Abstract
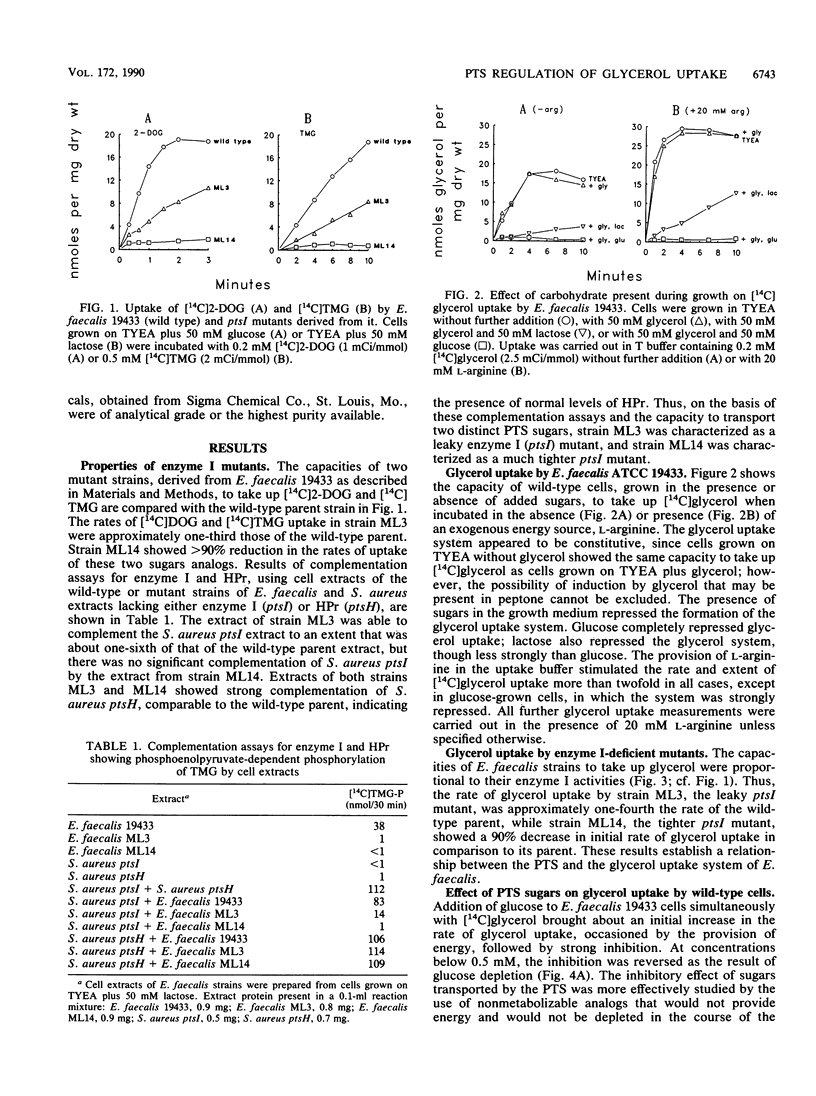
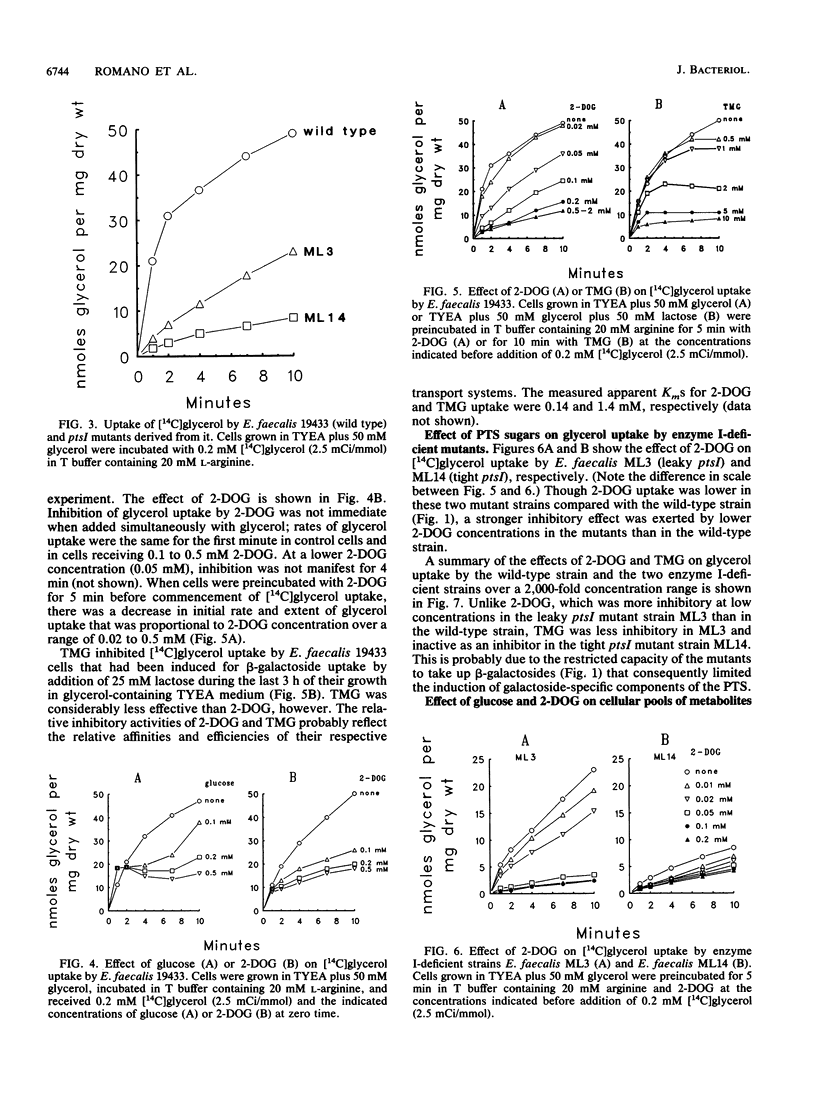
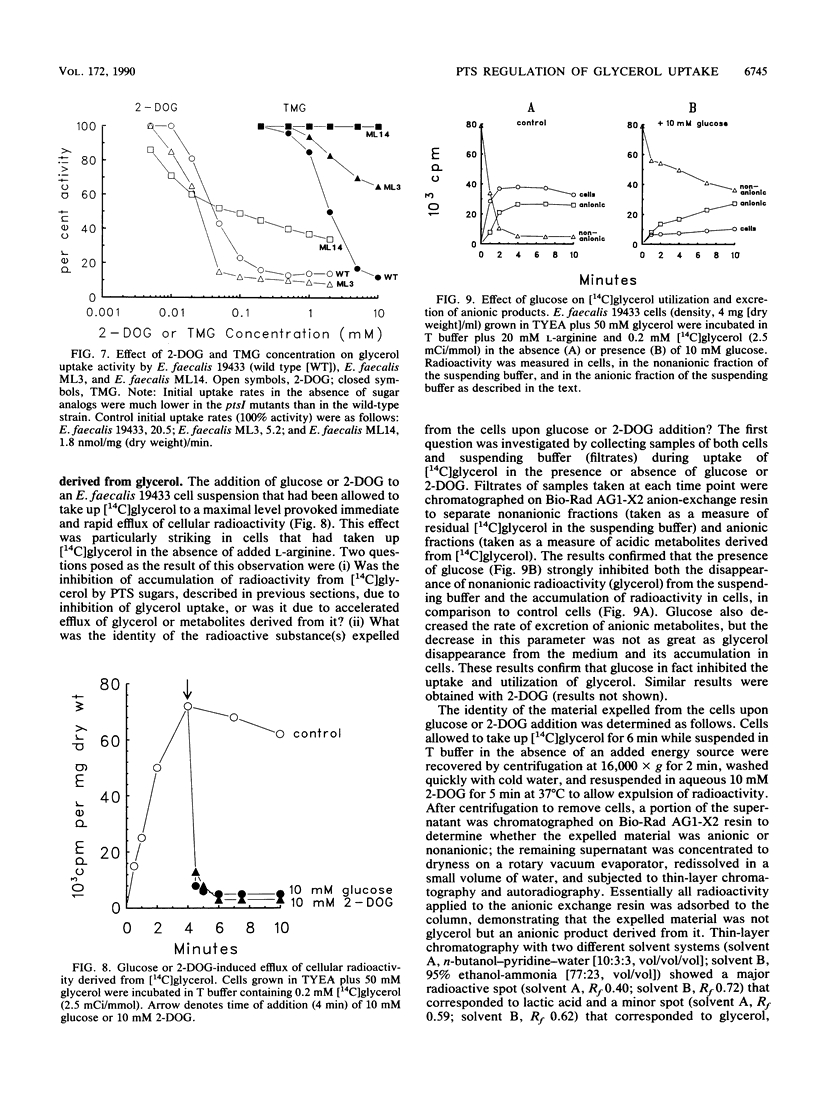
In vitro studies with purified glycerol kinase from Enterococcus faecalis have established that this enzyme is activated by phosphorylation of a histidyl residue in the protein, catalyzed by the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system (PTS), but the physiological significance of this observation is not known. In the present study, the regulation of glycerol uptake was examined in a wild-type strain of E. faecalis as well as in tight and leaky ptsI mutants, altered with respect to their levels of enzyme I of the PTS. Glycerol kinase was shown to be weakly repressible by lactose and strongly repressible by glucose in the wild-type strain. Greatly reduced levels of glycerol kinase activity were also observed in the ptsI mutants. Uptake of glycerol into intact wild-type and mutant cells paralleled the glycerol kinase activities in extracts. Glycerol uptake in the leaky ptsI mutant was hypersensitive to inhibition by low concentrations of 2-deoxyglucose or glucose even though the rates and extent of 2-deoxyglucose uptake were greatly reduced. These observations provide strong support for the involvement of reversible PTS-mediated phosphorylation of glycerol kinase in the regulation of glycerol uptake in response to the presence or absence of a sugar substrate of the PTS in the medium. Glucose and 2-deoxyglucose were shown to elicit rapid efflux of cytoplasmic [14C]lactate derived from [14C]glycerol. This phenomenon was distinct from the inhibition of glycerol uptake and was due to phosphorylation of the incoming sugar by cytoplasmic phosphoenolpyruvate. Lactate appeared to be generated by sequential dephosphorylation and reduction of cytoplasmic phosphoenolpyruvate present in high concentrations in resting cells.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chassy B. M., Thompson J. Regulation of lactose-phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system and beta-D-phosphogalactoside galactohydrolase activities in Lactobacillus casei. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1195–1203. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1195-1203.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dashper S. G., Reynolds E. C. Characterization of transmembrane movement of glucose and glucose analogs in Streptococcus mutants Ingbritt. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):556–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.556-563.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher J., Sauerwald H. Stimulation of dihydroxyacetone and glycerol kinase activity in Streptococcus faecalis by phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphorylation catalyzed by enzyme I and HPr of the phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.829-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dills S. S., Seno S. Regulation of hexitol catabolism in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):861–866. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.861-866.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzy-Tréboul G., Zagorec M., Rain-Guion M. C., Steinmetz M. Phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system of Bacillus subtilis: nucleotide sequence of ptsX, ptsH and the 5'-end of ptsI and evidence for a ptsHI operon. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jan;3(1):103–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton I. R., St Martin E. J. Evidence for the involvement of proton motive force in the transport of glucose by a mutant of Streptococcus mutans strain DR0001 defective in glucose-phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase activity. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):567–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.567-575.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Levin E. Lactic acid translocation: terminal step in glycolysis by Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1141–1148. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1141-1148.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S. I., Lin E. C. Product induction of glycerol kinase in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):515–521. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller K. B., Lin E. C., Wilson T. H. Substrate specificity and transport properties of the glycerol facilitator of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):274–278. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.274-278.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengstenberg W., Penberthy W. K., Hill K. L., Morse M. L. Phosphotransferase system of Staphylococcus aureus: its requirement for the accumulation and metabolism of galactosides. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):383–388. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.383-388.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Poy F., Lengeler J. W. Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans by the antibiotic streptozotocin: mechanisms of uptake and the selection of carbohydrate-negative mutants. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):543–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.543-549.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Roseman S. Sugar transport. II. Characterization of constitutive membrane-bound enzymes II of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1407–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengeler J. Analysis of the physiological effects of the antibiotic streptozotocin on Escherichia coli K 12 and other sensitive bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Dec;128(2):196–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00406158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengeler J. Characterisation of mutants of Escherichia coli K12, selected by resistance to streptozotocin. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):49–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00268445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman E. S., Bleiweis A. S. Role of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent glucose phosphotransferase system of Streptococcus mutans GS5 in the regulation of lactose uptake. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):536–542. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.536-542.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE M. L., ALIRE M. L. An agar medium indicating acid production. J Bacteriol. 1958 Sep;76(3):270–271. