Abstract
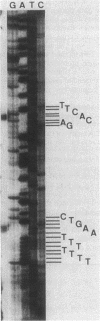
The start point for transcription of the subtilisin (aprE) gene was determined by primer extension analysis and was found to be at a point significantly different from that identified in a previously published report (S. L. Wong, C. W. Price, D. S. Goldfarb, and R. H. Doi, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:1184-1188, 1984). An aprE-lacZ fusion was used to analyze expression of the promoter. Deletion analyses of the promoter were performed to determine the extent of the upstream region necessary for activity. This was found to be between -52 and -41 with respect to the transcription start site. Expression of the aprE-lacZ fusion was unimpaired in a mutant deleted for the sigma B subunit of RNA polymerase. Mutations in the gene for the sigma H subunit of RNA polymerase decreased expression of the aprE-lacZ fusion to approximately 25% of that of the wild type. These results leave the identity of the sigma factor responsible for transcription of this gene in question. Mutations in the spo0A gene drastically decreased the activity of the aprE promoter and its upstream deletion derivatives, while the abrB gene, a phenotypic suppressor of spo0 mutations, restored activity of the aprE promoter in all of the deletion derivatives. Thus, inhibition of transcription by the spo0A mutation and its restoration by an abrB mutation could not be separated from the promoter of the aprE gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnie C., Lampe M., Losick R. Gene encoding the sigma 37 species of RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5943–5947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari E., Howard S. M., Hoch J. A. Effect of stage 0 sporulation mutations on subtilisin expression. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):173–179. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.173-179.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Trach K., Hoch J. A. Sequence analysis of the spo0B locus reveals a polycistronic transcription unit. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):556–562. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.556-562.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A. Genetics of bacterial sporulation. Adv Genet. 1976;18:69–98. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marahiel M. A., Zuber P., Czekay G., Losick R. Identification of the promoter for a peptide antibiotic biosynthesis gene from Bacillus brevis and its regulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2215–2222. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2215-2222.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins J. B., Youngman P. J. Construction and properties of Tn917-lac, a transposon derivative that mediates transcriptional gene fusions in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):140–144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Henner D. J. Construction of a single-copy integration vector and its use in analysis of regulation of the trp operon of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferrari E. Replacement of the Bacillus subtilis subtilisin structural gene with an In vitro-derived deletion mutation. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):411–418. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.411-418.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Chen S. M., Hoch J. A. Genetic analysis of a class of polymyxin resistant partial revertants of stage O sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis: map of the chromosome region near the origin of replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 23;173(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00267691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J., Dubnau E., Ramakrishna N., Smith I. Bacillus subtilis spo0H gene. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):405–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.405-412.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Ferrari E., Henner D. J., Estell D. A., Chen E. Y. Cloning, sequencing, and secretion of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subtilisin in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7911–7925. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. L., Price C. W., Goldfarb D. S., Doi R. H. The subtilisin E gene of Bacillus subtilis is transcribed from a sigma 37 promoter in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M. Y., Ferrari E., Henner D. J. Cloning of the neutral protease gene of Bacillus subtilis and the use of the cloned gene to create an in vitro-derived deletion mutation. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.15-21.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Losick R. Role of AbrB in Spo0A- and Spo0B-dependent utilization of a sporulation promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2223–2230. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2223-2230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]