Abstract
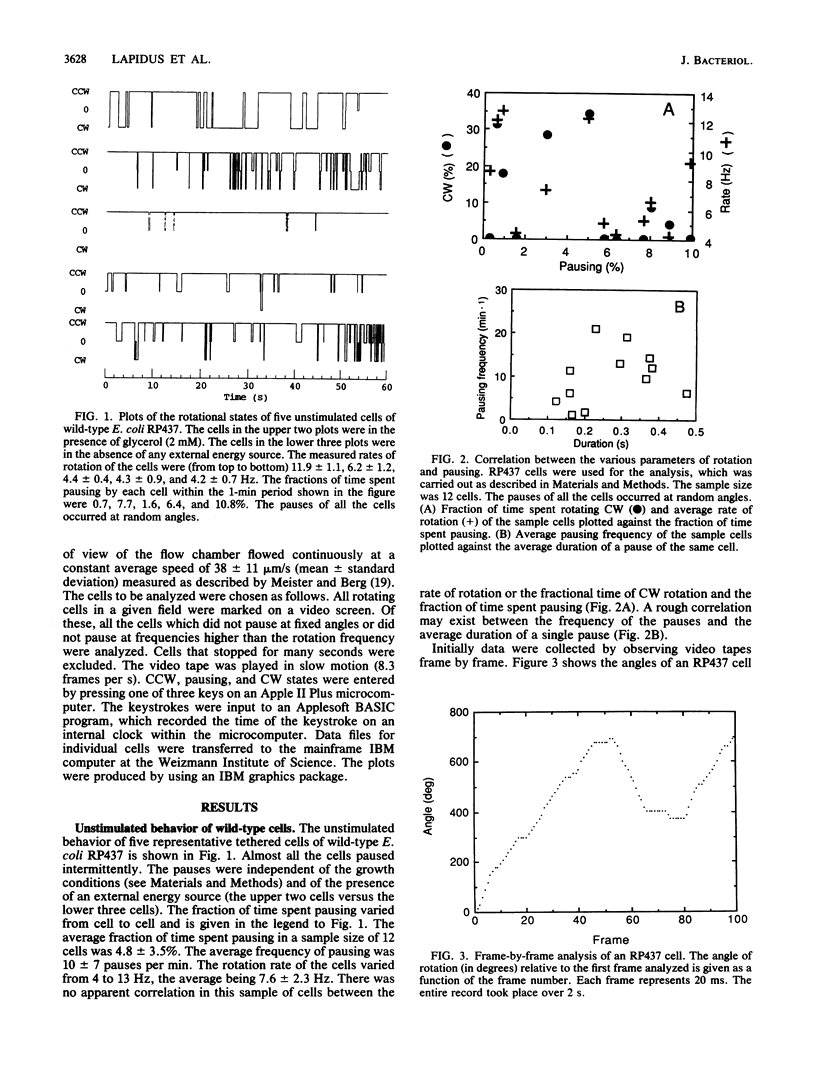
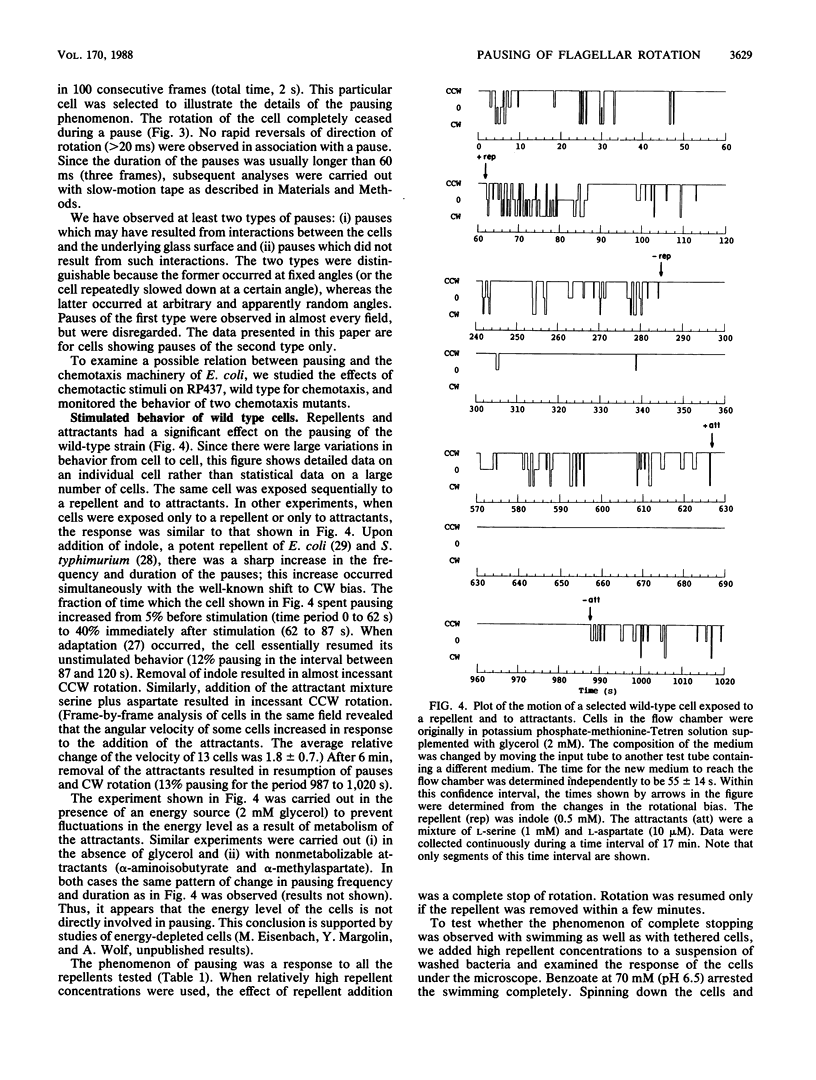
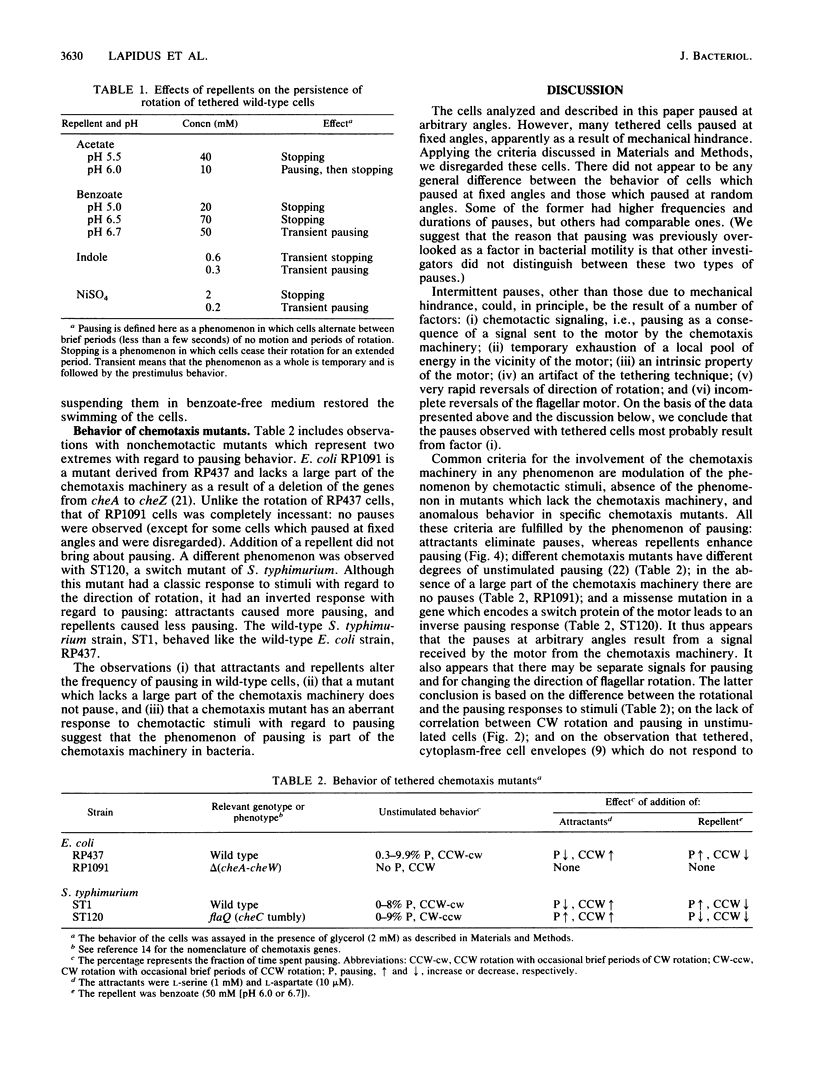
When bacterial cells are tethered to glass by their flagella, many of them spin. On the basis of experiments with tethered cells it has generally been thought that the motor which drives the flagellum is a two-state device, existing in either a counterclockwise or a clockwise state. Here we show that a third state of the motor is that of pausing, the duration and frequency of which are affected by chemotactic stimuli. We have recorded on video tape the rotation of tethered Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium cells and analyzed the recordings frame by frame and in slow motion. Most wild-type cells paused intermittently. The addition of repellents caused an increase in the frequency and duration of the pauses. The addition of attractants sharply reduced the number of pauses. A chemotaxis mutant which lacks a large part of the chemotaxis machinery owing to a deletion of the genes from cheA to cheZ did not pause at all and did not respond to repellents by pausing. A tumbly mutant of S. typhimurium responded to repellents by smooth swimming and to attractants by tumbling. When tethered, these cells exhibited a normal rotational response but an inverse pausing response to chemotactic stimuli: the frequency of pauses decreased in response to repellents and increased in response to attractants. It is suggested that (i) pausing is an integral part of bacterial motility and chemotaxis, (ii) pausing is independent of the direction of flagellar rotation, and (iii) pausing may be one of the causes of tumbling.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M., Oesterhelt D. Morphology, function and isolation of halobacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):459–475. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage J. P., Macnab R. M. Unidirectional, intermittent rotation of the flagellum of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):514–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.514-518.