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.3.270-271.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny M. J., Frederickson W. L., Waygood E. B., Saier M. H., Jr Allosteric regulation of glycerol kinase by enzyme IIIglc of the phosphotransferase system in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):810–816. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.810-816.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Royer T. J., Mainzer S. E., Schmidt B. F. Lactose transport system of Streptococcus thermophilus: a hybrid protein with homology to the melibiose carrier and enzyme III of phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase systems. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):244–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.244-253.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Epstein W., Schuitema A. R., Nelson S. O. Interaction between IIIGlc of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system and glycerol kinase of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):351–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.351-353.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Novotny M. J., Stuiver I., Saier M. H., Jr Regulation of glycerol uptake by the phosphoenolpyruvate-sugar phosphotransferase system in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.243-250.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J. Regulation of sugar uptake and efflux in gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;5(1-2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Saier M. H., Jr, Deutscher J., Grenier F., Thompson J., Hengstenberg W. The phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in gram-positive bacteria: properties, mechanism, and regulation. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1988;15(4):297–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418809104461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Protein phosphorylation and allosteric control of inducer exclusion and catabolite repression by the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):109–120. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.109-120.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Roseman S., Saier M. H., Jr Sugar transport. Properties of mutant bacteria defective in proteins of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6584–6597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Saier M. H., Jr Regulation of methyl-beta-d-thiogalactopyranoside-6-phosphate accumulation in Streptococcus lactis by exclusion and expulsion mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):885–894. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.885-894.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadeboncoeur C. Structure and properties of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system of oral streptococci. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Apr;30(4):495–502. doi: 10.1139/m84-073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer M., Broekhuizen C. P., Postma P. W. Regulation of glycerol kinase by enzyme IIIGlc of the phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):393–395. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.393-395.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


