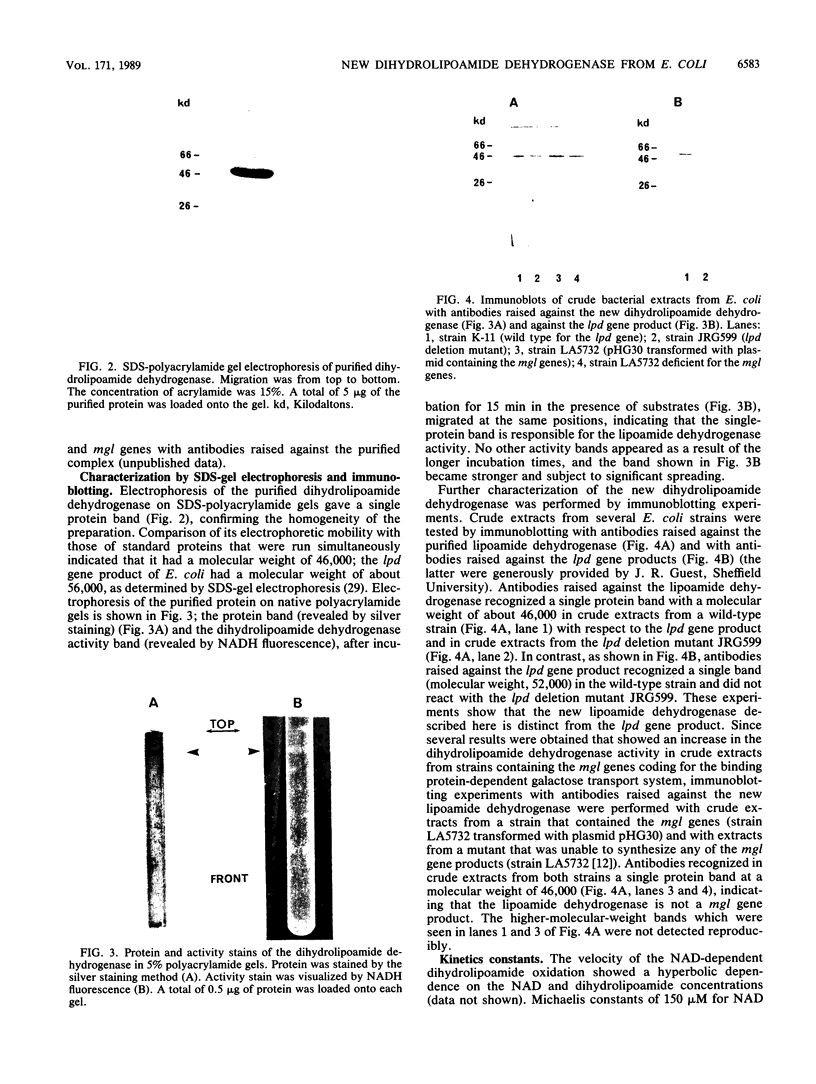
I purified a new dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase from a lpd mutant of Escherichia coli deficient in the lipoamide dehydrogenase (EC 1.6.4.3) common to the pyruvate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.4.1) and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes. The occurrence of the new lipoamide dehydrogenase in lpd mutants, including a lpd deletion mutant and the immunological properties of the enzyme, showed that it is different from the lpd gene product. The new dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase had a molecular weight of 46,000, as determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. It was expressed in low amounts. It catalyzed the NAD+-dependent reduction of dihydrolipoamide with a maximal activity of 20 mumol/min per mg of protein and exhibited a hyperbolic dependence of catalytic activity on the concentration of both dihydrolipoamide and NAD+. The possible implication of the new dihydrolipoamide in the function of 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complexes is discussed, as is its relation to binding protein-dependent transport.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Conroy K., McQuattie A., Stevenson K. J. Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase from Trypanosoma brucei. Characterization and cellular location. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):661–665. doi: 10.1042/bj2430661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Eisenthal R., Hall S., Kessell S. R., Williams D. L. Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase from halophilic archaebacteria. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj2180811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Creaghan I. T. Further studies with lipoamide dehydrogenase mutants of Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):237–245. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Creaghan I. T. Gene-protein relationships of the alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes of Escherichia coli K12: isolation and characterization of lipoamide dehydrogenase mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Mar;75(1):197–210. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishidate K., Creeger E. S., Zrike J., Deb S., Glauner B., MacAlister T. J., Rothfield L. I. Isolation of differentiated membrane domains from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, including a fraction containing attachment sites between the inner and outer membranes and the murein skeleton of the cell envelope. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):428–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley D., Guest J. R. Biochemical genetics of the alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes of Escherichia coli K12: isolation and biochemical properties of deletion mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):263–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr A. G., Ingraham J. L. EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE COMPOSITION OF FATTY ACIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1260–1267. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1260-1267.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N., Heine H. G., Boos W. Characterization of the Salmonella typhimurium mgl operon and its gene products. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):37–45. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.37-45.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Yoshizawa K., Ejima A., Hayashi T., Kaneda T. Coenzyme A- and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4437–4447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. 8. Comparison of dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenases from pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1126–1130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G. Binding protein-dependent transports in 2-oxo acids dehydrogenase mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 10;893(2):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(87)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G., Heine H. G. Galactose- and maltose-stimulated lipoamide dehydrogenase activities related to the binding-protein-dependent transport of galactose and maltose in toluenized cells of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 15;156(2):399–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G. Possible involvement of lipoic acid in binding protein-dependent transport systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):286–293. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.286-293.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G. Reconstitution du transport de haute affinité du galactose de Salmonella typhimurium dans des protéoliposomes: énergisation par le lipoamide et le NAD ou par le potentiel de membrane; inhibition par l'ATP. C R Acad Sci III. 1987;305(3):55–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scouten W. H., McManus I. R. Microbial lipoamide dehydrogenase. Purification and some characteristics of the enzyme derived from selected microorganisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 10;227(2):248–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokatch J. R., Burns G. Oxidation of glycine by Pseudomonas putida requires a specific lipoamide dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 1;228(2):660–666. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokatch J. R., McCully V., Gebrosky J., Sokatch D. J. Isolation of a specific lipoamide dehydrogenase for a branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):639–646. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.639-646.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokatch J. R., McCully V., Roberts C. M. Purification of a branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):647–652. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.647-652.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. J., Perham R. N. Purification of 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes from ox heart by a new method. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):147–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1910147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer R. C., 3rd, Merril C. R., Shifrin S. A highly sensitive silver stain for detecting proteins and peptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90732-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes P. J., Burns G., Menard J., Hatter K., Sokatch J. R. Molecular cloning of genes encoding branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1619–1625. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1619-1625.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]