Abstract
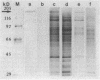
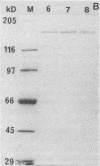
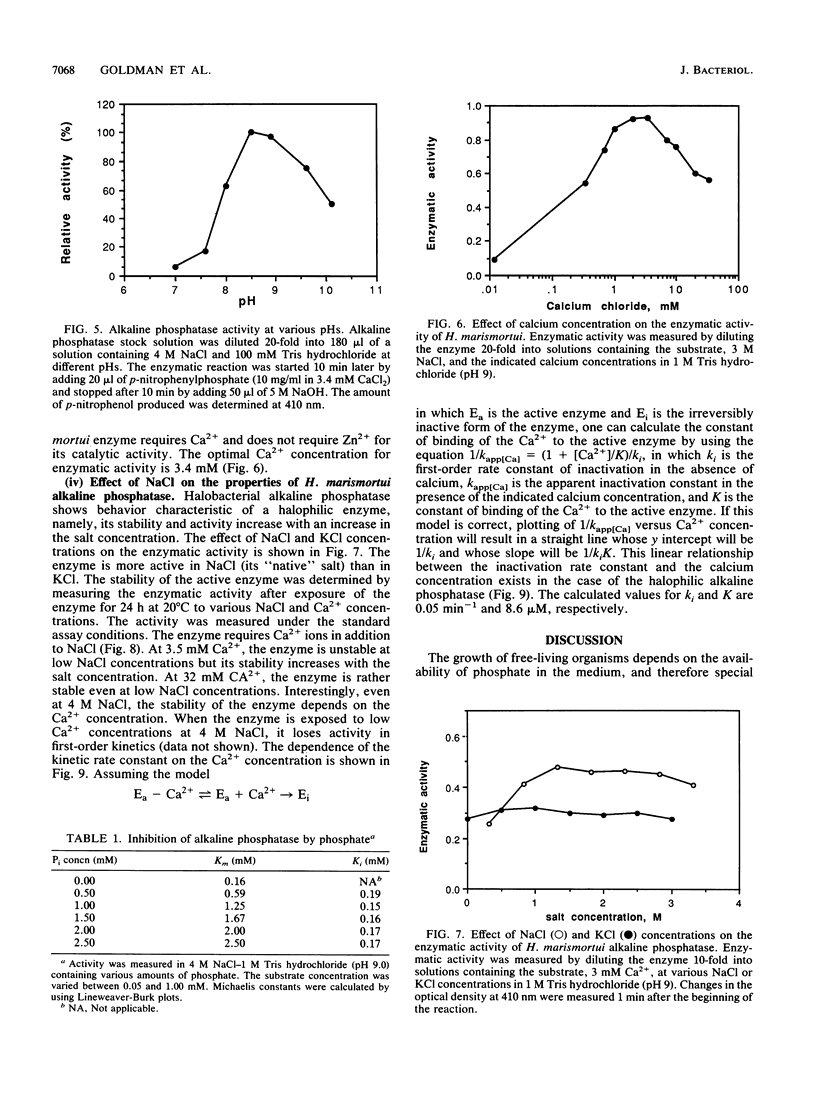
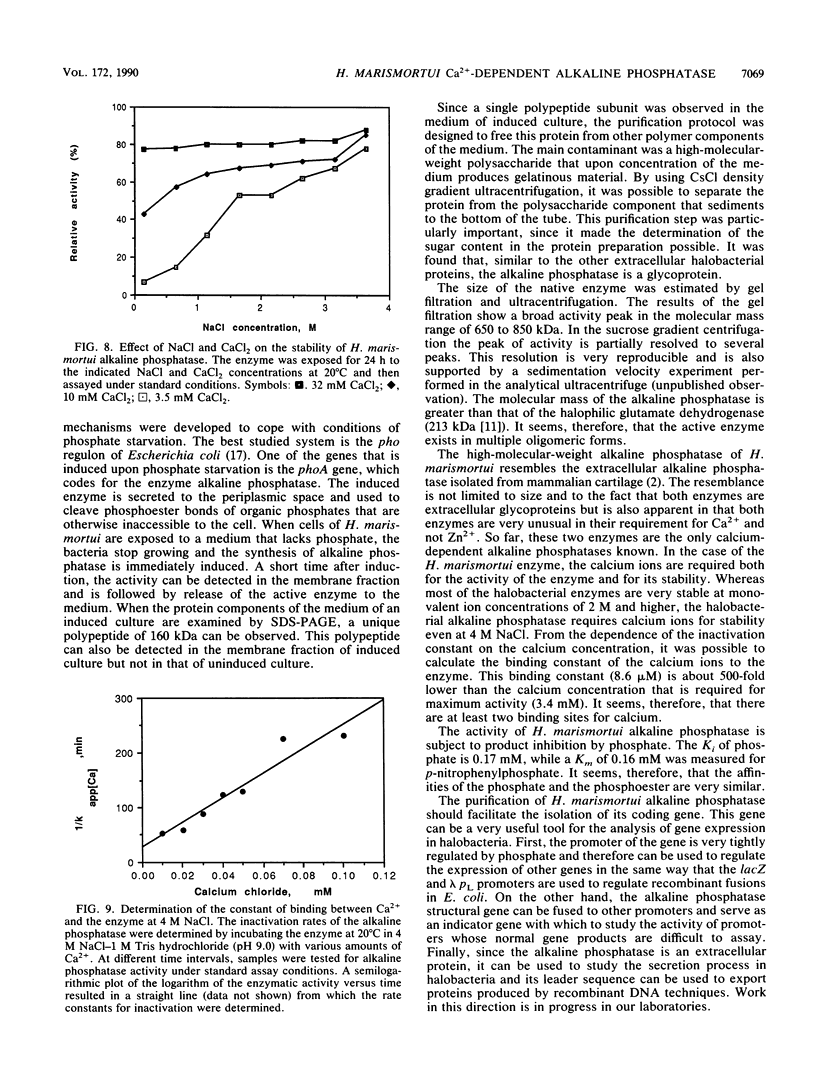
When starved of inorganic phosphate, the extremely halophilic archaebacterium Haloarcula marismortui produces the enzyme alkaline phosphatase and secretes it to the medium. This inducible extracellular enzyme is a glycoprotein whose subunit molecular mass is 160 kDa, as estimated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis. The native form of the enzyme is heterogeneous and composed of multiple oligomeric forms. The enzymatic activity of the halophilic alkaline phosphatase is maximal at pH 8.5, and the enzyme is inhibited by phosphate. Unlike most alkaline phosphatases, the halobacterial enzyme requires Ca2+ and not Zn2+ ions for its activity. Both calcium ions (in the millimolar range) and NaCl (in the molar range) are required for the stability of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg H., Wachtel E. J. Structural studies of halophilic proteins, ribosomes, and organelles of bacteria adapted to extreme salt concentrations. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:69–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerl L., Sumper M. Halobacterial flagellins are encoded by a multigene family. Characterization of five flagellin genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13246–13251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg M., Sachs L., Ginzburg B. Z. Ion metabolism in a Halobacterium. I. Influence of age of culture on intracellular concentrations. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Feb;55(2):187–207. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J., Sumper M. The primary structure of a procaryotic glycoprotein. Cloning and sequencing of the cell surface glycoprotein gene of halobacteria. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9724–9729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J., Wieland F. Structure and biosynthesis of prokaryotic glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:173–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leicht W., Werber M. M., Eisenberg H. Purification and characterization of glutamate dehydrogenase from Halobacterium of the Dead Sea. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):4004–4010. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mevarech M., Werczberger R. Genetic transfer in Halobacterium volcanii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):461–462. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.461-462.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumper M. Halobacterial glycoprotein biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 27;906(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(87)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland F., Paul G., Sumper M. Halobacterial flagellins are sulfated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15180–15185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bernard B., Bianco P., Bonucci E., Costantini M., Lunazzi G. C., Martinuzzi P., Modricky C., Moro L., Panfili E., Pollesello P. Biochemical and immunohistochemical evidence that in cartilage an alkaline phosphatase is a Ca2+-binding glycoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1615–1623. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]