Abstract
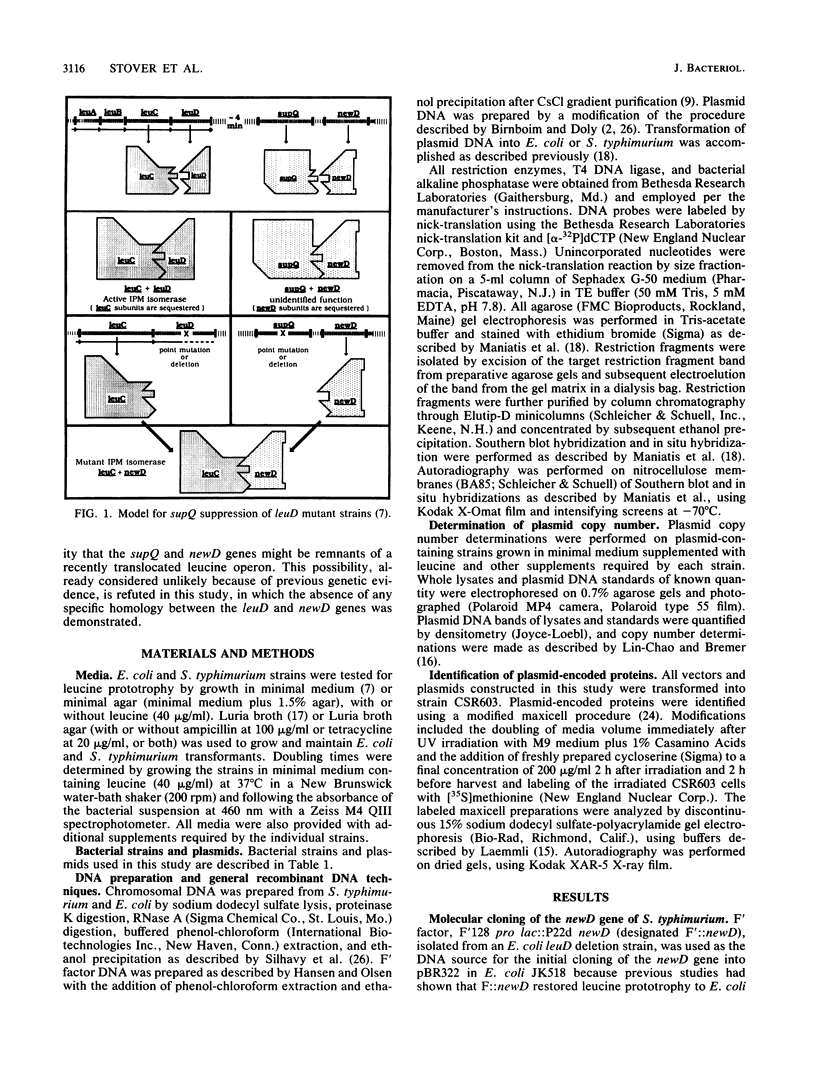
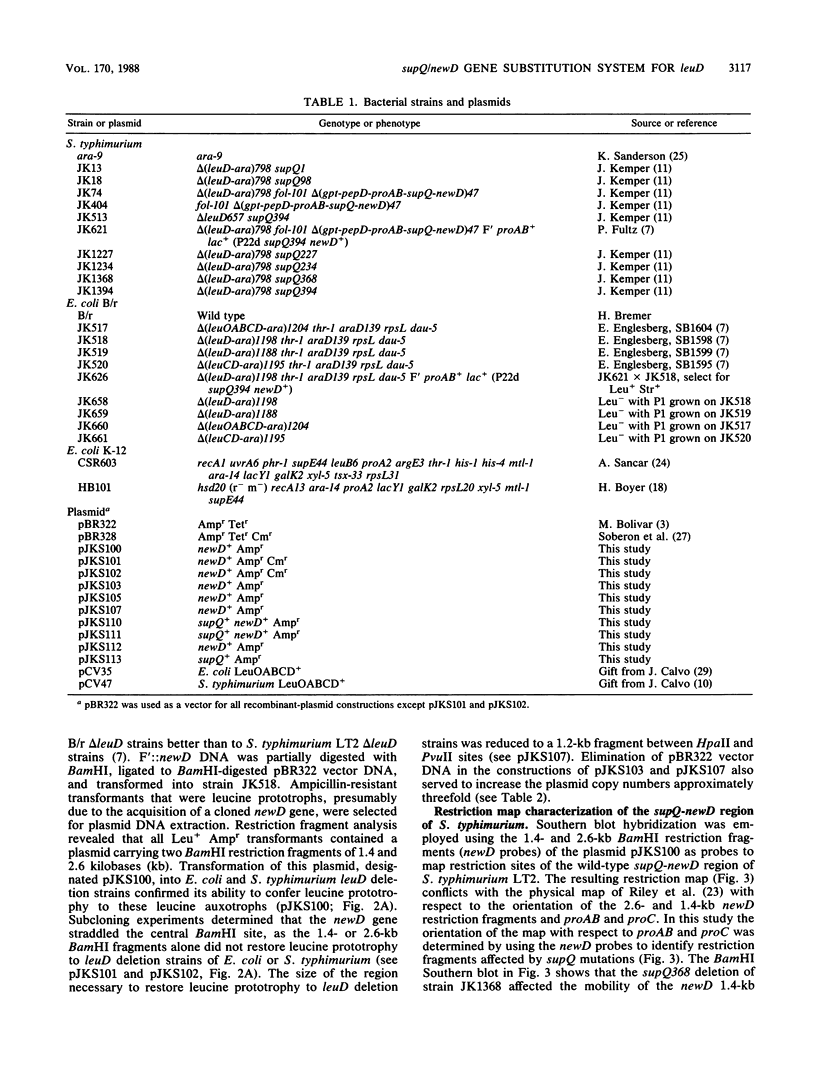
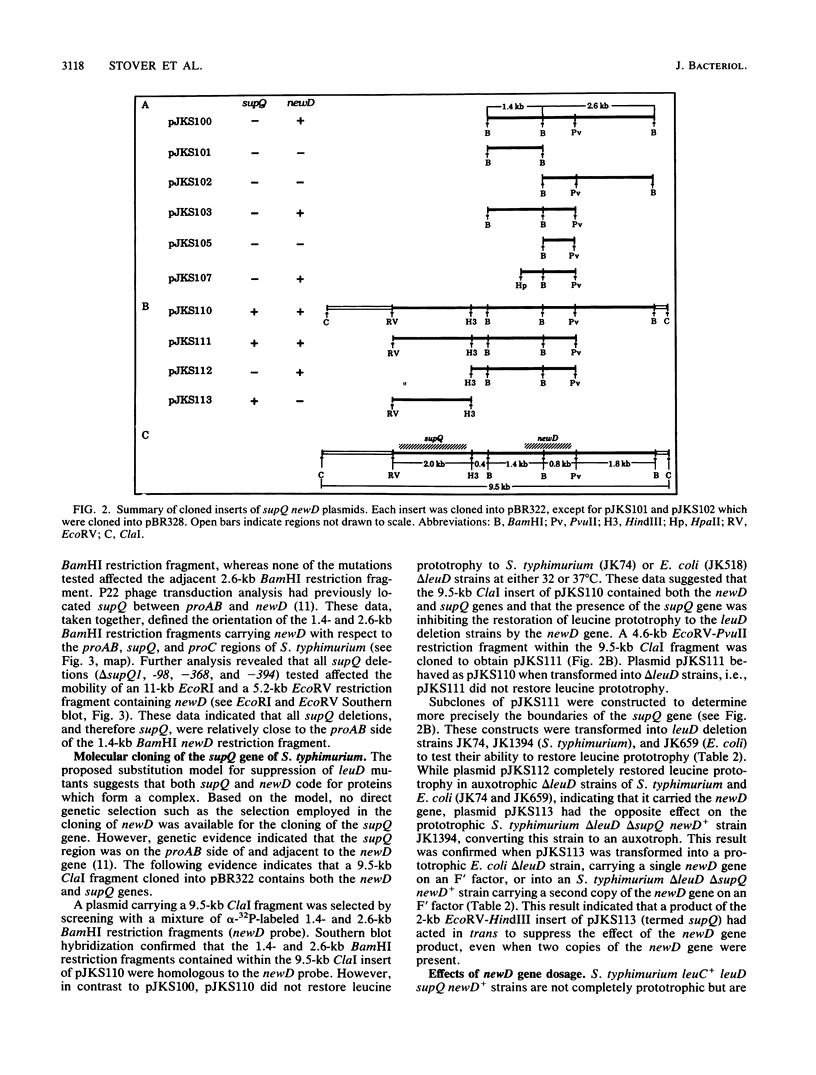
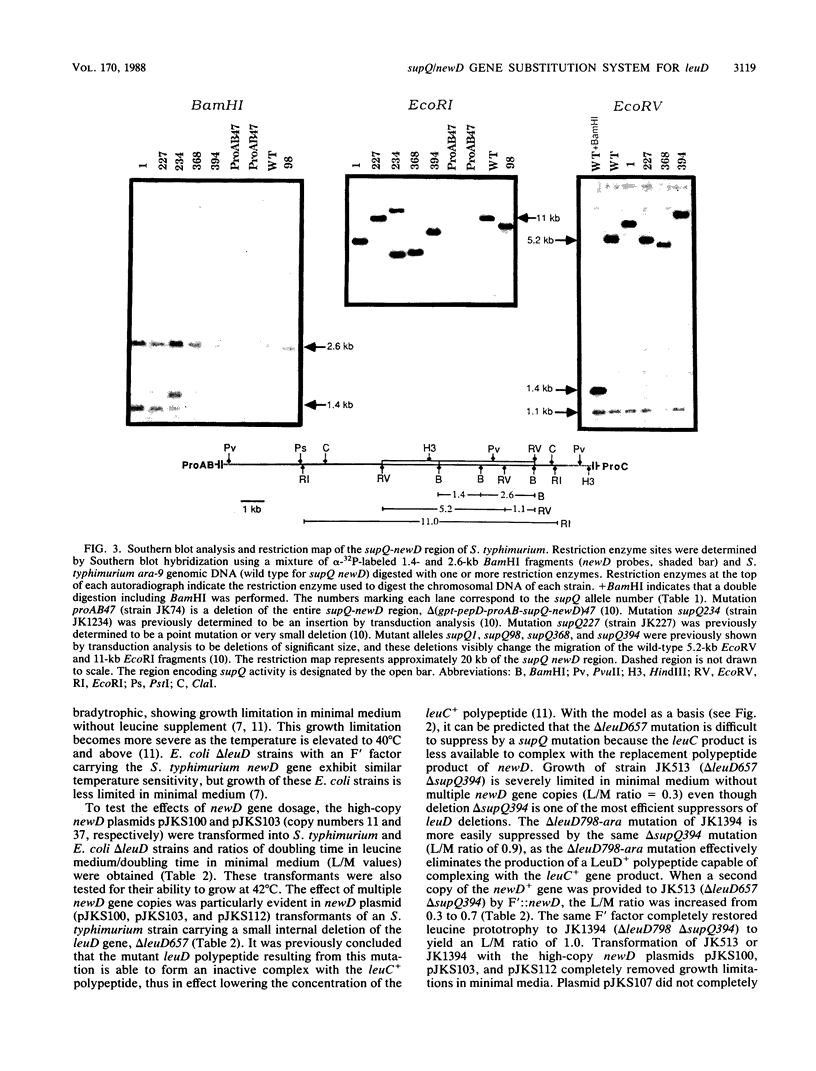
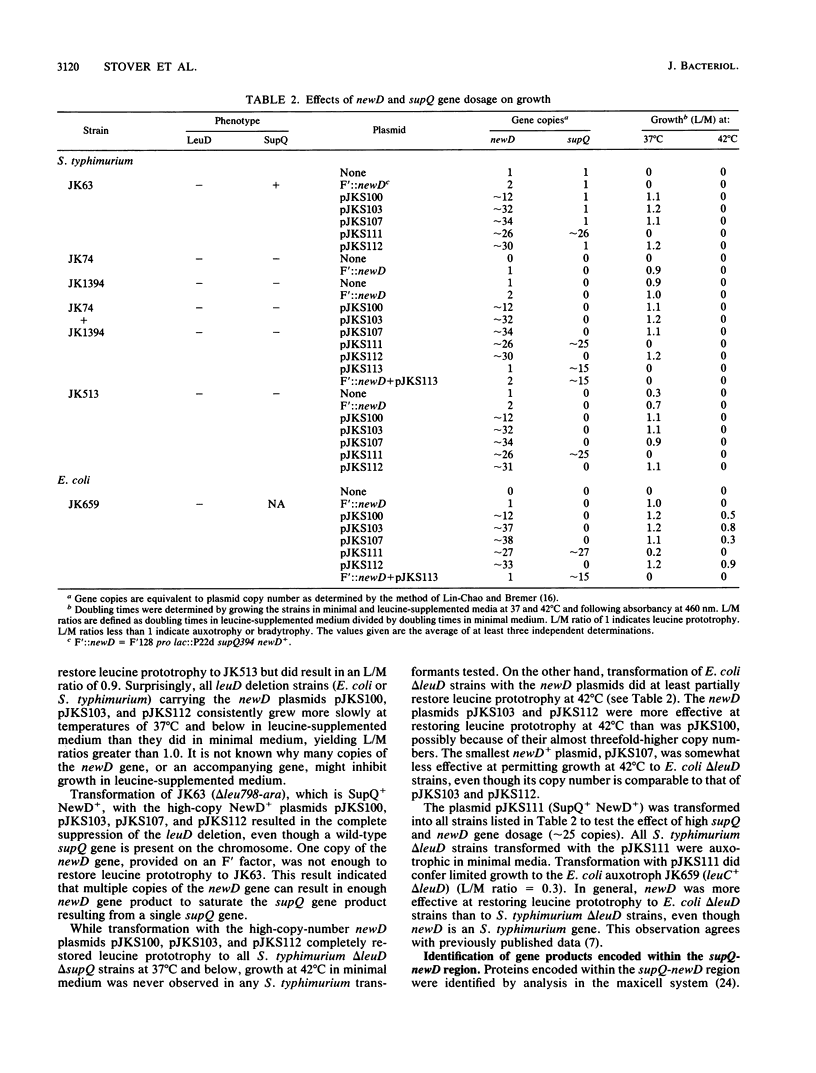
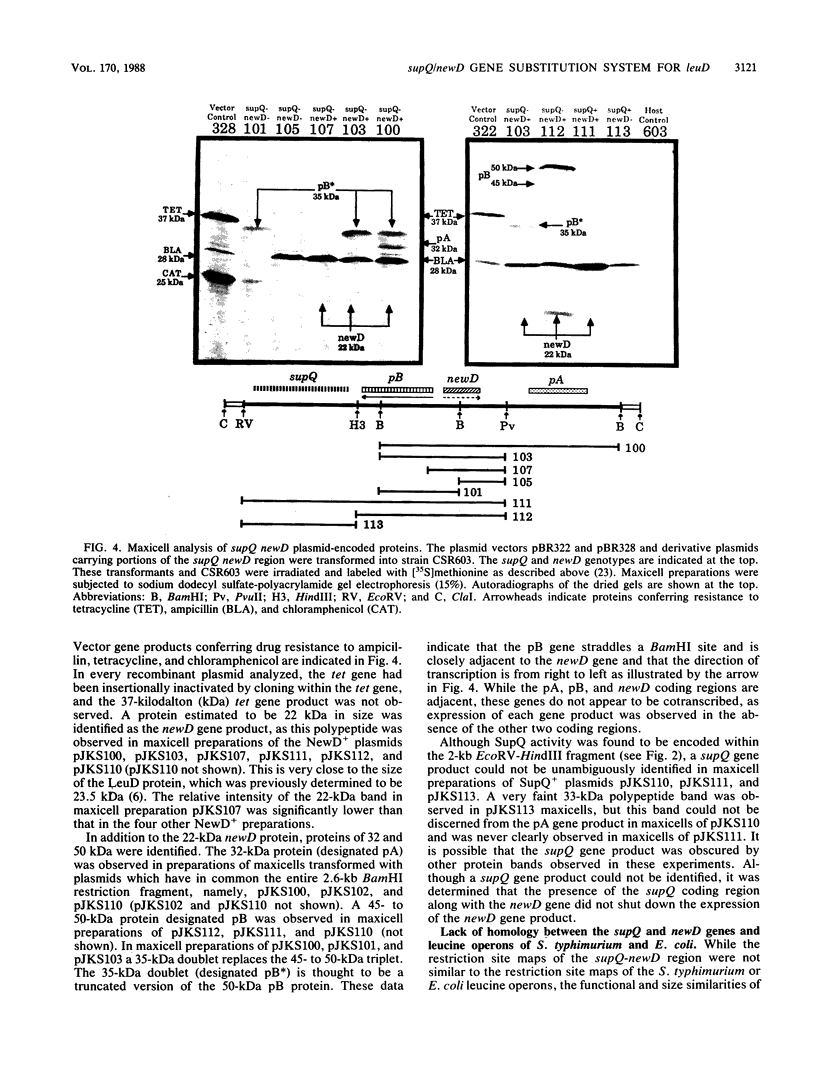
The isopropylmalate isomerase of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli is a complex of the leuC and leuD gene products. The supQ/new D gene substitution system in S. typhimurium restores leucine prototrophy to leuD mutants of S. typhimurium. Previous genetic evidence supports a model that indicates the replacement of the missing LeuD polypeptide by the newD gene product. This model proposed that this gene substitution is possible when a mutation at the supQ locus (near newD) liberates unaltered newD polypeptide from its normal complex with the supQ protein product. In this study, recombinant plasmids carrying newD, supQ, or both were transformed into E. coli and S. typhimurium strains deleted for the leuD and supQ genes to test the supQ/newD gene substitution model for suppression of leucine auxotrophy. It was determined that the newD gene encodes a 22-kilodalton polypeptide which can restore leucine prototrophy to leuD deletion strains and that a functional supQ gene prevents this suppression. It was also determined that the supQ and newD genes are separated by a gene encoding a 50-kilodalton protein, pB. While