Abstract
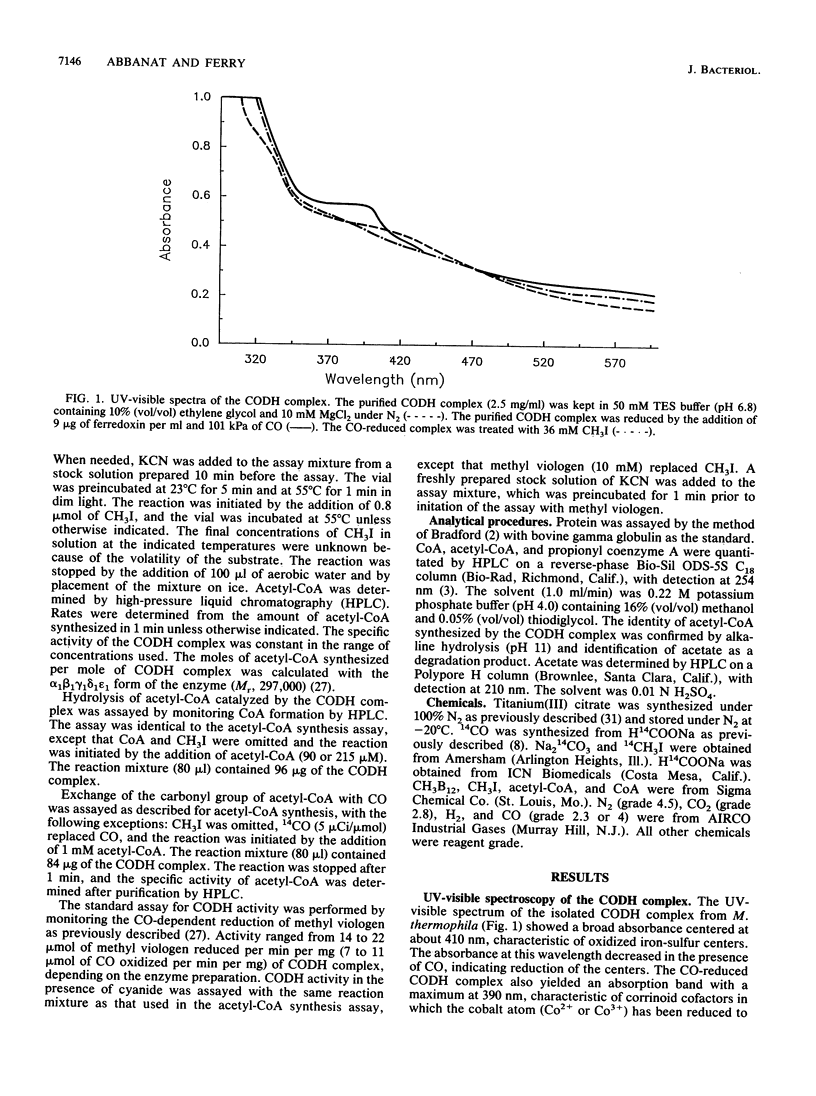
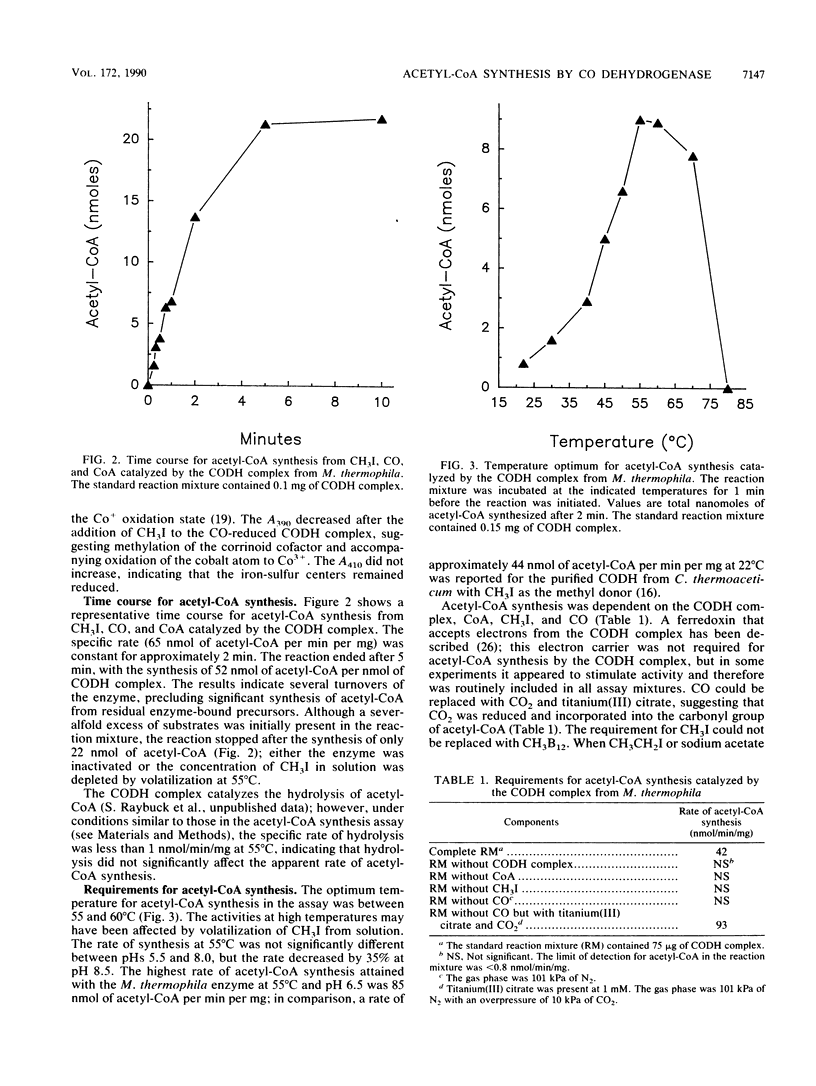
The carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (CODH) complex from Methanosarcina thermophila catalyzed the synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) from CH3I, CO, and coenzyme A (CoA) at a rate of 65 nmol/min/mg at 55 degrees C. The reaction ended after 5 min with the synthesis of 52 nmol of acetyl-CoA per nmol of CODH complex. The optimum temperature for acetyl-CoA synthesis in the assay was between 55 and 60 degrees C; the rate of synthesis at 55 degrees C was not significantly different between pHs 5.5 and 8.0. The rate of acetyl-CoA synthesis was independent of CoA concentrations between 20 microM and 1 mM; however, activity was inhibited 50% with 5 mM CoA. Methylcobalamin did not substitute for CH3I in acetyl-CoA synthesis; no acetyl-CoA or propionyl coenzyme A was detected when sodium acetate or CH3CH2I replaced CH3I in the assay mixture. CO could be replaced with CO2 and titanium(III) citrate. When CO2 and 14CO were present in the assay, the specific activity of the acetyl-CoA synthesized was 87% of the specific activity of 14CO, indicating that CO was preferentially incorporated into acetyl-CoA without prior oxidation to free CO2. Greater than 100 microM potassium cyanide was required to significantly inhibit acetyl-CoA synthesis, and 500 microM was required for 50% inhibition; in contrast, oxidation of CO by the CODH complex was inhibited 50% by approximately 10 microM potassium cyanide.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bott M., Eikmanns B., Thauer R. K. Coupling of carbon monoxide oxidation to CO2 and H2 with the phosphorylation of ADP in acetate-grown Methanosarcina barkeri. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):393–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough R. C., Barnum S. R., Jaworski J. G. Synthesis of radiolabeled acetyl-coenzyme A from sodium acetate. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):82–84. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMoll E., Grahame D. A., Harnly J. M., Tsai L., Stadtman T. C. Purification and properties of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase from Methanococcus vannielii. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3916–3920. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3916-3920.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs G., Schnitker U., Thauer R. K. Carbon monoxide oxidation by growing cultures of Clostridium pasteurianum. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):111–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten M. S., Stams A. J., Zehnder A. J. Purification and characterization of an oxygen-stable carbon monoxide dehydrogenase of Methanothrix soehngenii. Eur J Biochem. 