Abstract
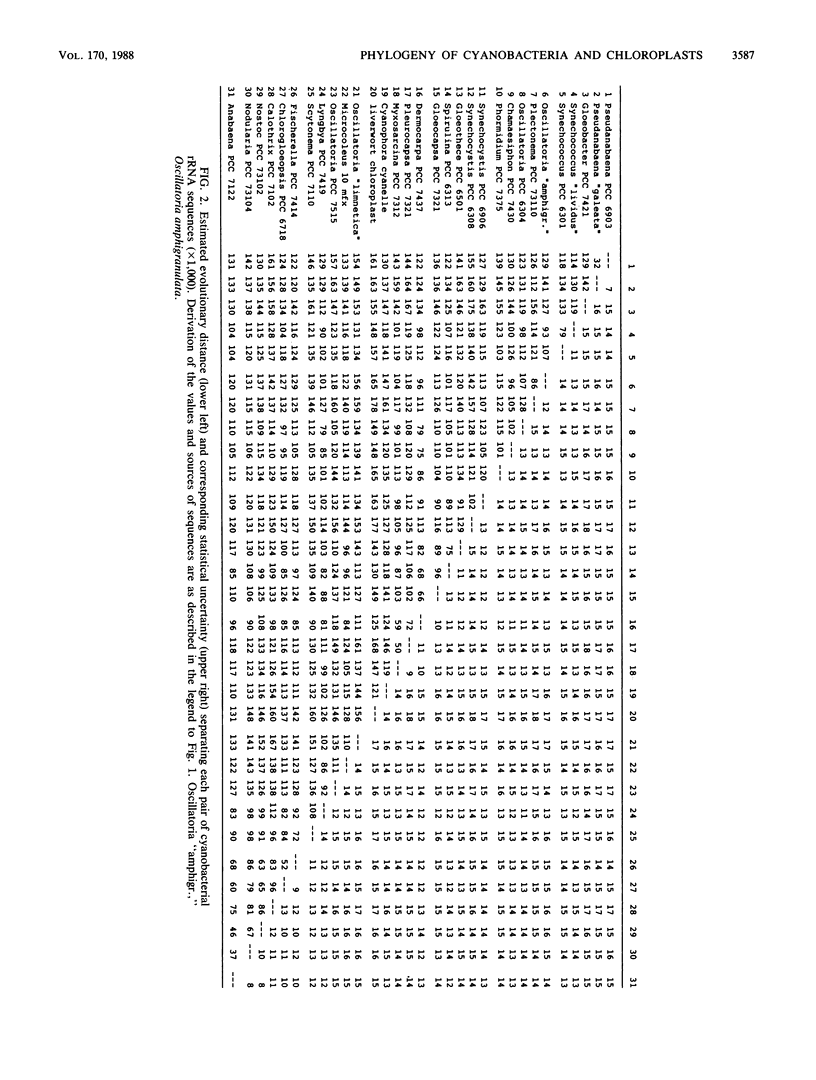
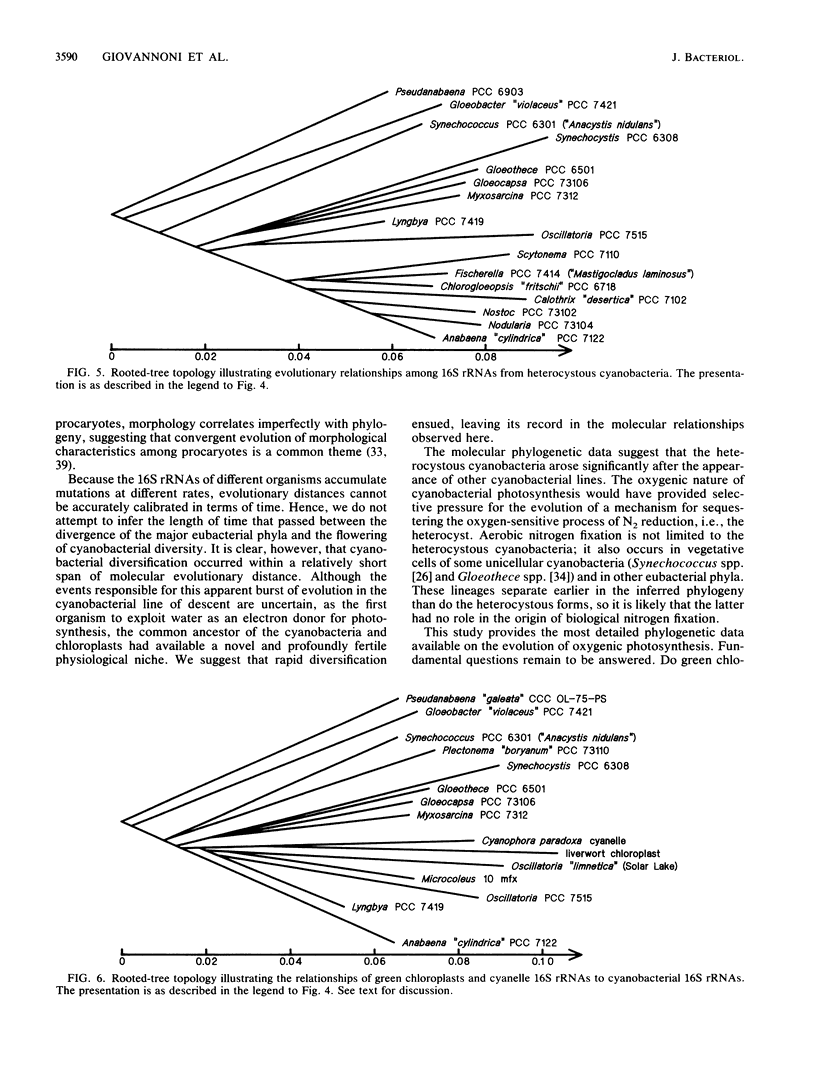
The 16S rRNAs from 29 cyanobacteria and the cyanelle of the phytoflagellate Cyanophora paradoxa were partially sequenced by a dideoxynucleotide-terminated, primer extension method. A least-squares distance matrix analysis was used to infer phylogenetic trees that include green chloroplasts (those of euglenoids, green algae, and higher plants). The results indicate that many diverse forms of cyanobacteria diverged within a short span of evolutionary distance. Evolutionary depth within the surveyed cyanobacteria is substantially less than that separating the major eubacterial taxa, as though cyanobacterial diversification occurred significantly after the appearance of the major eubacterial groups. Three of the five taxonomic sections defined by Rippka et al. (R. Rippka, J. Deruelles, J. B. Waterbury, M. Herdman, and R. Y. Stanier, J. Gen. Microbiol. 111:1-61, 1979) (sections II [pleurocapsalean], IV [heterocystous, filamentous, nonbranching], and V [heterocystous, filamentous, branching]) are phylogenetically coherent. However, the other two sections (I [unicellular] and III [nonheterocystous, filamentous]) are intermixed and hence are not natural groupings. Our results not only support the conclusion of previous workers that the cyanobacteria and green chloroplasts form a coherent phylogenetic group but also suggest that the chloroplast lineage, which includes the cyanelle of C. paradoxa, is not just a sister group to the free-living forms but rather is contained within the cyanobacterial radiation.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonen L., Doolittle W. F., Fox G. E. Cyanobacterial evolution: results of 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid sequence analyses. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):879–888. doi: 10.1139/o79-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonen L., Doolittle W. F. On the prokaryotic nature of red algal chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2310–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonen L., Doolittle W. F. Partial sequences of 16S rRNA and the phylogeny of blue-green algae and chloroplasts. Nature. 1976 Jun 24;261(5562):669–673. doi: 10.1038/261669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Sequence of the chloroplast 16S rRNA gene and its surrounding regions of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7609–7620. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf L., Roux E., Stutz E., Kössel H. Nucleotide sequence of a Euglena gracilis chloroplast gene coding for the 16S rRNA: homologies to E. coli and Zea mays chloroplast 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6369–6381. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. J., Stewart G. C., Hollis M. A., Vold B. S., Bott K. F. Nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis ribosomal RNA operon, rrnB. