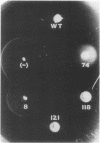
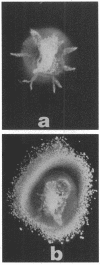
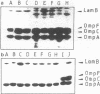
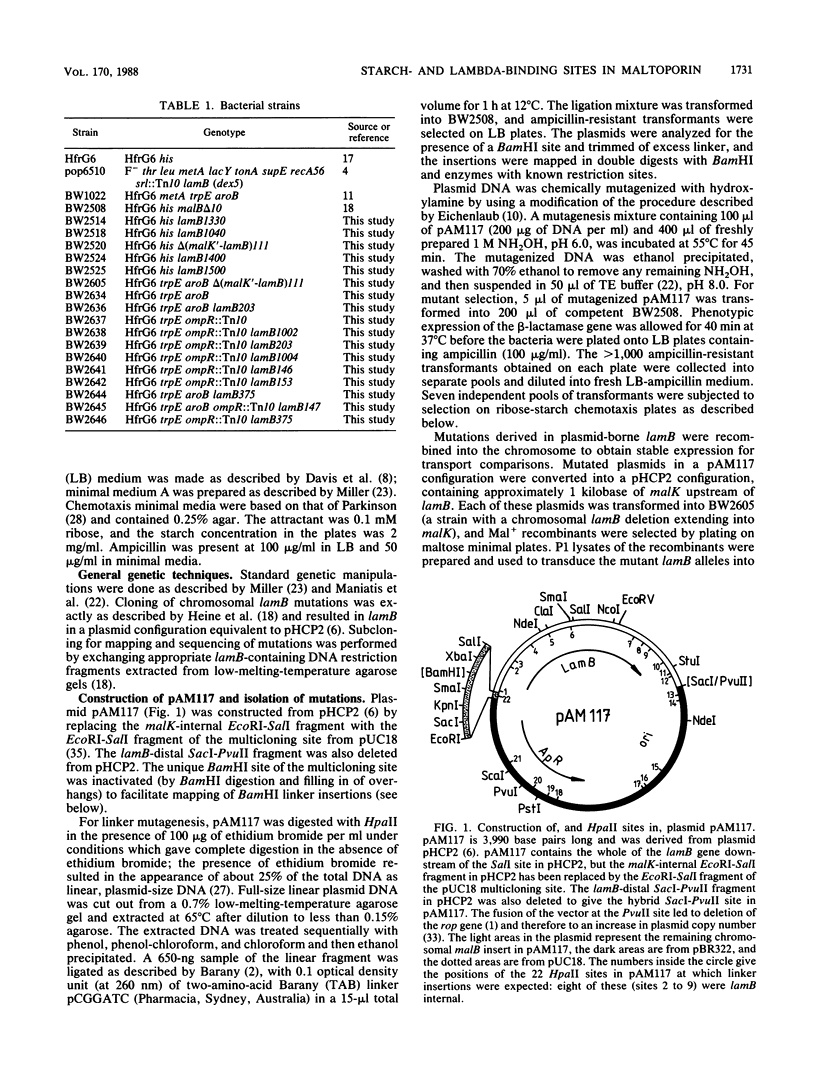
Abstract
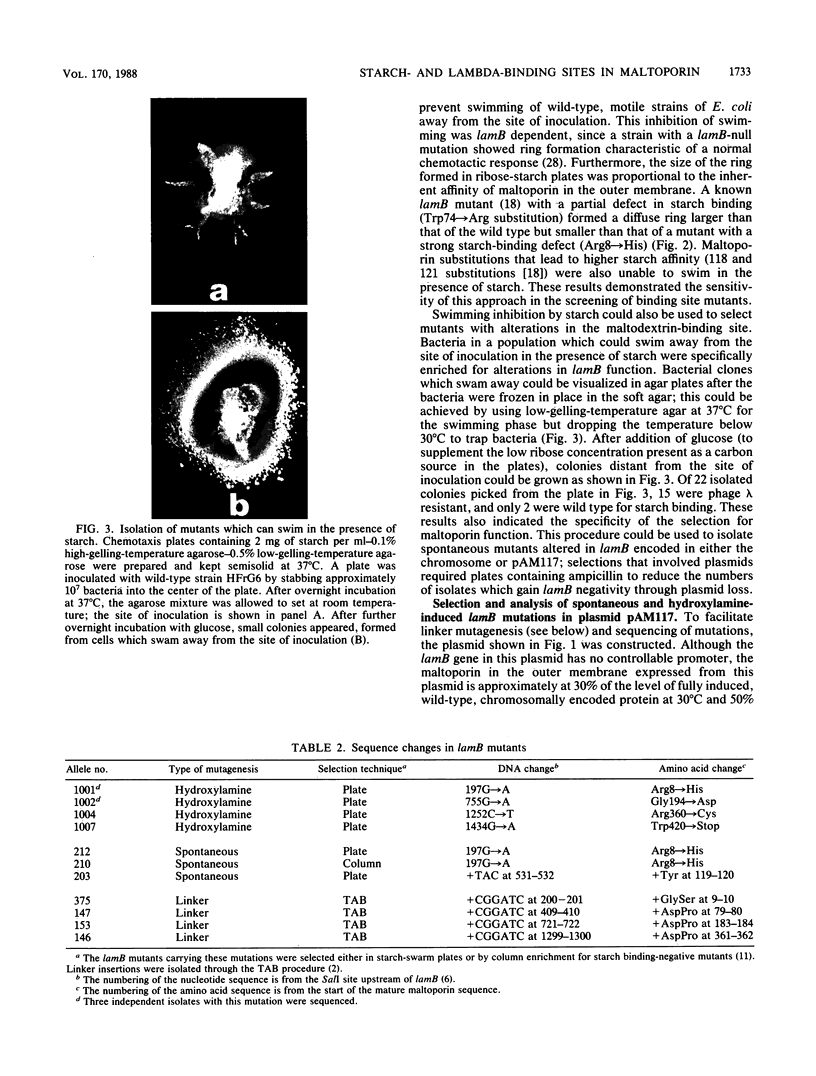
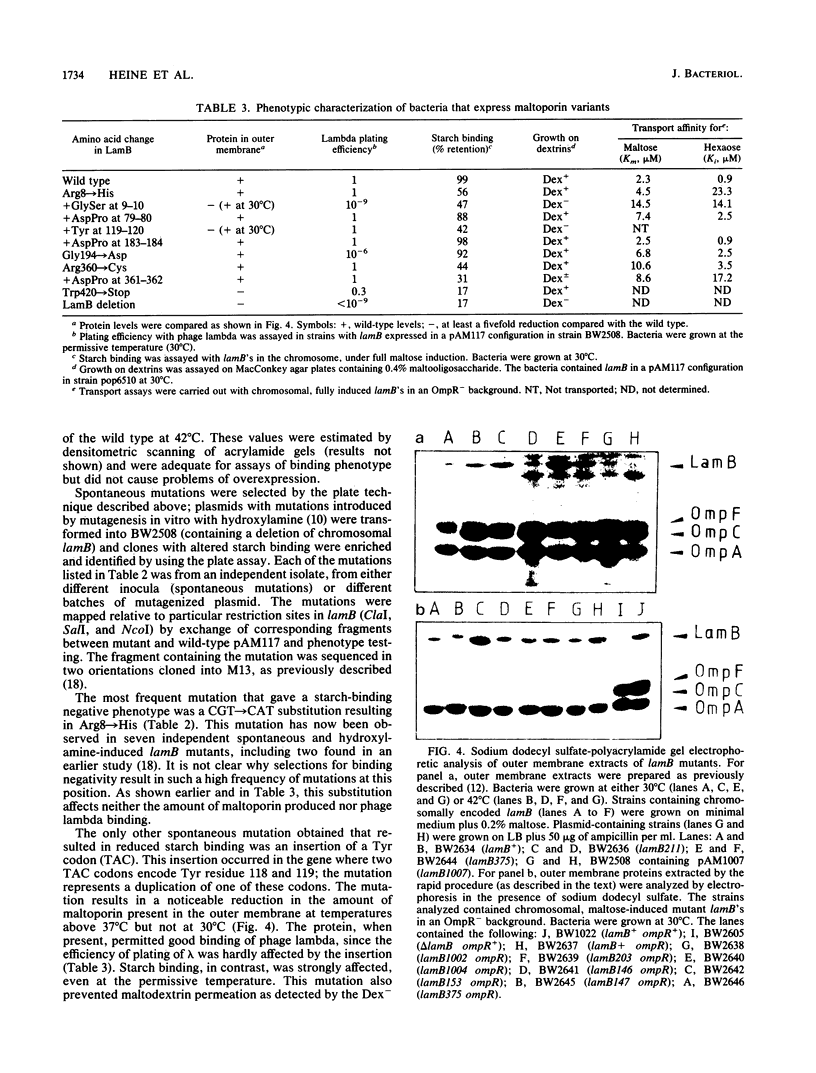
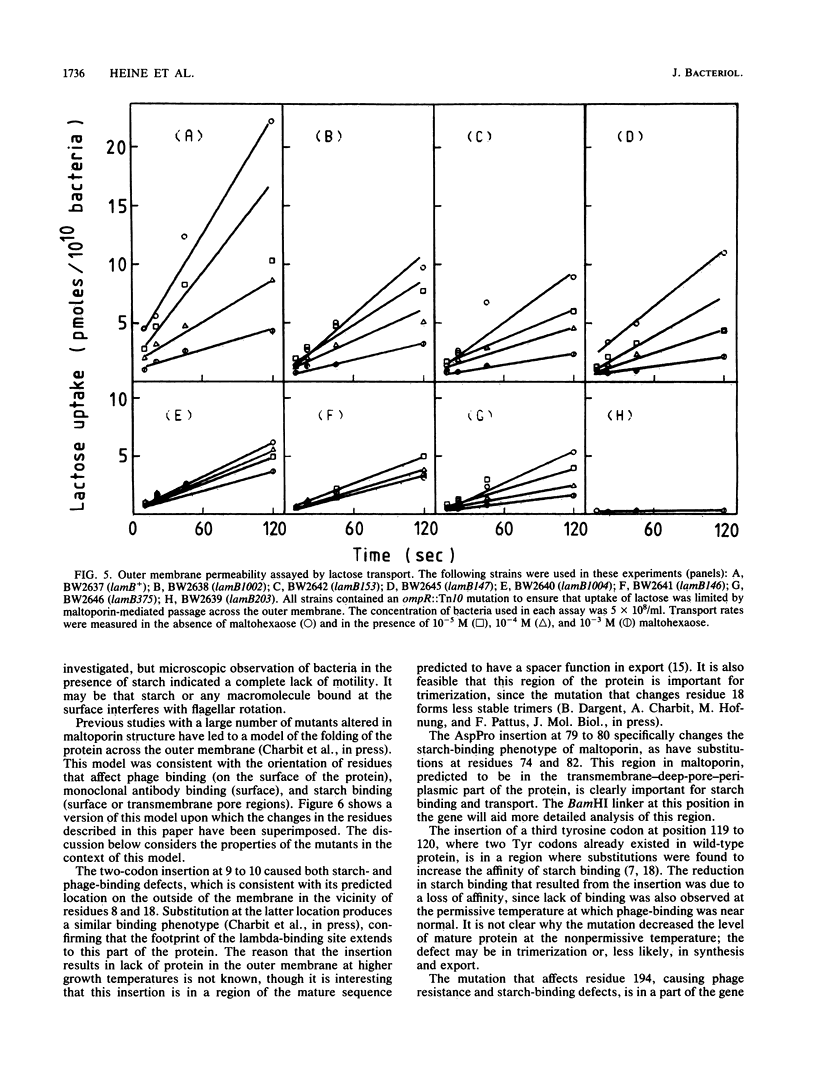
Maltoporin (LamB protein) is a maltodextrin transport protein in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli with binding sites for bacteriophage lambda and maltosaccharides. Binding of starch by bacteria was found to inhibit swarming of Escherichia coli in soft agar plates; the inhibition was dependent on the maltodextrin affinity of maltoporin. On the basis of this observation, chemotactic cell-sorting techniques were developed for the isolation and analysis of mutants with an altered starch-binding phenotype. Fifteen lamB mutations generated by hydroxylamine and linker mutagenesis, as well as spontaneous mutations, were analyzed. The effects of the mutations on starch and lambda-binding, as well as transport specificity, were assayed. Mutations that affect residues near 8 to 18, 74 to 82, and 118 to 121 were found to affect starch binding and maltodextrin-selective functions strongly, confirming and extending previous results with substitutions at these regions. Substitutions and insertions in two previously undefined regions in the protein, in or near residues 194 and 360, also resulted in defects in maltodextrin-specific functions and indicate that C-terminal parts of the protein also contribute to the discontinuous binding and pore domains. There was a detectable transport defect in all binding-affected mutants, and one mutation caused near-total pore blocking towards both maltose and nonmaltoside. The highly discontinuous phage lambda-binding site was affected by mutations near residues 9 and 10 and 194, as well as previously established regions near residues 18, 148 to 165, 245 to 259, and 380 to 400. The significance of these mutations is discussed in the context of a model of the functional topology of maltoporin. The additional role of regions near residues 10 and 120 in maltoporin assembly, as well as starch binding, was suggested by the temperature-sensitive biogenesis of maltoporin in strains with one- or two-codon insertion at these sites.