there is extensive DNA sequence homology between the leucine operons of S. typhimurium and E. coli, DNA hybridization experiments did not indicate substantial homology between the newD and leuD genes. These data, taken together with previously obtained genetic data, eliminate the possibility that supQ and newD are recently translocated segments of the leucine operon.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. O., Calvo J., Margolin P., Umbarger H. E. Expression of the leucine operon. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1570–1576. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1570-1576.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., Choung K. K., Kemper J. Construction and characterization of Salmonella typhimurium strains that accumulate and excrete alpha- and beta-isopropylmalate. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):513–520. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.513-520.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., Kemper J. Wild-type isopropylmalate isomerase in Salmonella typhimurium is composed of two different subunits. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):210–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.210-219.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., Kwoh D. Y., Kemper J. Salmonella typhimurium newD and Escherichia coli leuC genes code for a functional isopropylmalate isomerase in Salmonella typhimurium-Escherichia coli hybrids. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1253–1262. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1253-1262.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS S. R., BURNS R. O., UMBARGER H. E. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF LEUCINE. II. THE ENZYMIC ISOMERIZATION OF BETA-CARBOXY-BETA-HYDROXYISOCAPROATE AND ALPHA-HYDROXY-BETA-CARBOXYISOCAPROATE. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:1046–1052. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg K. M., Gemmill R., Jones J., Calvo J. M. Cloning of an EcoRI-generated fragment of the leucine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. Gene. 1980 Jan;8(2):135–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper J. Evolution of a new gene substituting for the leuD gene of Salmonella typhimurium: characterization of supQ mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):937–951. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.937-951.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper J. Evolution of a new gene substituting for the leuD gene of Salmonella typhimurium: origin and nature of supQ and newD mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1176–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1176-1185.