Abstract
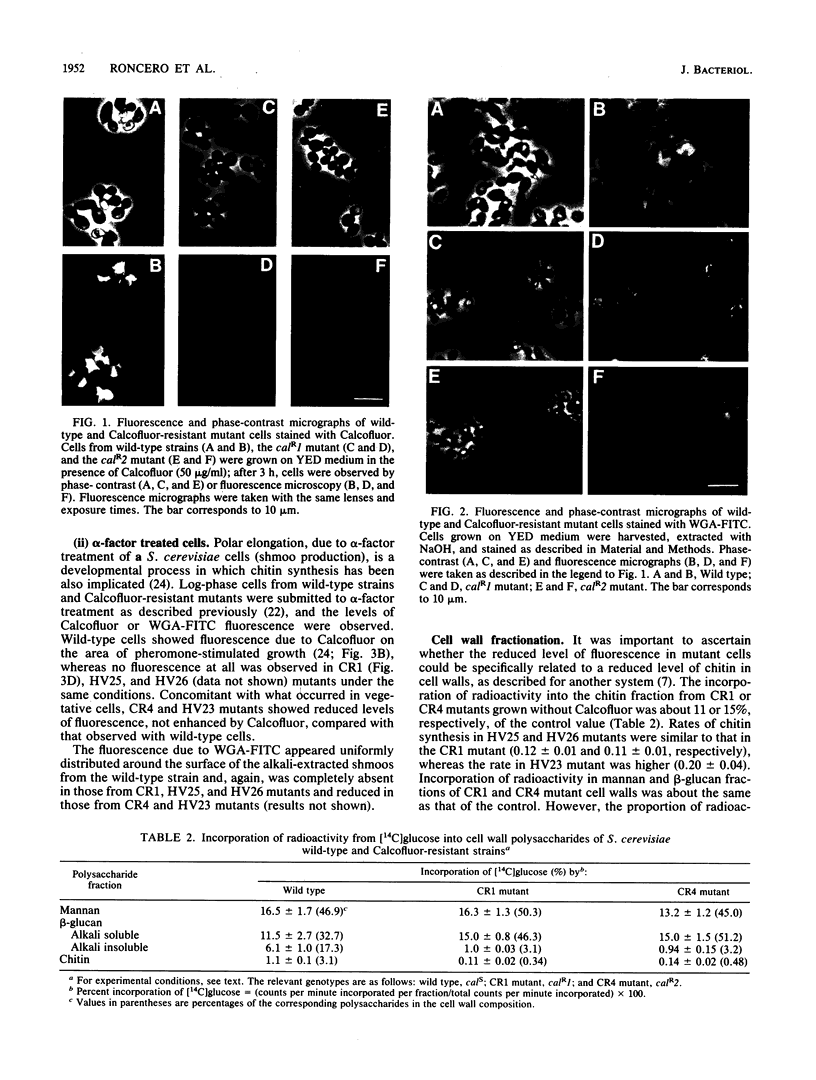
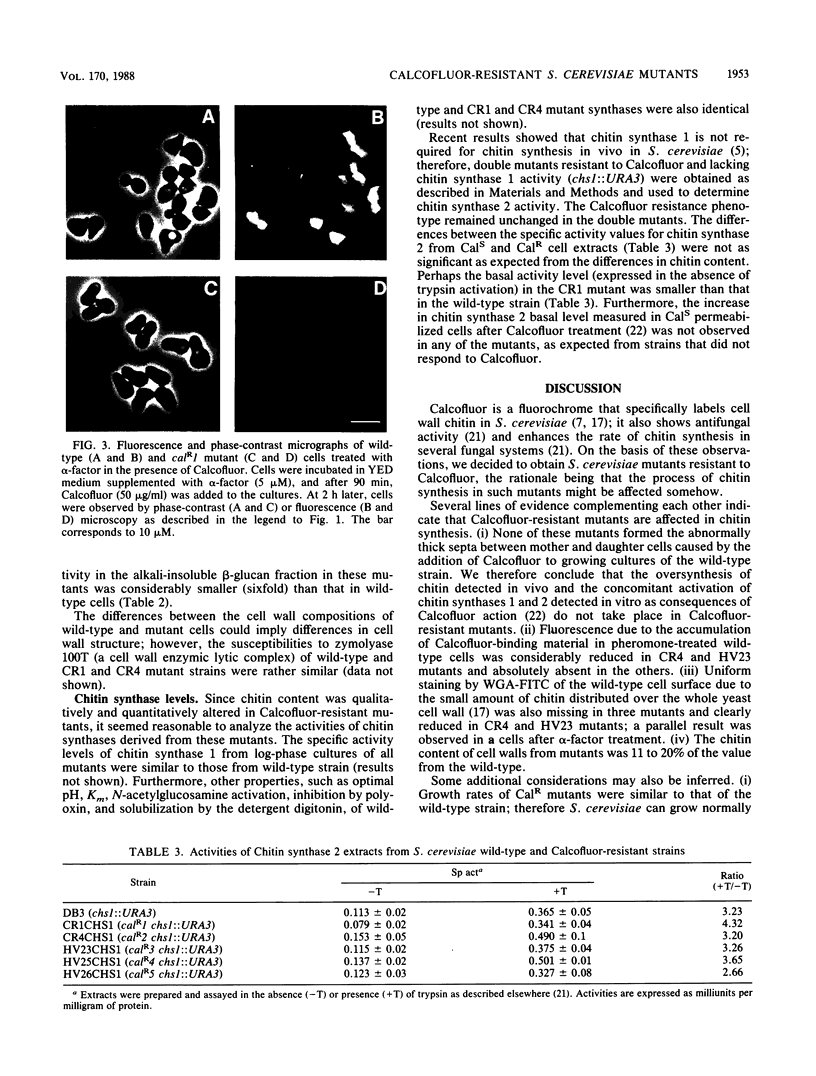
Calcofluor is a fluorochrome that exhibits antifungal activity and a high affinity for yeast cell wall chitin. We isolated Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants resistant to Calcofluor. The resistance segregated in a Mendelian fashion and behaved as a recessive character in all the mutants analyzed. Five loci were defined by complementation analysis. The abnormally thick septa between mother and daughter cells caused by Calcofluor in wild-type cells were absent in the mutants. The Calcofluor-binding capacity, observed by fluorescence microscopy, in a S. cerevisiae wild-type cells during alpha-factor treatment was also absent in some mutants and reduced in others. Staining of cell walls with wheat germ agglutinin-fluorescein complex indicated that the chitin uniformly distributed over the whole cell wall in vegetative or in alpha-factor-treated cells was almost absent in three of the mutants and reduced in the two others. Cell wall analysis evidenced a five- to ninefold reduction in the amount of chitin in mutants compared with that in the wild-type strain. The total amounts of cell wall mannan and beta-glucan in wild-type and mutant strains were similar; however, the percentage of beta-glucan that remained insoluble after alkali extraction was considerably reduced in mutant cells. The susceptibilities of the mutants and the wild-type strains to a cell wall enzymic lytic complex were rather similar. The in vitro levels of chitin synthase 2 detected in all mutants were similar to that in the wild type. The significance of these results is discussed in connection with the mechanism of chitin synthesis and cell wall morphogenesis in S. cerevisiae.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. E., Pringle J. R. Relationship of actin and tubulin distribution to bud growth in wild-type and morphogenetic-mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):934–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon J. S., Farmer V. C., Jones D., Taylor I. F. The glucan components of the cell wall of baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) considered in relation to its ultrastructure. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(3):557–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1140557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benziman M., Haigler C. H., Brown R. M., White A. R., Cooper K. M. Cellulose biogenesis: Polymerization and crystallization are coupled processes in Acetobacter xylinum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6678–6682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E., Slater M., Cabib E., Au-Young J., Sburlati A., Adair W. L., Jr, Robbins P. W. The S. cerevisiae structural gene for chitin synthase is not required for chitin synthesis in vivo. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):213–225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90738-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Bowers B. Chitin and yeast budding. Localization of chitin in yeast bud scars. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):152–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Bowers B. Timing and function of chitin synthesis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1586–1593. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1586-1593.