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balbás P., Soberón X., Merino E., Zurita M., Lomeli H., Valle F., Flores N., Bolivar F. Plasmid vector pBR322 and its special-purpose derivatives--a review. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):3–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barany F. Two-codon insertion mutagenesis of plasmid genes by using single-stranded hexameric oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4202–4206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Schmid A., Nakae T., Vos-Scheperkeuter G. H. Pore formation by LamB of Escherichia coli in lipid bilayer membranes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):978–986. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.978-986.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouges-Bocquet B., Villarroya H., Hofnung M. Linker mutagenesis in the gene of an outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli, lamB. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(3):217–228. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbit A., Clement J. M., Hofnung M. Further sequence analysis of the phage lambda receptor site. Possible implications for the organization of the lamB protein in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clune A., Lee K. S., Ferenci T. Affinity engineering of maltoporin: variants with enhanced affinity for particular ligands. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 31;121(1):34–40. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90684-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément J. M., Hofnung M. Gene sequence of the lambda receptor, an outer membrane protein of E. coli K12. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90392-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desaymard C., Débarbouillé M., Jolit M., Schwartz M. Mutations affecting antigenic determinants of an outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1383–1388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Lee K. S. Directed evolution of the lambda receptor of Escherichia coli through affinity chromatographic selection. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 25;160(3):431–444. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Lee K. S. Isolation, by affinity chromatography, of mutant escherichia coli cells with novel regulation of lamB expression. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):984–987. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.984-987.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Lee K. S. The influence of maltoporin affinity on the transport of maltose and maltohexaose into Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 26;896(2):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90193-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Schwentorat M., Ullrich S., Vilmart J. Lambda receptor in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli as a binding protein for maltodextrins and starch polysaccharides. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):521–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.521-526.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Silhavy T. J. Sequence information required for protein translocation from the cytoplasm. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5339–5342. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5339-5342.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring K., Charbit A., Brissaud E., Hofnung M. Bacteriophage lambda receptor site on the Escherichia coli K-12 LamB protein. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2103–2106. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2103-2106.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D., Hofnung M., Schwartz M. Genetic analysis of the maltose A region in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):559–567. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.559-567.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine H. G., Kyngdon J., Ferenci T. Sequence determinants in the lamB gene of Escherichia coli influencing the binding and pore selectivity of maltoporin. Gene. 1987;53(2-3):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckey M., Nikaido H. Diffusion of solutes through channels produced by phage lambda receptor protein of Escherichia coli: inhibition by higher oligosaccharides of maltose series. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):166–171. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckey M., Nikaido H. Specificity of diffusion channels produced by lambda phage receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T., Ishii J., Ferenci T. The role of the maltodextrin-binding site in determining the transport properties of the LamB protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):622–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T., Ishii J. Permeability properties of Escherichia coli outer membrane containing, pore-forming proteins: comparison between lambda receptor protein and porin for saccharide permeation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):735–740. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.735-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus J. M., Schindler H., Rosenbusch J. P. The periplasmic maltose-binding protein modifies the channel-forming characteristics of maltoporin. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1987–1991. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01689.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterlund M., Luthman H., Nilsson S. V., Magnusson G. Ethidium-bromide-inhibited restriction endonucleases cleave one strand of circular DNA. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. cheA, cheB, and cheC genes of Escherichia coli and their role in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):758–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.758-770.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall-Hazelbauer L., Schwartz M. Isolation of the bacteriophage lambda receptor from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1436–1446. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1436-1446.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Tsugita A., Schwartz M., Rosenbusch J. P. Topology of phage lambda receptor protein. Mapping targets of proteolytic cleavage in relation to binding sites for phage or monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7570–7576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmelcman S., Hofnung M. Maltose transport in Escherichia coli K-12: involvement of the bacteriophage lambda receptor. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):112–118. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.112-118.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C., Schwartz M., Ferenci T. Escherichia coli mutants impaired in maltodextrin transport. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.1-13.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]