Abstract
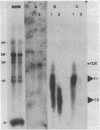
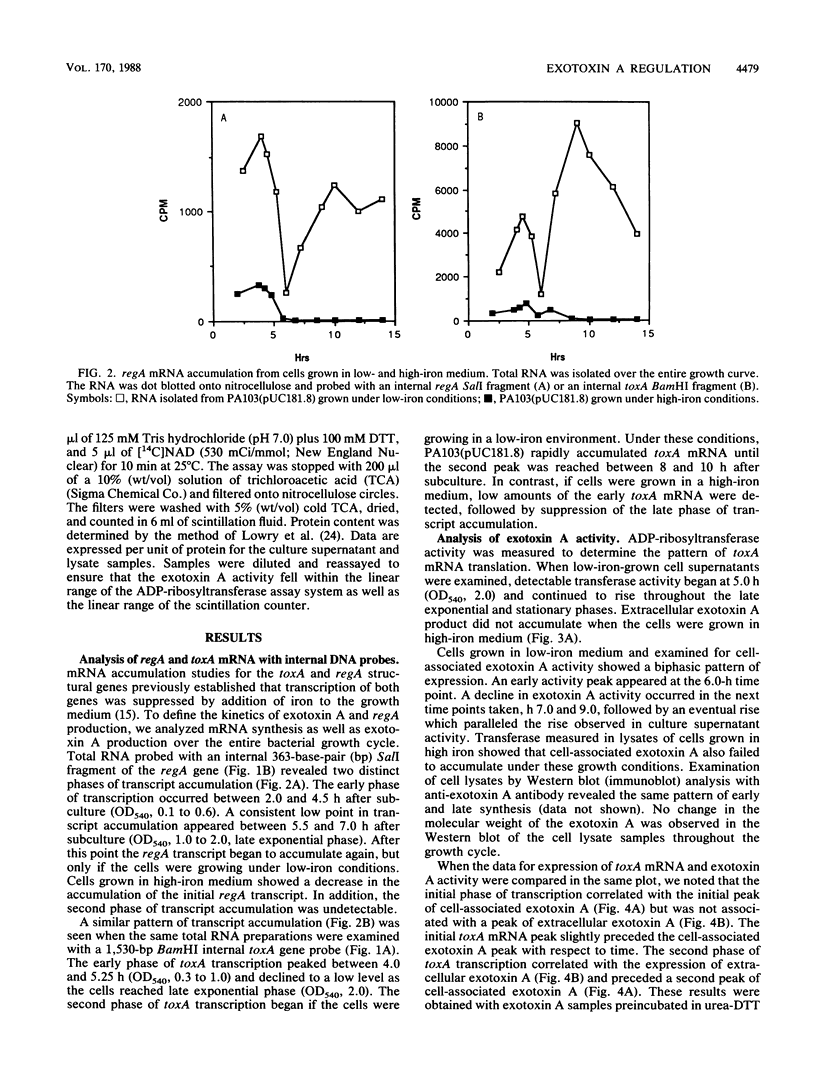
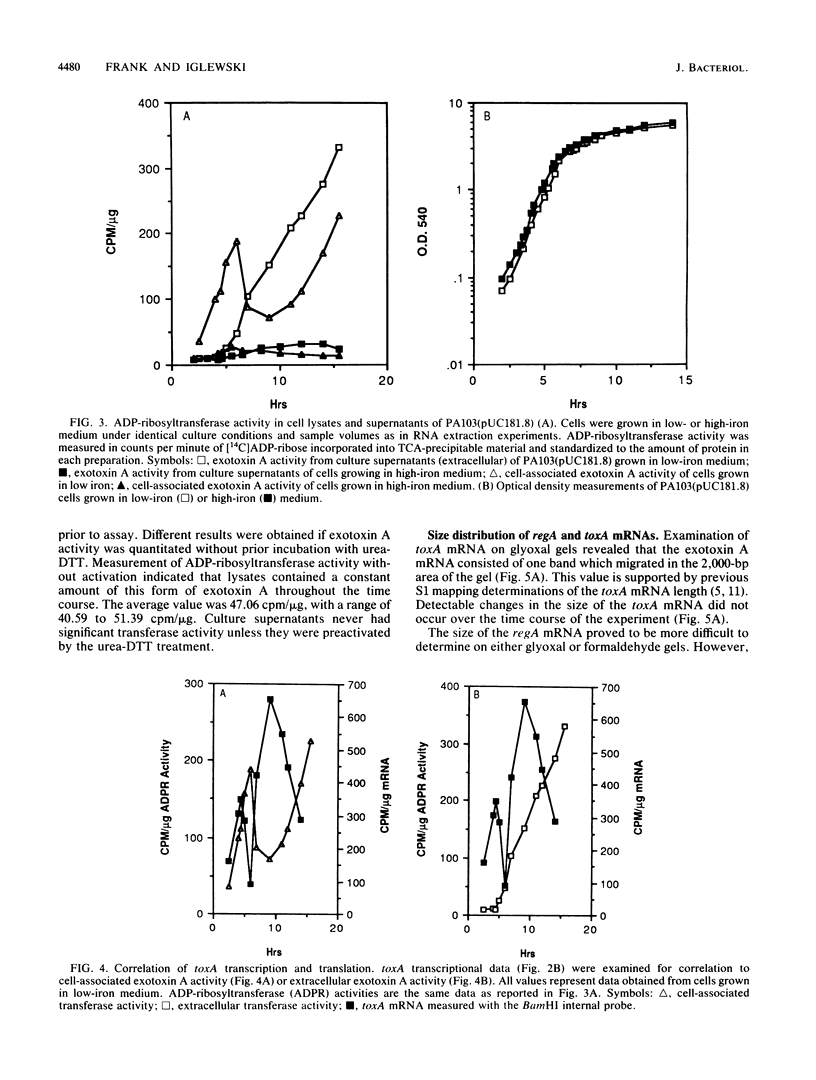
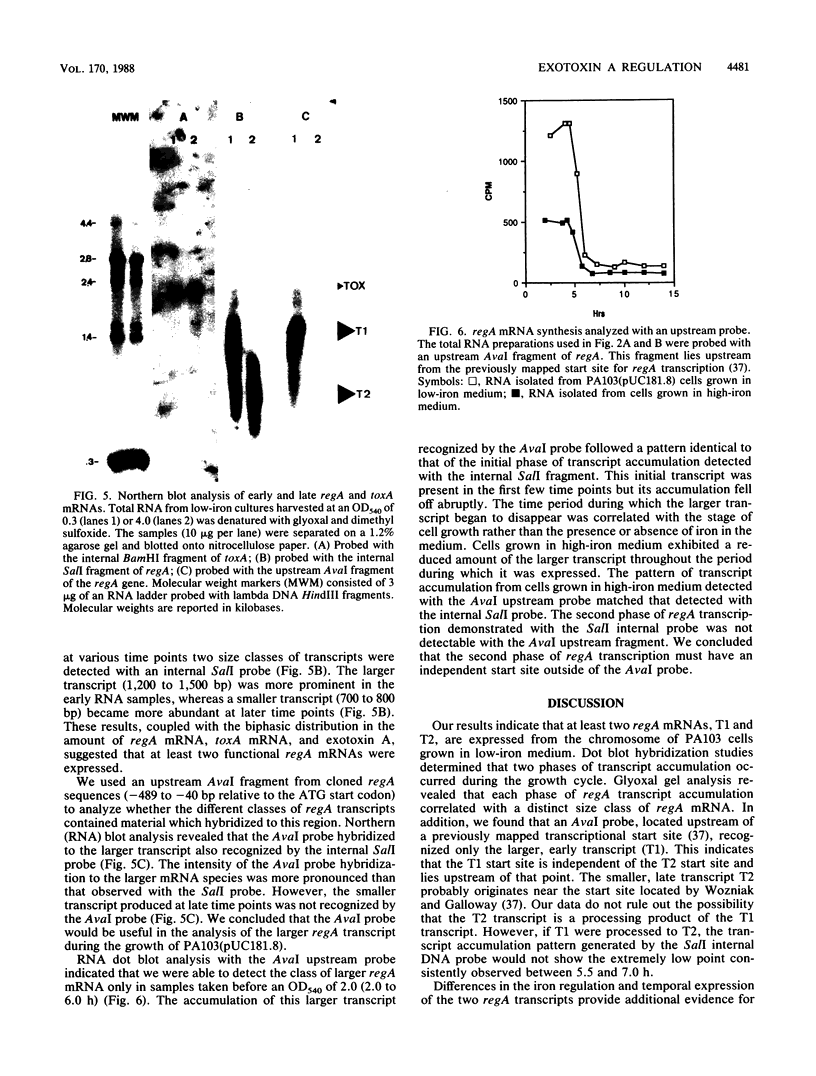
DNA probes specific for an internal portion of the toxA and regA genes were used to examine the synthesis of mRNA during the growth cycle of P. aeruginosa PA103. RNA dot blot analysis revealed that in a low-iron growth medium, the synthesis of regA and toxA mRNA followed a biphasic expression pattern. Analysis of ADP-ribosyltransferase activity also indicated that an early and late phase of exotoxin A synthesis occurred. Utilizing an internal SalI probe, examination of the size distribution of the regA mRNA during the cell cycle indicated that a large transcript (T1) was present at early time points, followed by the appearance of a smaller transcript (T2) during late exponential to early stationary phase. An upstream AvaI regA probe was found to hybridize to the T1 transcript but not to the T2 transcript. The data indicate that at least two separate functional regA mRNA species were produced. Analysis of mRNA accumulation for the regA gene when cells were grown in high-iron medium provided additional evidence for two separately controlled transcripts being produced from the regA chromosomal locus. Both regA transcripts were correlated with exotoxin A transcription and production.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorn M. J., Iglewski B. H., Ives S. K., Sadoff J. C., Vasil M. L. Effect of iron on yields of exotoxin A in cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA-103. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):785–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.785-791.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorn M. J., Sokol P. A., Iglewski B. H. Influence of iron on yields of extracellular products in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):193–200. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.193-200.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. T., Jordan E. M., Wilson R. B., Draper R. K., Clowes R. C. Transcription and expression of the exotoxin A gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Nov;133(11):3081–3091. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-11-3081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Collier R. J. Enzymatically active peptide from the adenosine diphosphate-ribosylating toxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):832–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.832-841.