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper J., Margolin P. Suppression by gene substitution for the leuD gene of Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1969 Oct;63(2):263–279. doi: 10.1093/genetics/63.2.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., HUMAN M. L. A nonhereditary, host-induced variation of bacterial viruses. J Bacteriol. 1952 Oct;64(4):557–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.4.557-569.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Chao S., Bremer H. Effect of relA function on the replication of plasmid pBR322 in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Apr;203(1):150–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00330396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIN P. Genetic fine structure of the leucine operon in Salmonella. Genetics. 1963 Mar;48:441–457. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.3.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton R. B. The genetic homology of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1971 Nov;69(3):303–315. doi: 10.1093/genetics/69.3.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Burleigh B. D., Jr, Hartley B. S. Gene duplication in experimental enzyme evolution. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):200–204. doi: 10.1038/251200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Anilionis A. Evolution of the bacterial genome. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., O'Reilly C., McConnell D. Physical map of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 DNA in the vicinity of the proA gene. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):655–657. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.655-657.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, Edition VI. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):410–453. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.410-453.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers J. M., Amzallag A., Middleton R. B. Genetic fine structure of the leucine operon of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1268–1272. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1268-1272.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C. H., De Felice M., Wessler S. R., Calvo J. M. Physical characterization of the ilvHI operon of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):797–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.797-804.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. L., Kessler D. P. Genetic analysis of the leucine region in Escherichia coli B-r: gene-enzyme assignments. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):63–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.63-72.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]