Abstract
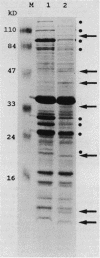
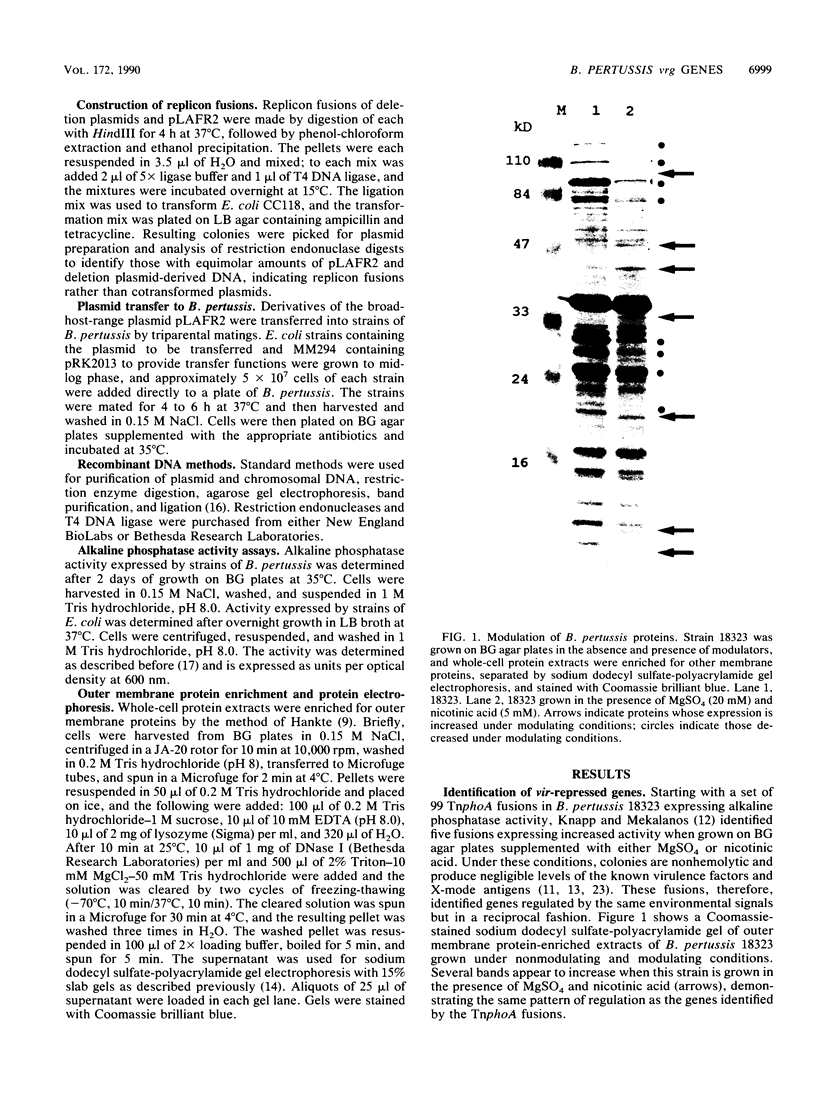
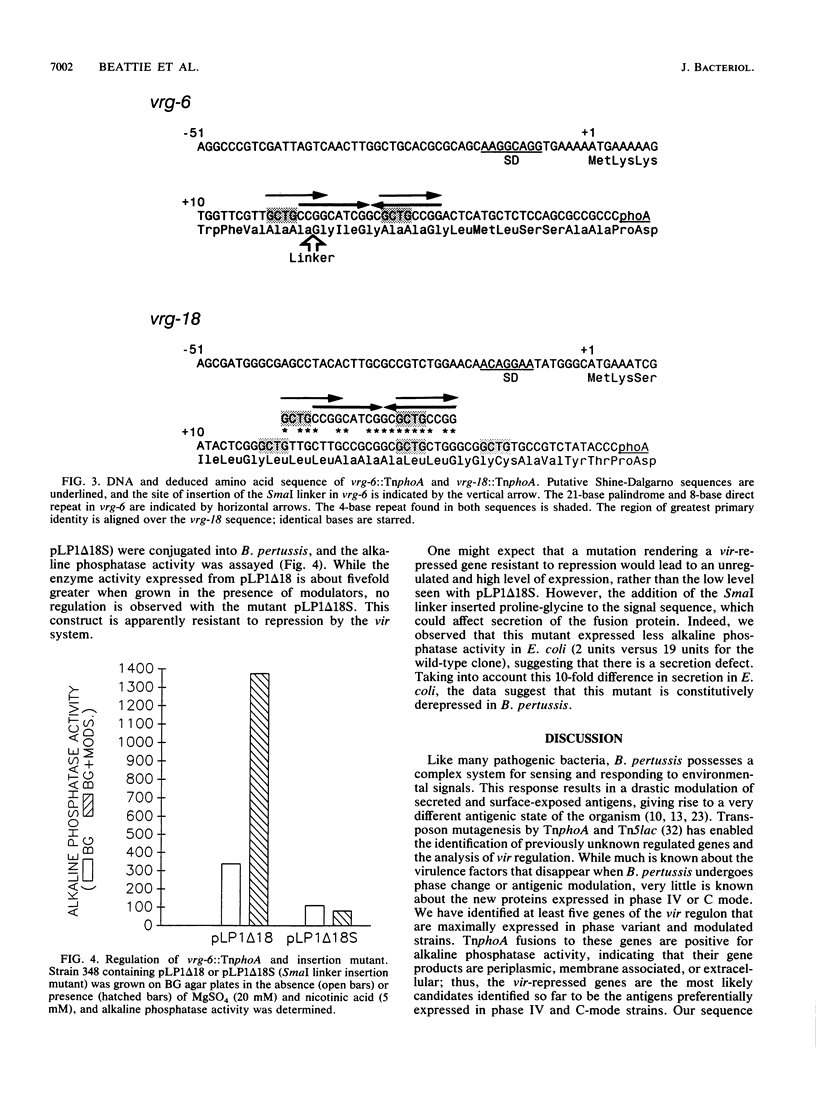
Gene expression in Bordetella pertussis is altered by environmental signals in a process called antigenic modulation. In the presence of modulating signals, expression of several known virulence factors and outer membrane proteins is coordinately reduced. From a bank of TnphoA fusions, we have identified five genes whose expression profiles are reciprocal of those of the major virulence determinants; that is, alkaline phosphatase activity is maximal during growth in the presence of the modulators nicotinic acid and MgSO4 (S. Knapp and J. J. Mekalanos, J. Bacteriol. 170:5059-5066, 1988). We have called these loci vir-repressed genes (vrg). Two of these gene fusions (vrg-6 and vrg-18) have been cloned in Escherichia coli, returned on low-copy-number plasmids to several strains of B. pertussis, and found to be regulated similarly to the fusions harbored on the chromosome. Deletions of the two vrg promoters were constructed and returned to B. pertussis. Regulation was maintained even when all but 24 nucleotides upstream of the vrg-18 initiation codon and 60 nucleotides upstream of the vrg-6 initiation codon were deleted, suggesting that cis-acting regulatory elements of these genes lie very near or within the coding region. We observed a 21-base palindromic sequence overlapping an 8-base direct repeat within the signal sequence coding region of vrg-6; insertion of a 6-bp linker in this region abolished regulation. These repetitive sequences are also at the site of greatest primary sequence identify between vrg-6 and vrg-18 and correspond to the signal sequence coding region. We propose models that involve recognition of this region by a vir-regulated gene product.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aricó B., Miller J. F., Roy C., Stibitz S., Monack D., Falkow S., Gross R., Rappuoli R. Sequences required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors share homology with prokaryotic signal transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechhofer D. H., Dubnau D. Induced mRNA stability in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. lac Repressor blocks transcribing RNA polymerase and terminates transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4134–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewanowich C. A., Melton A. R., Weiss A. A., Sherburne R. K., Peppler M. S. Invasion of HeLa 229 cells by virulent Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2698–2704. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2698-2704.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K. Regulation of ferric iron transport in Escherichia coli K12: isolation of a constitutive mutant. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):288–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00269672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idigbe E. O., Parton R., Wardlaw A. C. Rapidity of antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis in modified Hornibrook medium. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(4):409–418. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-4-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. Two trans-acting regulatory genes (vir and mod) control antigenic modulation in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5059–5066. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5059-5066.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K., Roberts A. L., Finn T. M., Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. A new assay for invasion of HeLa 229 cells by Bordetella pertussis: effects of inhibitors, phenotypic modulation, and genetic alterations. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2516–2522. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2516-2522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton A. R., Weiss A. A. Environmental regulation of expression of virulence determinants in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6206–6212. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6206-6212.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Roy C. R., Falkow S. Analysis of Bordetella pertussis virulence gene regulation by use of transcriptional fusions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6345–6348. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6345-6348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monack D. M., Arico B., Rappuoli R., Falkow S. Phase variants of Bordetella bronchiseptica arise by spontaneous deletions in the vir locus. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1719–1728. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Belasco J. G., Cohen S. N., von Gabain A. Growth-rate dependent regulation of mRNA stability in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):75–77. doi: 10.1038/312075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppler M. S. Isolation and characterization of isogenic pairs of domed hemolytic and flat nonhemolytic colony types of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):840–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.840-851.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. R., Miller J. F., Falkow S. The bvgA gene of Bordetella pertussis encodes a transcriptional activator required for coordinate regulation of several virulence genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6338–6344. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6338-6344.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler P., Weisblum B. Erythromycin-induced ribosome stall in the ermA leader: a barricade to 5'-to-3' nucleolytic cleavage of the ermA transcript. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6680–6688. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6680-6688.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Aaronson W., Monack D., Falkow S. Phase variation in Bordetella pertussis by frameshift mutation in a gene for a novel two-component system. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):266–269. doi: 10.1038/338266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of a region of the Bordetella pertussis chromosome encoding filamentous hemagglutinin and the pleiotropic regulatory locus vir. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2904–2913. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2904-2913.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. R., Adari H. Y., Spicer E. K. Bacteriophage T4 regA protein binds to the Shine-Dalgarno region of gene 44 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):10047–10068. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.10047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of phase change in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.263-269.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Melton A. R., Walker K. E., Andraos-Selim C., Meidl J. J. Use of the promoter fusion transposon Tn5 lac to identify mutations in Bordetella pertussis vir-regulated genes. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2674–2682. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2674-2682.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]