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita N., Ishihama A. Heat-shock induction of RNA polymerase sigma-32 synthesis in Escherichia coli: transcriptional control and a multiple promoter system. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Nov;210(1):10–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00337752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. C., Vasil M. L. Analysis of transcription of the exotoxin A gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1112–1119. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1112-1119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Smith D. H., Baldridge J. S., Harkins R. N., Vasil M. L., Chen E. Y., Heyneker H. L. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the exotoxin A structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2645–2649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs D. W., Tharp B. B., Konisky J. Cloning and promoter identification of the iron-regulated cir gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5343–5352. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5343-5352.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom R. C., Funk C. R., Kaper J. B., Pavlovskis O. R., Galloway D. R. Cloning of a gene involved in regulation of exotoxin A expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):37–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.37-42.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindahl M. S., Frank D. W., Iglewski B. H. Molecular studies of a positive regulator of toxin A synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:279–289. doi: 10.1159/000414353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J., Fitzgerald D. J., Adhya S., Pastan I. Functional domains of Pseudomonas exotoxin identified by deletion analysis of the gene expressed in E. coli. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajitani M., Ishihama A. Promoter selectivity of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Differential stringent control of the multiple promoters from ribosomal RNA and protein operons. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1951–1957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Factors that influence the production of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):506–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. 