Abstract
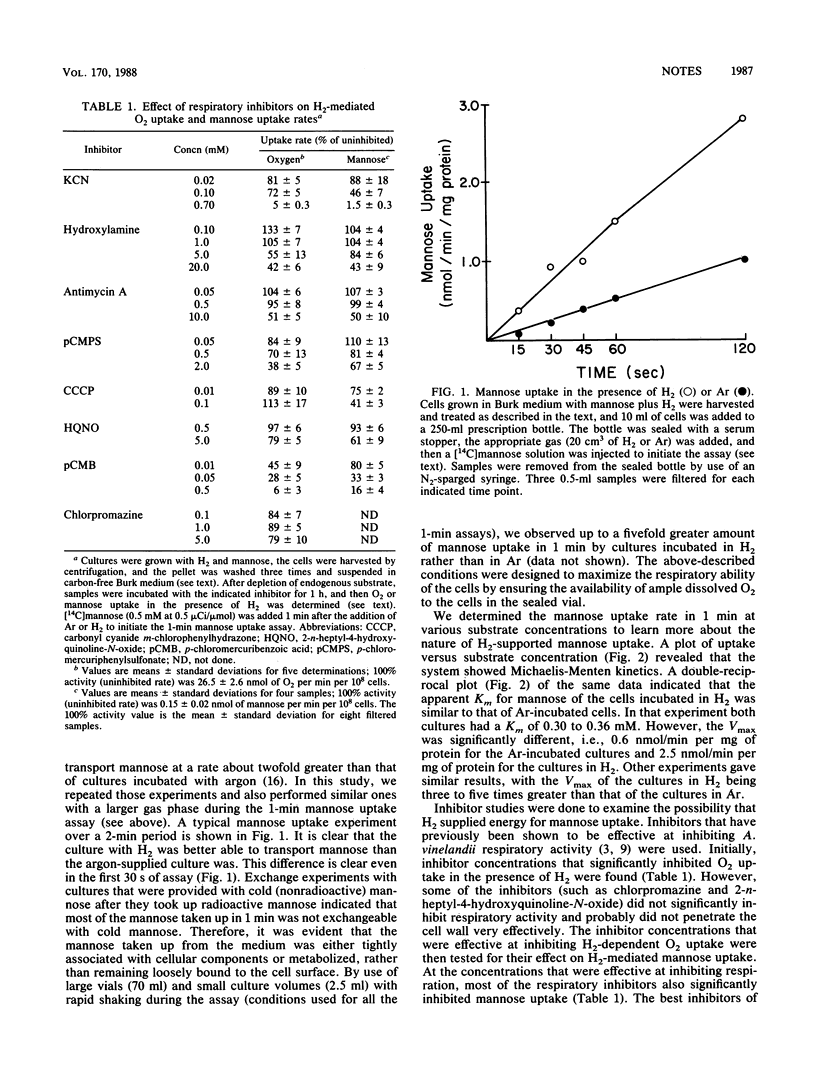
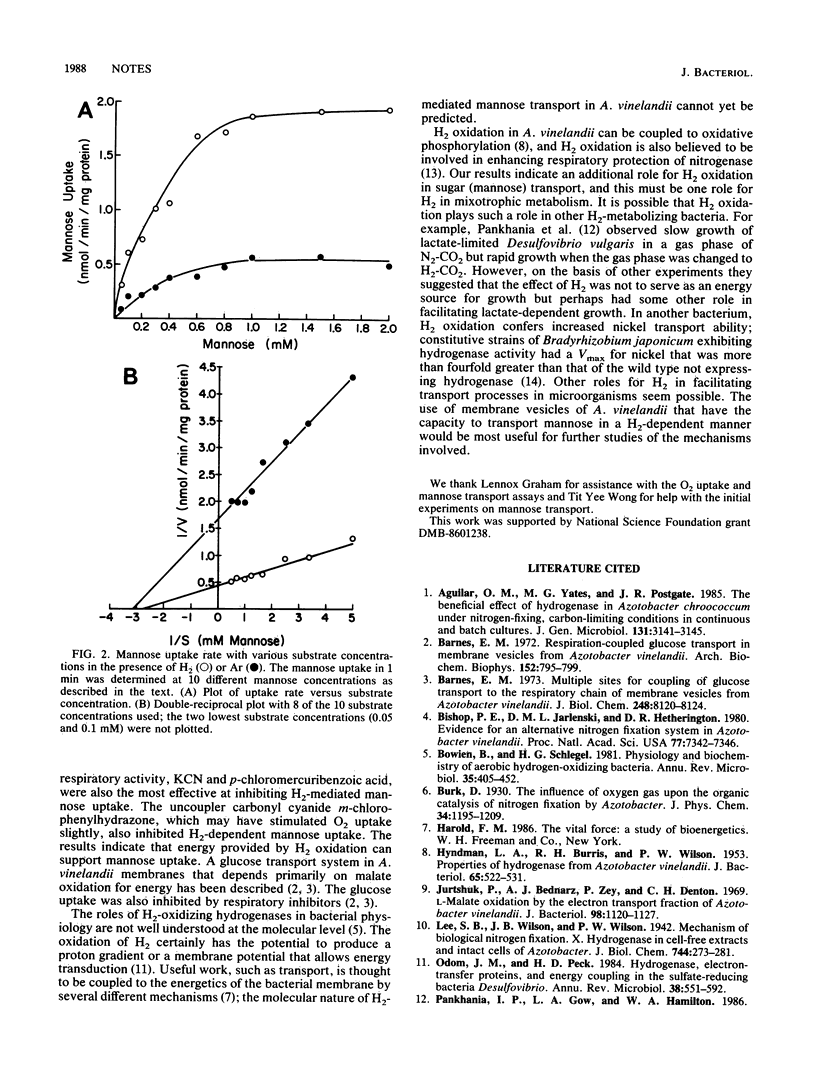
Azotobacter vinelandii can grow mixotrophically with H2 plus mannose under N2-fixing conditions (T. Y. Wong and R. J. Maier, J. Bacteriol. 163:528-533, 1985). Mixotrophically grown cultures incubated in H2 transported mannose with a Vmax fourfold greater than that observed for cultures incubated in argon, but H2 did not change the apparent Km for mannose. Respiratory inhibitors, such as potassium cyanide, hydroxylamine, and p-chloromercuribenzoic acid, as well as the proton conductor carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl-hydrazone inhibited mannose uptake. We suggest that one of the roles of H2 in mixotrophic metabolism is to supply energy that facilitates mannose transport.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes E. M., Jr Multiple sites for coupling of glucose transport to the respiratory chain of membrane vesicles from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):8120–8124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Jr Respiration-coupled glucose transport in membrane vesicles from Azotobacter vinelandii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):795–799. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Jarlenski D. M., Hetherington D. R. Evidence for an alternative nitrogen fixation system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7342–7346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowien B., Schlegel H. G. Physiology and biochemistry of aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:405–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYNDMAN L. A., BURRIS R. H., WILSON P. W. Properties of hydrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1953 May;65(5):522–531. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.5.522-531.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurtshuk P., Bednarz A. J., Zey P., Denton C. H. L-malate oxidation by the electron transport fraction of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1120–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1120-1127.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom J. M., Peck H. D., Jr Hydrogenase, electron-transfer proteins, and energy coupling in the sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:551–592. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.003003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. L., Postgate J. R. Oxygen and hydrogen in biological nitrogen fixation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:183–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stults L. W., Mallick S., Maier R. J. Nickel uptake in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1398–1402. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1398-1402.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. Y., Maier R. J. H2-dependent mixotrophic growth of N2-fixing Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):528–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.528-533.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. Y., Maier R. J. Hydrogen-oxidizing electron transport components in nitrogen-fixing Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):348–352. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.348-352.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