1989 May 1;181(2):437–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W. R., Zeikus J. G. One-carbon metabolism in methanogens: evidence for synthesis of a two-carbon cellular intermediate and unification of catabolism and anabolism in Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):932–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.932-941.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzycki J. A., Lehman L. J., Zeikus J. G. Acetate catabolism by Methanosarcina barkeri: evidence for involvement of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase, methyl coenzyme M, and methylreductase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1000–1006. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1000-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzycki J. A., Zeikus J. G. Characterization and purification of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase from Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):231–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.231-237.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu W. P., Harder S. R., Ragsdale S. W. Controlled potential enzymology of methyl transfer reactions involved in acetyl-CoA synthesis by CO dehydrogenase and the corrinoid/iron-sulfur protein from Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3124–3133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Länge S., Fuchs G. Autotrophic synthesis of activated acetic acid from CO2 in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Synthesis from tetrahydromethanopterin-bound C1 units and carbon monoxide. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 16;163(1):147–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Ferry J. G. Carbon monoxide-dependent methyl coenzyme M methylreductase in acetotrophic Methosarcina spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):526–532. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.526-532.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale S. W., Lindahl P. A., Münck E. Mössbauer, EPR, and optical studies of the corrinoid/iron-sulfur protein involved in the synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A by Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14289–14297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale S. W., Wood H. G. Acetate biosynthesis by acetogenic bacteria. Evidence that carbon monoxide dehydrogenase is the condensing enzyme that catalyzes the final steps of the synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):3970–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale S. W., Wood H. G., Antholine W. E. Evidence that an iron-nickel-carbon complex is formed by reaction of CO with the CO dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6811–6814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raybuck S. A., Bastian N. R., Orme-Johnson W. H., Walsh C. T. Kinetic characterization of the carbon monoxide-acetyl-CoA (carbonyl group) exchange activity of the acetyl-CoA synthesizing CO dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7698–7702. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer N. L., Ferry J. G. Properties of formate dehydrogenase in Methanobacterium formicicum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.1-7.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh J., Whitman W. B. Autotrophic acetyl coenzyme A biosynthesis in Methanococcus maripaludis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3072–3079. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3072-3079.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Lequerica J. L., Hart M. R. Inhibition of methanogenesis and carbon metabolism in Methanosarcina sp. by cyanide. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):67–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.67-71.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terlesky K. C., Barber M. J., Aceti D. J., Ferry J. G. EPR properties of the Ni-Fe-C center in an enzyme complex with carbon monoxide dehydrogenase activity from acetate-grown Methanosarcina thermophila. Evidence that acetyl-CoA is a physiological substrate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15392–15395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terlesky K. C., Ferry J. G. Ferredoxin requirement for electron transport from the carbon monoxide dehydrogenase complex to a membrane-bound hydrogenase in acetate-grown Methanosarcina thermophila. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4075–4079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terlesky K. C., Nelson M. J., Ferry J. G. Isolation of an enzyme complex with carbon monoxide dehydrogenase activity containing corrinoid and nickel from acetate-grown Methanosarcina thermophila. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1053–1058. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1053-1058.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Käufer B., Fuchs G. The active species of 'CO2' utilized by reduced ferredoxin:CO2 oxidoreductase from Clostridium pasteurianum. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):111–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Möller-Zinkhan D., Spormann A. M. Biochemistry of acetate catabolism in anaerobic chemotrophic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:43–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Wuhrmann K. Titanium (III) citrate as a nontoxic oxidation-reduction buffering system for the culture of obligate anaerobes. Science. 1976 Dec 10;194(4270):1165–1166. doi: 10.1126/science.793008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


