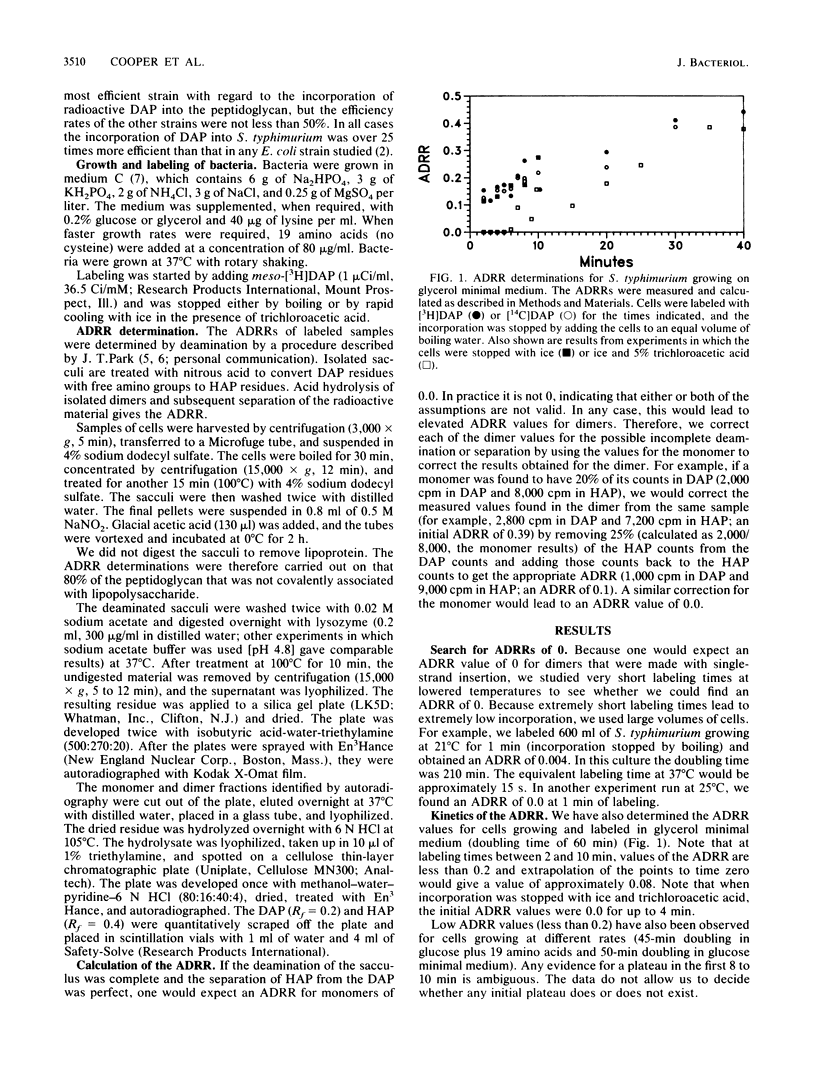
Abstract
The synthesis of peptidoglycan by Salmonella typhimurium at the molecular level has been analyzed by studying the pattern of insertion of newly synthesized strands into the preexisting cell wall. We have measured the acceptor-donor radioactivity ratio during short labeling periods, and we found values between 0 and 0.2. This is less than the ratio observed by Burman and Park (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 81:1844-1848) for peptidoglycan synthesis in Escherichia coli. We propose that insertion of new strands occurs as single strands.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burman L. G., Park J. T. Molecular model for elongation of the murein sacculus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1844–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Schwarz U. Cleavage and resynthesis of peptide cross bridges in Escherichia coli murein. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):136–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.136-140.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwer R. W., Nanninga N., Keck W., Schwarz U. Arrangement of glycan chains in the sacculus of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):723–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.723-729.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pedro M. A., Schwarz U. Heterogeneity of newly inserted and preexisting murein in the sacculus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5856–5860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