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL W. T., CLAUS G. ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE BLUE-GREEN ALGAL SYMBIONT IN CYANOPHORA PARADOXA KORSCHIKOFF. J Cell Biol. 1963 Dec;19:551–563. doi: 10.1083/jcb.19.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Ota T. On the stochastic model for estimation of mutational distance between homologous proteins. J Mol Evol. 1972 Dec 29;2(1):87–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01653945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell E. S., Liu J., Shively J. M. Nucleotide sequences of Cyanophora paradoxa cellular and cyanelle-associated 5S ribosomal RNAs: the cyanelle as a potential intermediate in plastid evolution. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(4):300–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02100638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J. Earliest phylogenetic branchings: comparing rRNA-based evolutionary trees inferred with various techniques. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:825–837. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyaizu H., Debrunner-Vossbrinck B., Mandelco L., Studier J. A., Woese C. R. The green non-sulfur bacteria: a deep branching in the eubacterial line of descent. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1987;9:47–53. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(87)80055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippka R., Herdman M. Division patterns and cellular differentiation in cyanobacteria. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Jan-Feb;136A(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopf J. W., Packer B. M. Early Archean (3.3-billion to 3.5-billion-year-old) microfossils from Warrawoona Group, Australia. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237:70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.11539686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohdoh N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of 16S ribosomal RNA gene from tobacco chloroplasts. Gene. 1982 Feb;17(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from a blue-green alga, Anacystis nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):46–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00330888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Woese C. R., Dobson M. E., Weiss E. A common origin of rickettsiae and certain plant pathogens. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):556–558. doi: 10.1126/science.3931222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D., Oyaizu Y., Oyaizu H., Olsen G. J., Woese C. R. Mitochondrial origins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4443–4447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