3. Identity of the lethal toxins produced in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S. Effect of iron on accumulation of exotoxin A-specific mRNA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1451–1456. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1451-1456.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. Mechanism of protein excretion by gram-negative bacteria: Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):695–702. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.695-702.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozola M. A., Wilson R. B., Jordan E. M., Draper R. K., Clowes R. C. Cloning and expression of a gene segment encoding the enzymatic moiety of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):683–687. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.683-687.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Toxin A-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):899–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.899-908.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., DeBusscher G., McCombie W. R. Development of broad-host-range vectors and gene banks: self-cloning of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):60–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.60-69.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Expression of glnA in Escherichia coli is regulated at tandem promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1979–1983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Sancar A., Little J. W., Rupp W. D. The uvrB gene of Escherichia coli has both lexA-repressed and lexA-independent promoters. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Chamberlain C., Grant C. C. Molecular studies of Pseudomonas exotoxin A gene. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):538–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.538-548.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak D. J., Cram D. C., Daniels C. J., Galloway D. R. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of toxR: a gene involved in exotoxin A regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2123–2135. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Wee S., Herrero M., Neilands J. B. Operator sequences of the aerobactin operon of plasmid ColV-K30 binding the ferric uptake regulation (fur) repressor. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2624–2630. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2624-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]