Abstract
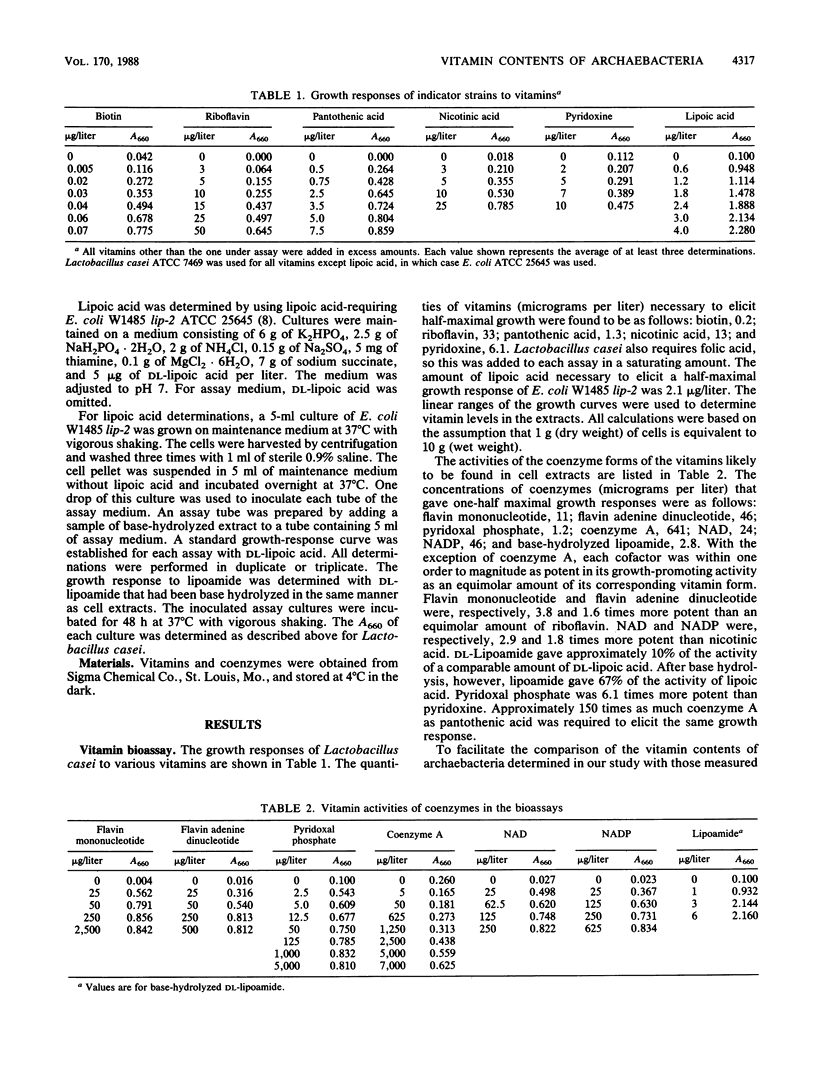
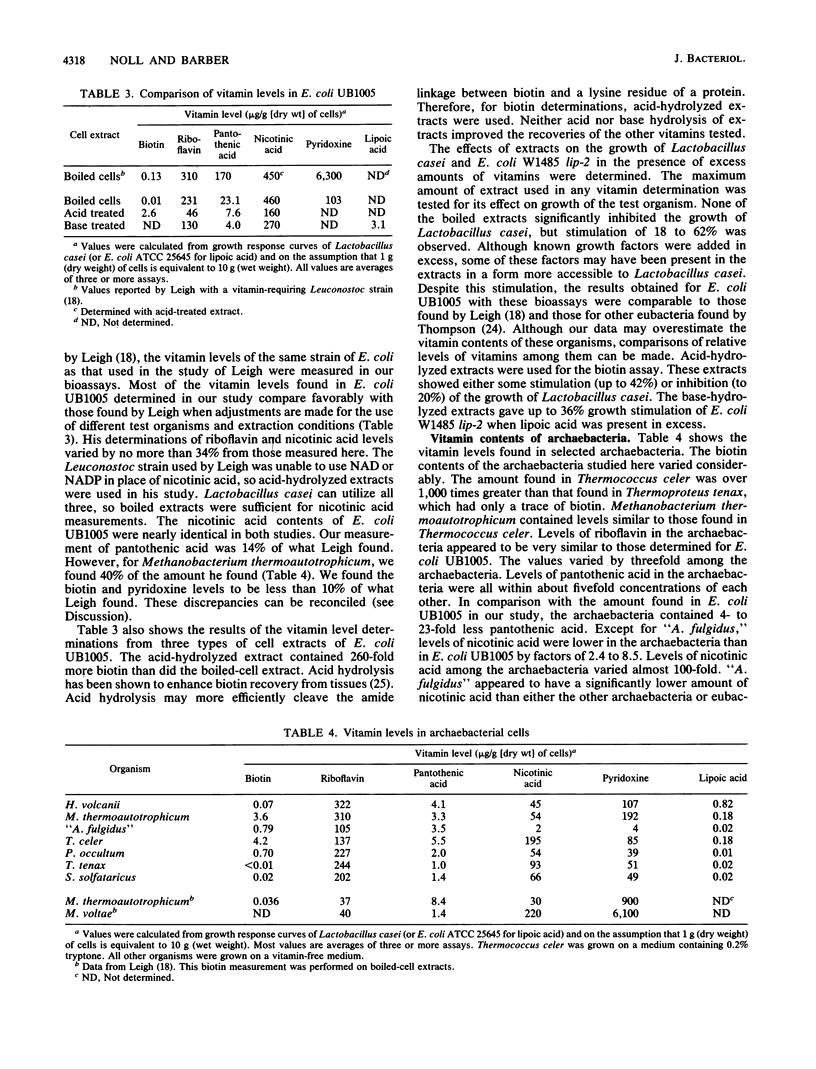
The levels of six water-soluble vitamins of seven archaebacterial species were determined and compared with the levels found in a eubacterium, Escherichia coli. Biotin, riboflavin, pantothenic acid, nicotinic acid, pyridoxine, and lipoic acid contents of Halobacterium volcanii, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum delta H, "Archaeoglobus fulgidus" VC-16, Thermococcus celer, Pyrodictium occultum, Thermoproteus tenax, and Sulfolobus solfataricus were measured by using bioassays. The archaebacteria examined were found to contain these vitamins at levels similar to or significantly below the levels found in in E. coli. Riboflavin was found at levels comparable to those in E. coli. Pyridoxine was as abundant among the archaebacteria of the methanogenhalophile branch as in E. coli. It was only one-half as abundant in the sulfur-metabolizing branch. "A. fulgidus," however, contained only 4% as much pyridoxine as E. coli. Nicotinic and pantothenic acids were approximately 10-fold less abundant (except for a 200-fold-lower nicotinic acid level in "A. fulgidus"). Nicotinic acid may be replaced by an 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin coenzyme (factor F420) in some archaebacteria (such as "A. fulgidus"). Compared with the level in E. coli, biotin was equally as abundant in Thermococcus celer and Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum, about one-fourth less abundant in P. occultum and "A. fulgidus," and 25 to over 100 times less abundant in the others. The level of lipoic acid was up to 20 times lower in H. volcanii, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum, and Thermococcus celer. It was over two orders of magnitude lower among the remaining organisms. With the exception of "A. fulgidus," lipoic acid, pantothenic acid, and pyridoxine were more abundant in the members of the methanogen-halophile branch of the archaebacteria than in the sulfur-metabolizing branch.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achenbach-Richter L., Stetter K. O., Woese C. R. A possible biochemical missing link among archaebacteria. Nature. 1987 May 28;327(6120):348–349. doi: 10.1038/327348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Brock K. M., Belly R. T., Weiss R. L. Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(1):54–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00408082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eirich L. D., Vogels G. D., Wolfe R. S. Distribution of coenzyme F420 and properties of its hydrolytic fragments. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):20–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.20-27.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmerich P., Massey V. Flavin and 5-deazaflavin: a chemical evaluation of 'modified' flavoproteins with respect to the mechanisms of redox biocatalysis. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 1;84(1):5–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)81047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert A. A., Guest J. R. Biochemical and genetic studies with lysine+methionine mutants of Escherichia coli: lipoic acid and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase-less mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):363–381. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. J., Nagle D. P., Jr, Whitman W. B. Methanogens and the diversity of archaebacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):135–177. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.135-177.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M., Wassef M. K., Kushner D. J. Radioisotopic studies on the biosynthesis of the glyceryl diether lipids of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Biochem. 1968 Aug;46(8):971–977. doi: 10.1139/o68-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerscher L., Oesterhelt D. Purification and properties of two 2-oxoacid:ferredoxin oxidoreductases from Halobacterium halobium. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun 1;116(3):587–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R., Smith P. F. Long-chain glycerol diether and polyol dialkyl glycerol triether lipids of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):106–116. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.106-116.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langworthy T. A., Smith P. F., Mayberry W. R. Lipids of Thermoplasma acidophilum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1193–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1193-1200.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A. Levels of water-soluble vitamins in methanogenic and non-methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):800–803. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.800-803.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X. L., White R. H. Occurrence of coenzyme F420 and its gamma-monoglutamyl derivative in nonmethanogenic archaebacteria. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):444–448. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.444-448.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullakhanbhai M. F., Larsen H. Halobacterium volcanii spec. nov., a Dead Sea halobacterium with a moderate salt requirement. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Aug 28;104(3):207–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00447326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetter K. O., Lauerer G., Thomm M., Neuner A. Isolation of extremely thermophilic sulfate reducers: evidence for a novel branch of archaebacteria. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):822–824. doi: 10.1126/science.236.4803.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Eakin R. E., Williams R. J. THE EXTRACTION OF BIOTIN FROM TISSUES. Science. 1941 Dec 19;94(2451):589–590. doi: 10.1126/science.94.2451.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Langworthy T. A. Diphytanyl and dibiphytanyl glycerol ether lipids of methanogenic archaebacteria. Science. 1979 Jan 5;203(4375):51–53. doi: 10.1126/science.758677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki S., Tsai L. Purification and properties of 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin-dependent NADP+ reductase from Methanococcus vannielii. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6462–6465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rosa M., Gambacorta A., Bu'lock J. D. Extremely thermophilic acidophilic bacteria convergent with Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):156–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


