Abstract
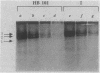
A mutant of Escherichia coli K-12 is described that is specifically impaired in only one hydrogenase isoenzyme. By means of Tn5-mediated insertional mutagenesis, a class of mutants was isolated (class I) that had retained 20% of the overall hydrogenase activity. As determined by neutral polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the mutant contained normal amounts of the hydrogenase isoenzymes 1 and 2. Therefore, the hydrogenase activity affected seemed to be electrophoretically labile and was called hydrogenase L. The presence of such an activity was recently suggested in various papers and was called isoenzyme 3. Hydrogenase L might be identical or part of the latter isoenzyme. By DEAE ion-exchange chromatography it could be separated from hydrogenases 1 and 2. Hydrogenase activity in the parent strain HB101, determined manometrically with cell-free preparations and methylviologen as the electron acceptor, immediately showed maximal activity. However, class I mutants showed a lag phase which was dependent on the protein concentration utilized in the assay. This suggested that the fast initial activity of HB101 was due to hydrogenase L. The enzyme or enzyme complex showed an Mr around 300,000 and a pH optimum between 7 and 8. Strong indications about its physiological role were provided by the finding that in class I mutants H2 production by the formate-hydrogen lyase pathway was unimpaired, whereas fumarate-dependent H2 uptake was essentially zero. Complementation with F-prime factor F'116 but not with F'143 and coconjugation and cotransduction experiments localized the mutation (hydL) close to metC at approximately 64.8 min.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackrell B. A., Asato R. N., Mower H. F. Multiple forms of bacterial hydrogenases. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):828–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.828-838.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams M. W., Mortenson L. E., Chen J. S. Hydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec;594(2-3):105–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(80)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantine S. P., Boxer D. H. Isolation and characterisation of a soluble active fragment of hydrogenase isoenzyme 2 from the membranes of anaerobically grown Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 15;156(2):277–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantine S. P., Boxer D. H. Nickel-containing hydrogenase isoenzymes from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):454–459. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.454-459.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B. R., Wang P. Y., Schneider H., Martin W. G. Identification and partial characterization of an Escherichia coli mutant with altered hydrogenase activity. Can J Biochem. 1980 Apr;58(4):361–367. doi: 10.1139/o80-047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingledew W. J., Poole R. K. The respiratory chains of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Sep;48(3):222–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.3.222-271.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. W. The role of the membrane-bound hydrogenase in the energy-conserving oxidation of molecular hydrogen by Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1980 May 15;188(2):345–350. doi: 10.1042/bj1880345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn P. L. Isolation of high-frequency recombining strains from Escherichia coli containing the V colicinogenic factor. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):205–214. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.205-214.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Roth J., Botstein D. Genetic engineering in vivo using translocatable drug-resistance elements. New methods in bacterial genetics. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):125–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasna A. I. Mutants of Escherichia coli with altered hydrogenase activity. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Apr;130(4):779–787. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-4-779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Guest J. R. Mutants of Escherichia coli K12 unable to use fumarate as an anaerobic electron acceptor. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Dec;97(2):145–160. doi: 10.1099/00221287-97-2-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. H., Patel P., Sankar P., Shanmugam K. T. Isolation and characterization of mutant strains of Escherichia coli altered in H2 metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):344–352. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.344-352.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macy J., Kulla H., Gottschalk G. H2-dependent anaerobic growth of Escherichia coli on L-malate: succinate formation. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):423–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.423-428.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Ganem D., Lu P., Schmitz A. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. I. Correlation of mutational sites with specific amino acid residues: construction of a colinear gene-protein map. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 15;109(2):275–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECK H. D., Jr, GEST H. Formic dehydrogenase and the hydrogenlyase enzyme complex in coli-aerogenes bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jun;73(6):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.6.706-721.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PICHINOTY F. [Inhibition by oxygen of the biosynthesis and activity of hydrogenase and hydrogenlyase in some anaerobic bacteria]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;64:111–124. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90764-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINSKY M. J., STOKES J. L. Requirements for formic hydrogenlyase adaptation in nonproliferating suspensions of escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1952 Aug;64(2):151–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.2.151-161.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascal M. C., Casse F., Chippaux M., Lepelletier M. Genetic analysis of mutants of Escherichia coli K12 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2 deficient in hydrogenase activity. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Nov 24;141(2):173–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00267682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers R. G., Ballantine S. P., Boxer D. H. Differential expression of hydrogenase isoenzymes in Escherichia coli K-12: evidence for a third isoenzyme. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1324–1331. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1324-1331.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers R. G., Boxer D. H. Purification and properties of membrane-bound hydrogenase isoenzyme 1 from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 15;156(2):265–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers R. G., Jamieson D. J., Higgins C. F., Boxer D. H. Characterization and physiological roles of membrane-bound hydrogenase isoenzymes from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):398–404. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.398-404.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R., Boxer D. H. Pleiotropic hydrogenase mutants of Escherichia coli K12: growth in the presence of nickel can restore hydrogenase activity. Biochimie. 1986 Jan;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)81080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. F., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A. Genetic and physiological characterization of new Escherichia coli mutants impaired in hydrogenase activity. Biochimie. 1986 Jan;68(1):167–179. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)81081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T. A model for three-point analysis of random general transduction. Genetics. 1966 Aug;54(2):405–410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto I., Ishimoto M. Hydrogen-dependent growth of Escherichia coli in anaerobic respiration and the presence of hydrogenases with different functions. J Biochem. 1978 Sep;84(3):673–679. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]