Abstract
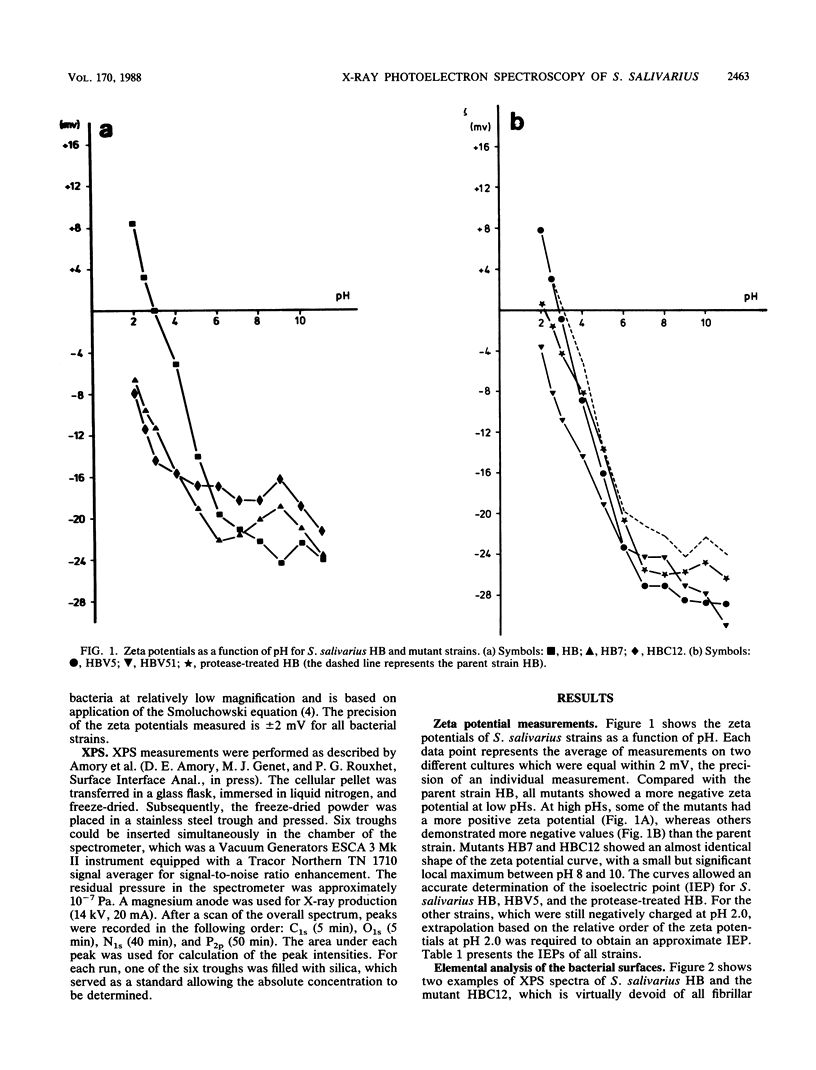
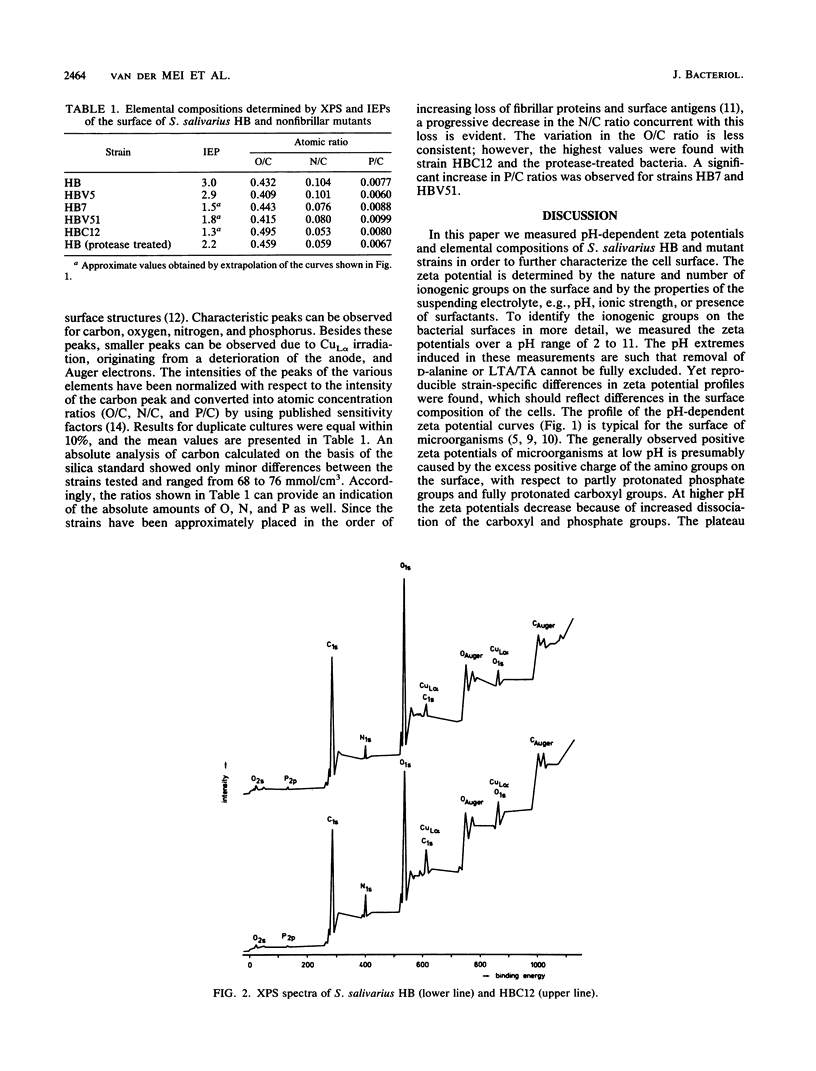
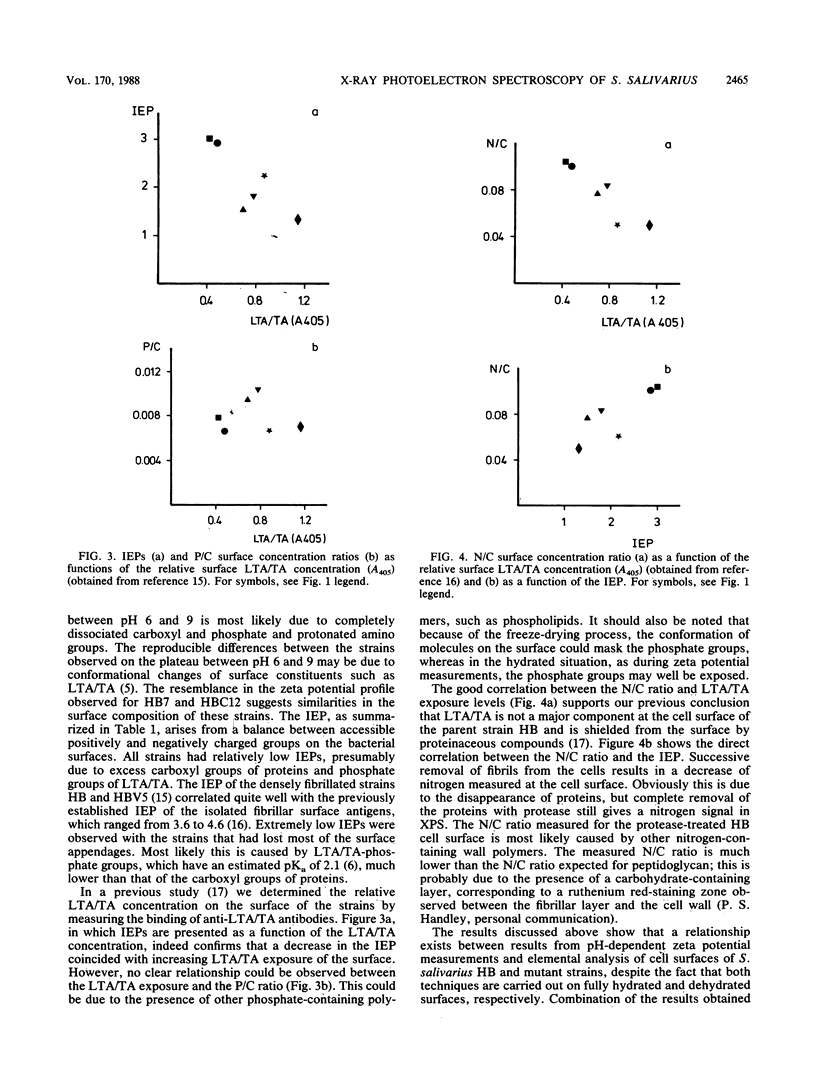
To characterize the functional cell surface, the zeta potentials and elemental surface composition of Streptococcus salivarius HB and a range of mutants with known molecular surface structures were determined. Zeta potentials of fully hydrated cells were measured as a function of pH in dilute potassium phosphate solutions, yielding isoelectric points of the strains. Elemental composition (O, C, N, and P) of the outer 2 to 5 nm of the freeze-dried cell surfaces were measured by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. An increasing loss of proteinaceous fibrillar surface antigens of the mutants was found to be accompanied by a progressive decrease in the N/C ratio from 0.104 in the parent strain HB to 0.053 in mutant HBC12. Simultaneously, the value of the isoelectric point shifted from 3.0 to 1.3. In a previous study (A.H. Weerkamp, H.C. van der Mei, and J. W. Slot, Infect. Immun. 55:438-455, 1987) on the cell surfaces of the same strains, it was shown that removal of fibrils led to increased exposure of (lipo)teichoic acid at the surface, which explains the low isoelectric point caused by the low pKa of the phosphate groups.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baddiley J., Hancock I. C., Sherwood P. M. X-ray photoelectron studies of magnesium ions bound to the cell walls of gram-positive bacteria. Nature. 1973 May 4;243(5401):43–45. doi: 10.1038/243043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa e Silva Filho F., Elias C. A., de Souza W. Further studies on the surface charge of various strains of Trichomonas vaginalis and Tritrichomonas foetus. Cell Biophys. 1986 Jun;8(3):161–176. doi: 10.1007/BF02788492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The interaction of magnesium ions with teichoic acid. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):519–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1490519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard M. M., Bartholomew J. C. Surface studies of mammalian cells grown in culture by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 1977 Aug;49(9):1290–1296. doi: 10.1021/ac50017a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. A., Moore N. F. Measurement of surface charge of baculovirus polyhedra. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Mar;53(3):598–602. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.3.598-602.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Handley P. S., Baars A., Slot J. W. Negative staining and immunoelectron microscopy of adhesion-deficient mutants of Streptococcus salivarius reveal that the adhesive protein antigens are separate classes of cell surface fibril. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):746–755. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.746-755.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Jacobs T. Cell wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus salivarius: purification, properties, and function in adherence. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):233–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.233-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., Slot J. W. Relationship of cell surface morphology and composition of Streptococcus salivarius K+ to adherence and hydrophobicity. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):438–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.438-445.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


