Abstract
Strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa causing chronic pulmonary infections in patients with cystic fibrosis are known to convert to a mucoid form in vivo characterized by the production of the exopolysaccharide alginate. The alginate production trait is not stable, and mucoid strains frequently convert back to the nonmucoid form in vitro. The DNA involved in these spontaneous alginate conversions, referred to as algS, was shown here to map near hisI and pru markers on the chromosome of strain FRD, an isolate from a cystic fibrosis patient. Although cloning algS+ by trans-complementation was not possible, a clone (pJF5) was isolated that caused algS mutants to convert to the Alg+ phenotype at detectable frequencies (approximately 0.1%) in vitro. Gene replacement with transposon-marked pJF5 followed by mapping studies showed that pJF5 contained DNA transducibly close to algS in the chromosome. Another clone was identified called pJF15 which did contain algS+ from mucoid P. aeruginosa. The plasmid-borne algS+ locus could not complement spontaneous algS mutations in trans, but its cis-acting activity was readily observed after gene replacement with the algS mutant chromosome by using an adjacent transposon as the selectable marker. pJF15 also contained a trans-active gene called algT+ in addition to the cis-active gene algS+. The algT gene was localized on pJF15 by using deletion mapping and transposon mutagenesis. By using gene replacement, algT::Tn501 mutants of P. aeruginosa were constructed which were shown to be complemented in trans by pJF15. Both algS and algT were located on a DNA fragment approximately 3 kilobases in size. The algS gene may be a genetic switch which regulates the process of alginate conversion.
Full text
PDF



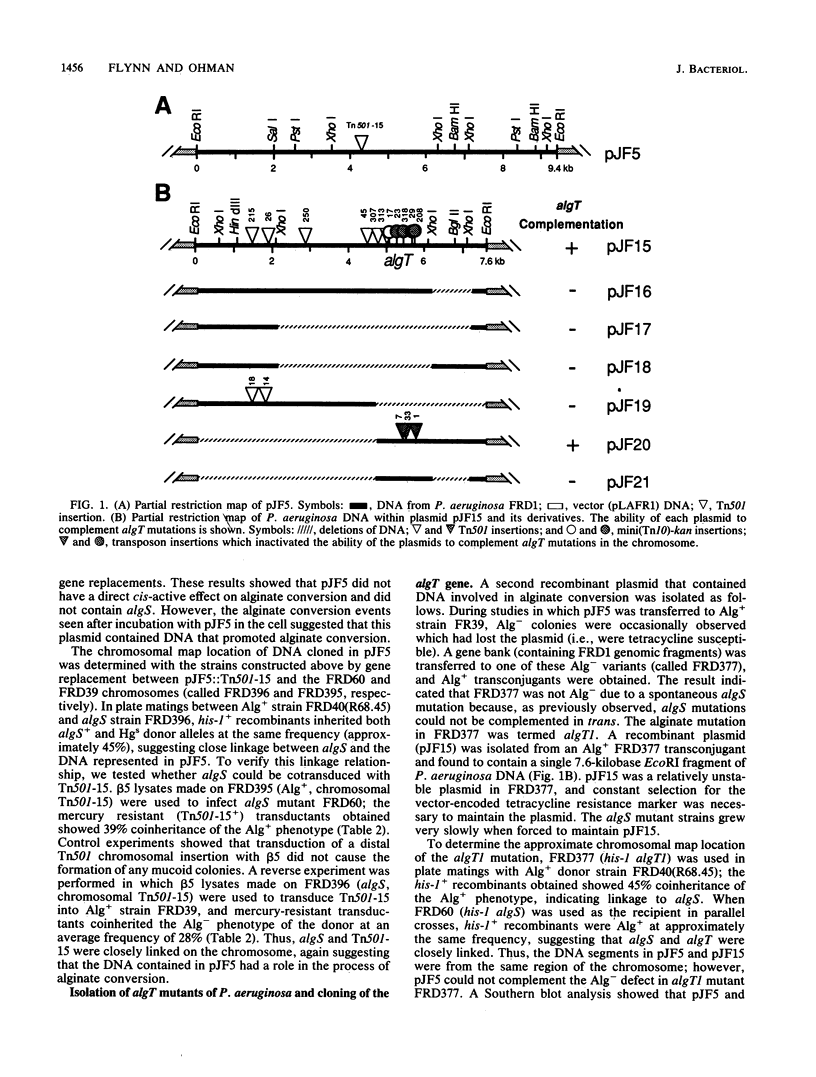
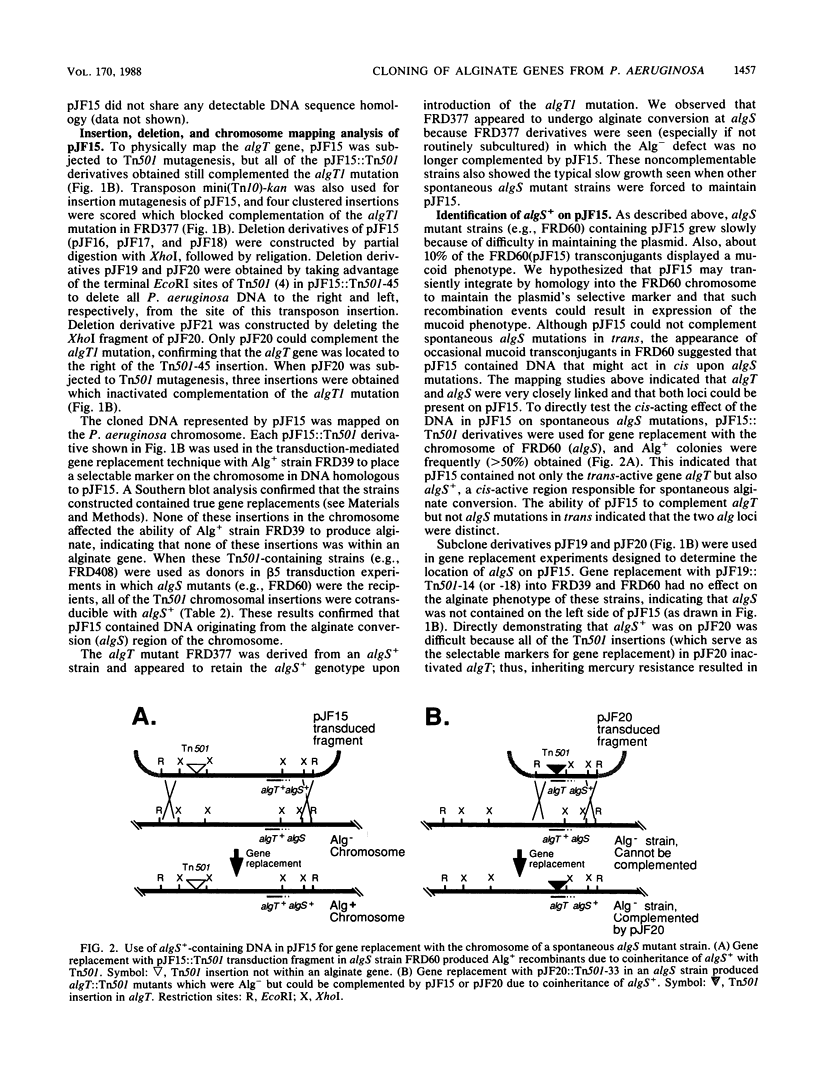



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. M., Freitag C. S., Clements J. R., Eisenstein B. I. An invertible element of DNA controls phase variation of type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5724–5727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. L., Choi C. L., Grinsted J., Richmond M. H., Whitehead P. R. Nucleotide sequences at the ends of the mercury resistance transposon, Tn501. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 10;8(9):1933–1945. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.9.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of genes controlling alginate biosynthesis from a mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):9–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.9-18.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Wang S. K., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M. Clustering of mutations affecting alginic acid biosynthesis in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):516–524. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.516-524.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Gill J. F., Chakrabarty A. M. Gene algD coding for GDPmannose dehydrogenase is transcriptionally activated in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.351-358.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. R., Linker A. Production and characterization of the slime polysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):915–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.915-924.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett W. F., Osman S. F., Fishman M. L., Siebles T. S. Alginate production by plant-pathogenic pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):466–473. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.466-473.