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Farkas V. The control of morphogenesis: an enzymatic mechanism for the initiation of septum formation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2052–2056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Roberts R., Bowers B. Synthesis of the yeast cell wall and its regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:763–793. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Ulane R., Bowers B. A molecular model for morphogenesis: the primary septum of yeast. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):1–32. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152808-9.50008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elorza M. V., Rico H., Sentandreu R. Calcofluor white alters the assembly of chitin fibrils in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1577–1582. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler C. H., Brown R. M., Jr, Benziman M. Calcofluor white ST Alters the in vivo assembly of cellulose microfibrils. Science. 1980 Nov 21;210(4472):903–906. doi: 10.1126/science.7434003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herth W. Calcofluor white and Congo red inhibit chitin microfibril assembly of Poterioochromonas: evidence for a gap between polymerization and microfibril formation. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):442–450. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manners D. J., Masson A. J., Patterson J. C., Björndal H., Lindberg B. The structure of a beta-(1--6)-D-glucan from yeast cell walls. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):31–36. doi: 10.1042/bj1350031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molano J., Bowers B., Cabib E. Distribution of chitin in the yeast cell wall. An ultrastructural and chemical study. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):199–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molano J., Durán A., Cabib E. A rapid and sensitive assay for chitinase using tritiated chitin. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):648–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez P., García-Acha I., Durán A. Effect of papulacandin B on the cell wall and growth of Geotrichum lactis. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jan;129(1):245–250. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-1-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncero C., Durán A. Effect of Calcofluor white and Congo red on fungal cell wall morphogenesis: in vivo activation of chitin polymerization. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1180-1185.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncero C., Valdivieso M. H., Ribas J. C., Durán A. Effect of calcofluor white on chitin synthases from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1945–1949. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1945-1949.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sburlati A., Cabib E. Chitin synthetase 2, a presumptive participant in septum formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15147–15152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schekman R., Brawley V. Localized deposition of chitin on the yeast cell surface in response to mating pheromone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):645–649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubenko G. S., Mitchell A. P., Jones E. W. Septum formation, cell division, and sporulation in mutants of yeast deficient in proteinase B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2395–2399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





