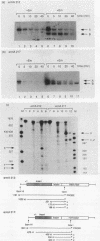
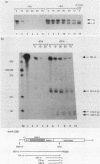
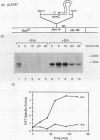
Abstract
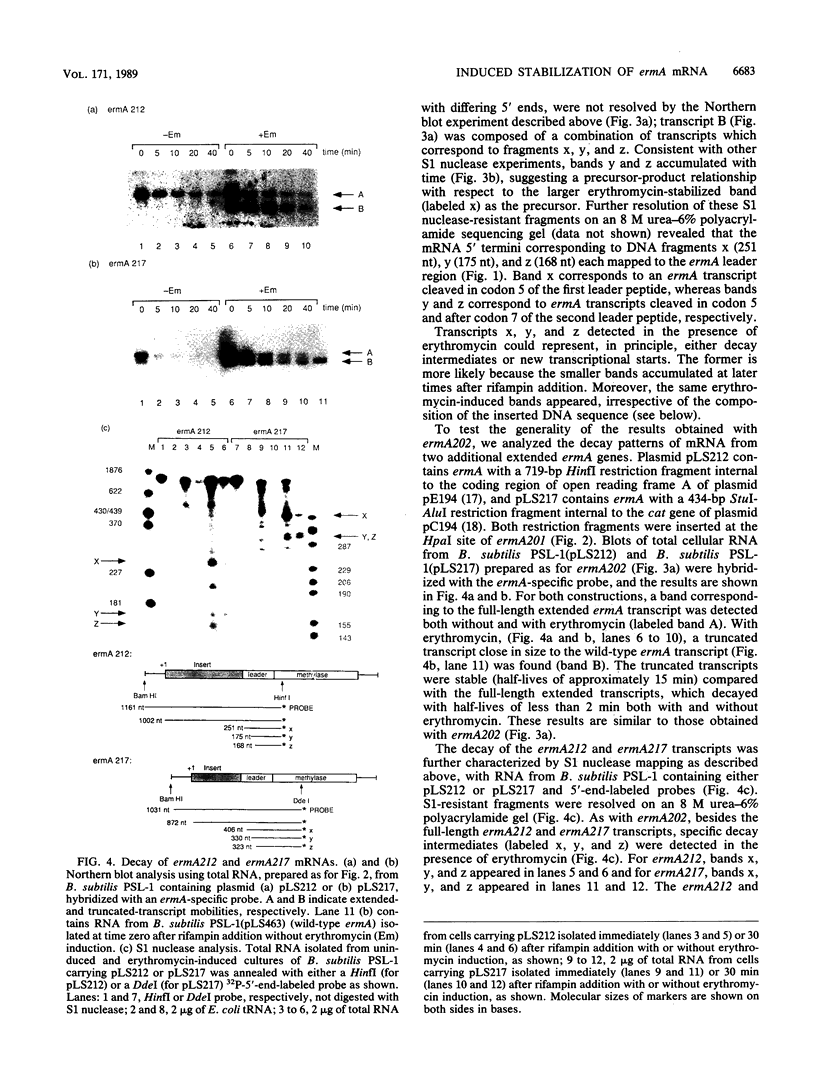
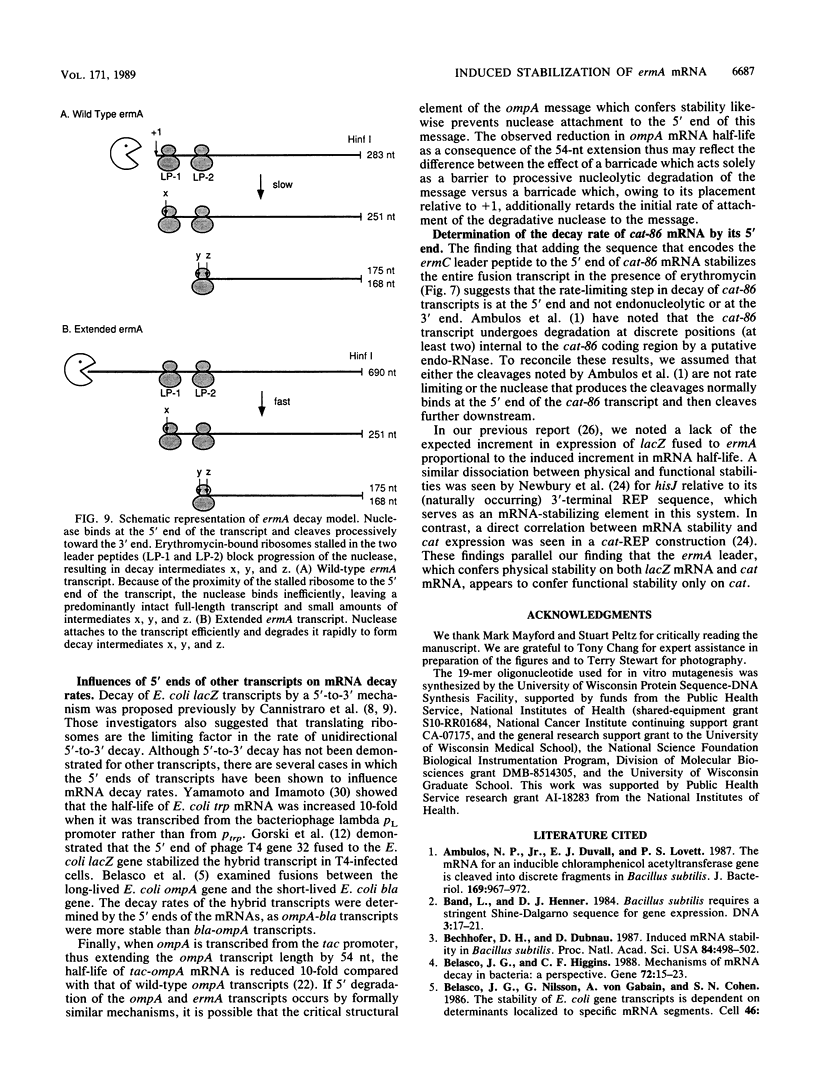
The Staphylococcus aureus ermA gene, whose product confers resistance to the macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B family of antibiotics, is induced at the level of translation by nanomolar concentrations of erythromycin. Erythromycin also specifically stabilizes ermA transcripts, and the induced stabilization requires in-phase translation of at least one of two small leader peptides in the 5' leader region of the transcript. Erythromycin-induced mRNA stabilization was tested in three constructions in which the ermA transcript was elongated by making insertions at the ermA transcription start. Whereas mRNA downstream of the leader peptide is stabilized by erythromycin, mRNA upstream is not. In the presence of erythromycin, specific mRNA decay intermediates in both the extended ermA genes and the wild-type ermA gene were detected by both Northern blotting and S1 nuclease mapping. The 5' ends of the intermediates map to the sequences that encode each of the two ermA leader peptides, suggesting that the intermediates are produced by stalled erythromycin-bound ribosomes acting as barricades to degradation by 5'-to-3' RNases. In addition, whereas erythromycin was found previously to stabilize ermA transcripts only physically, an ermC-cat-86 hybrid transcript was stabilized both physically and functionally by erythromycin.
Full text
PDF

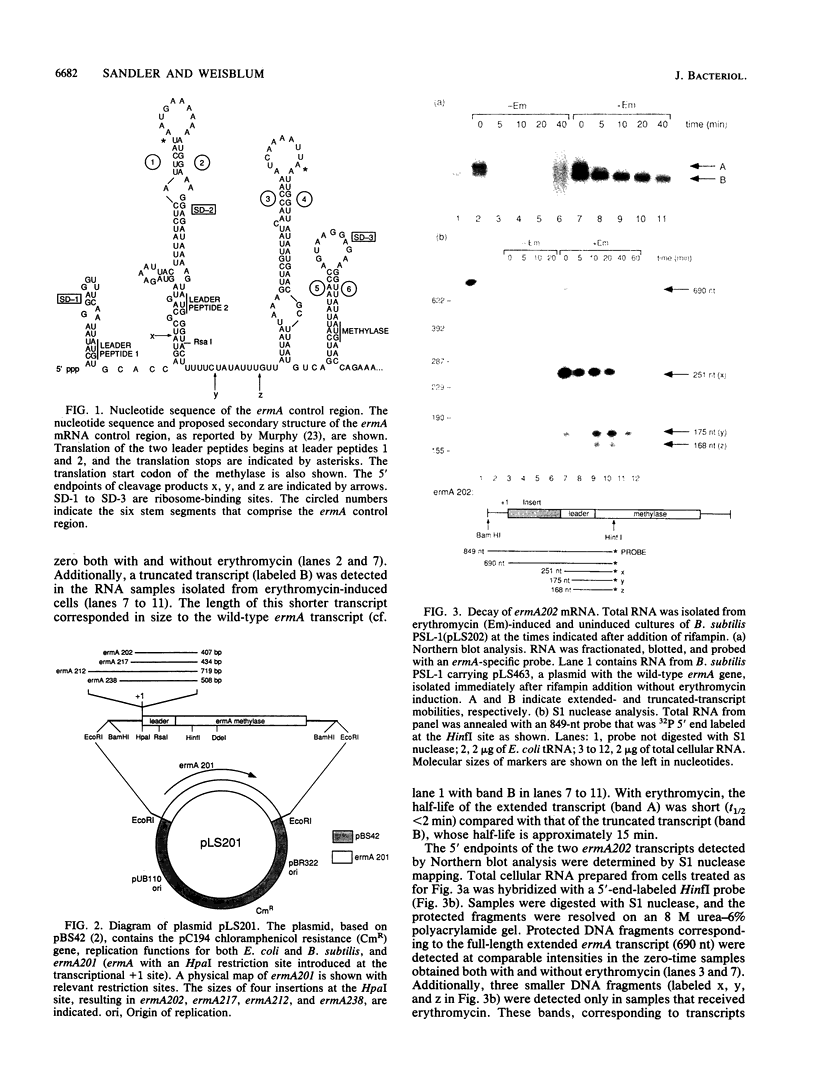




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambulos N. P., Jr, Duvall E. J., Lovett P. S. The mRNA for an inducible chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene is cleaved into discrete fragments in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):967–972. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.967-972.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Band L., Henner D. J. Bacillus subtilis requires a "stringent" Shine-Dalgarno region for gene expression. DNA. 1984;3(1):17–21. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechhofer D. H., Dubnau D. Induced mRNA stability in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belasco J. G., Higgins C. F. Mechanisms of mRNA decay in bacteria: a perspective. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. mRNA decay: finding the right targets. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannistraro V. J., Kennell D. Evidence that the 5' end of lac mRNA starts to decay as soon as it is synthesized. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):820–822. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.820-822.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannistraro V. J., Subbarao M. N., Kennell D. Specific endonucleolytic cleavage sites for decay of Escherichia coli mRNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 20;192(2):257–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P. E. coli RNases: making sense of alphabet soup. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):731–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Roch J. M., Prentki P., Krisch H. M. The stability of bacteriophage T4 gene 32 mRNA: a 5' leader sequence that can stabilize mRNA transcripts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J. A., Murray N. E. Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 5;166(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Grandi G., Hahn J., Grandi R., Dubnau D. Conformational alteration of mRNA structure and the posttranscriptional regulation of erythromycin-induced drug resistance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6081–6097. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood C. R., Williams D. M., Lovett P. S. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus pumilus gene specifying chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):815–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.815-825.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pE194, a plasmid that specifies inducible resistance to macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin type B antibodies. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):804–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.804-814.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation: mechanism that regulates erythromycin-induced resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7079–7083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. W., Cantor C. R. Structure of ribosome-bound messenger RNA as revealed by enzymatic accessibility studies. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. C., Sirdeskmukh R., Schlessinger D. Nucleolytic processing of ribonucleic acid transcripts in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):428–451. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.428-451.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayford M., Weisblum B. ermC leader peptide. Amino acid sequence critical for induction by translational attenuation. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90524-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melefors O., von Gabain A. Site-specific endonucleolytic cleavages and the regulation of stability of E. coli ompA mRNA. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):893–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. Nucleotide sequence of ermA, a macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B determinant in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):633–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.633-640.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbury S. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Hiles I. D., Higgins C. F. Stabilization of translationally active mRNA by prokaryotic REP sequences. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):297–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff G. R., Pène J. J. Molecular cloning with bifunctional plasmid vectors in Bacillus subtilis: isolation of a spontaneous mutant of Bacillus subtilis with enhanced transformability for Escherichia coli-propagated chimeric plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):934–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.934-936.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler P., Weisblum B. Erythromycin-induced stabilization of ermA messenger RNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):905–915. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Siddhikol C., Lai C. J., Demohn V. Erythromycin-inducible resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: requirements for induction. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):835–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.835-847.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Duvall E. J., Lovett P. S. Cloning restriction fragments that promote expression of a gene in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1162–1165. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1162-1165.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Imamoto F. Differential stability of trp messenger RNA synthesized originating at the trp promoter and pL promoter of lambda trp phage. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):289–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]