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Govan J. R. Alginate synthesis in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a chromosomal locus involved in control. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Aug;119(2):443–450. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. F., Deretic V., Chakrabarty A. M. Overproduction and assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa phosphomannose isomerase. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):611–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.611-615.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Cloning and expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of a gene involved in the production of alginate. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1115–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1115-1121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Construction and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa algB mutants: role of algB in high-level production of alginate. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1593–1602. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1593-1602.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A., Jarman T. R. Isolation of alginate-producing mutants of Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas mendocina. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jul;125(1):217–220. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-1-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A., McMillan C. The instability of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa: fluctuation test and improved stability of the mucoid form in shaken culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jan;110(1):229–232. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-1-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cystic fibrosis: resistance of the mucoid from to carbenicillin, flucloxacillin and tobramycin and the isolation of mucoid variants in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4(3):233–240. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Harris G. S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cystic fibrosis: unusual bacterial adaptation and pathogenesis. Microbiol Sci. 1986 Oct;3(10):302–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Holloway B. W. Chromosome mobilization by the R plasmid R68.45: a tool in Pseudomonas genetics. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jan 17;158(3):229–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00267194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Holloway B. W. R factor variants with enhanced sex factor activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 30;144(3):243–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00341722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Rossiter H., Burgess D., Dodge J. Aeruginocin tolerant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1973 Dec;22(3):239–253. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300013069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V. A novel transducing phage. Its role in recognition of a possible new host-controlled modification system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(2):134–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00332784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGeorge J., Korolik V., Morgan A. F., Asche V., Holloway B. W. Transfer of a chromosomal locus responsible for mucoid colony morphology in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from cystic fibrosis patients to P. aeruginosa PAO. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Jun;21(4):331–336. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-4-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. R. Mucoid variation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced by the action of phage. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Mlawer N., So M. Pilus expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae involves chromosomal rearrangement. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Rubero V. J. Mucoid conversion by phages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):717–719. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.717-719.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hoy K., Krishnapillai V. Recalibration of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO chromosome map in time units using high-frequency-of-recombination donors. Genetics. 1987 Apr;115(4):611–618. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic mapping of chromosomal determinants for the production of the exopolysaccharide alginate in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):142–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.142-148.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Chakrabarty A. M. Utilization of human respiratory secretions by mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa of cystic fibrosis origin. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):662–669. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.662-669.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E. Molecular genetics of exopolysaccharide production by mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;5(1):6–10. doi: 10.1007/BF02013452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., West M. A., Flynn J. L., Goldberg J. B. Method for gene replacement in Pseudomonas aeruginosa used in construction of recA mutants: recA-independent instability of alginate production. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1068-1074.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M., Holloway B. W. Chromosome mapping in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1972 Jun;19(3):251–260. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royle P. L., Matsumoto H., Holloway B. W. Genetic circularity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):145–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.145-155.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Hagblom P., Seifert H. S., So M. Antigenic variation of gonococcal pilus involves assembly of separated silent gene segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2177–2181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Zieg J., Silverman M., Mandel G., Doolittle R. Phase variation: evolution of a controlling element. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1370–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.6251543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldati L., Crockett R., Carrigan J. M., Leisinger T., Holloway B. W., Haas D. Revised locations of the hisI and pru (proline utilization) genes on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa chromosome map. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(3):431–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00382080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Davis M. A., Morisato D., Roberts D. E., Kleckner N. New Tn10 derivatives for transposon mutagenesis and for construction of lacZ operon fusions by transposition. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J., Govan J. R. Pyocine typing of mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from children with cystic fibrosis. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Aug;6(3):409–412. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