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Anderson R. A. Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature. 1973 Oct 19;245(5425):380–382. doi: 10.1038/245380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Block S. M. A miniature flow cell designed for rapid exchange of media under high-power microscope objectives. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2915–2920. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Dynamic properties of bacterial flagellar motors. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):77–79. doi: 10.1038/249077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Manson M. D., Conley M. P. Dynamics and energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982;35:1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach M., Adler J. Bacterial cell envelopes with functional flagella. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8807–8814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach M. Changes in membrane potential of Escherichia coli in response to temporal gradients of chemicals. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6818–6825. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz R., Schmitt R. Rhizobium meliloti swims by unidirectional, intermittent rotation of right-handed flagellar helices. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3146–3150. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3146-3150.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D., HOGNESS D. S. The transformation of Escherichia coli with deoxyribonucleic acid isolated from bacteriophage lambda-dg. J Mol Biol. 1960 Dec;2:392–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(60)80050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M., DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Inversion of a behavioral response in bacterial chemotaxis: explanation at the molecular level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4150–4154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Aizawa S. Bacterial motility and the bacterial flagellar motor. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:51–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Han D. P. Asynchronous switching of flagellar motors on a single bacterial cell. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Bacterial motility and chemotaxis: light-induced tumbling response and visualization of individual flagella. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Berg H. C. The stall torque of the bacterial flagellar motor. Biophys J. 1987 Sep;52(3):413–419. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83230-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Complementation analysis and deletion mapping of Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.45-53.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Houts S. E. Isolation and behavior of Escherichia coli deletion mutants lacking chemotaxis functions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Eisenbach M. Correlation between bacteriophage chi adsorption and mode of flagellar rotation of Escherichia coli chemotaxis mutants. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):604–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.604-611.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Eisenbach M. Direction of flagellar rotation in bacterial cell envelopes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):222–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.222-230.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Matsumura P., Eisenbach M. Restoration of flagellar clockwise rotation in bacterial envelopes by insertion of the chemotaxis protein CheY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubik B. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Potentiation, desensitization, and inversion of response in bacterial sensing of chemical stimuli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2820–2824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang N., Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Common mechanism for repellents and attractants in bacterial chemotaxis. Science. 1973 Jul 6;181(4094):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4094.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


