Abstract
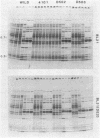
T7 DNA did not become susceptible to degradation by the host restriction enzymes EcoB, EcoK, or EcoP1 until 6 to 7 min after infection (at 30 degrees C). During this period, T7 gene 0.3 protein is made and inactivates EcoB and EcoK, allowing wild-type T7, or even a mutant that has recognition sites flanking gene 0.3, to escape restriction by these enzymes. However, T7 failed to escape restriction by EcoP1 even though 0.3 protein was made, evidently because 0.3 protein is unable to inactivate EcoP1. How T7 DNA can be accessible to transcription but not restriction in the first few minutes of infection is not yet understood, but we favor the idea that the entering DNA is initially segregated in a special place. Entry of T7 DNA into the cell is normally coupled to transcription. Tests of degradation of DNAs having their first restriction sites different distances from the end of the DNA indicated that only the first 1,000 or so base pairs (2.5%) of the molecule enter the cell without transcription. An exception was the only mutant tested that lacks base pairs 343 to 393 of T7 DNA; most or all of this DNA entered the cell without being transcribed, apparently because it lacks a sequence that normally arrests entry. This block to DNA entry would normally be relieved by the host RNA polymerase transcribing from an appropriately situated promoter, but the block can also be relieved by T7 RNA polymerase, if supplied by the host cell. T7 mutants that lack all three strong early promoters A1, A2, and A3 could grow by using a secondary promoter.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandyopadhyay P. K., Studier F. W., Hamilton D. L., Yuan R. Inhibition of the type I restriction-modification enzymes EcoB and EcoK by the gene 0.3 protein of bacteriophage T7. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunovskis I., Summers W. C. The process of infection with coliphage 17. VI. A phage gene controlling shutoff of host RNA synthesis. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):322–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., McGrath J., Waskell L. New RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T7. Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):227–231. doi: 10.1038/228227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golomb M., Chamberlin M. Characterization of T7-specific ribonucleic acid polymerase. IV. Resolution of the major in vitro transcripts by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2858–2863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Thomas C. A., Jr An intermediate in the replication of bacteriophage T7 DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):459–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger D. H., Bickle T. A. Bacteriophage survival: multiple mechanisms for avoiding the deoxyribonucleic acid restriction systems of their hosts. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):345–360. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.345-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger D. H., Reuter M., Hansen S., Schroeder C. Influence of phage T3 and T7 gene functions on a type III(EcoP1) DNA restriction-modification system in vivo. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):457–461. doi: 10.1007/BF00334140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark K. K., Studier F. W. Purification of the gene 0.3 protein of bacteriophage T7, an inhibitor of the DNA restriction system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2573–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., Morris C., Rosenberg A. H., Studier F. W. Utilization of bacteriophage T7 late promoters in recombinant plasmids during infection. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):527–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister W. T., Wu H. L. Regulation of transcription of the late genes of bacteriophage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt B. A., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao C. C., Speyer J. F. Order of injection of T7 bacteriophage DNA. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):1024–1026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.1024-1026.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Simon M. N., Studier F. W., Roberts R. J. Survey and mapping of restriction endonuclease cleavage sites in bacteriophage T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 25;135(4):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Formation, induction, and curing of bacteriophage P1 lysogens. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmon V. F., Lederberg S. Degradation of bacteriophage lambda deoxyribonucleic acid after restriction by Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):161–169. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.161-169.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogman G. S., Björk G. R. Effects of the phage P1 restriction system on coliphage phi W: degradation and complex formation of phage phi W DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Apr;31(1):9–20. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Bacteriophage T7. Science. 1972 Apr 28;176(4033):367–376. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4033.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Organization and expression of bacteriophage T7 DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):999–1007. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Gene 0.3 of bacteriophage T7 acts to overcome the DNA restriction system of the host. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 15;94(2):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Genetic analysis of non-essential bacteriophage T7 genes. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Genetic mapping of a mutation that causes ribonucleases III deficiency in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):307–316. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.307-316.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Simon M. N., Dunn J. J. Genetic and physical mapping in the early region of bacteriophage T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 25;135(4):917–937. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. The genetics and physiology of bacteriophage T7. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):562–574. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackernagel W., Hermanns U. Inhibition of exonuclease V after infection of E. coli by bacteriophage T7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 23;60(2):521–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan R. Structure and mechanism of multifunctional restriction endonucleases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:285–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavriev S. K., Shemyakin M. F. RNA polymerase-dependent mechanism for the stepwise T7 phage DNA transport from the virion into E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1635–1652. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]