Abstract
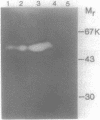
A major endopolygalacturonase excreted by Pseudomonas solanacearum was purified to greater than 95% homogeneity and shown to have an isoelectric point of 9.0 and a subunit molecular mass of 52 kilodaltons (kDa). The gene encoding this enzyme (pglA) was isolated from a genomic library of P. solanacearum DNA based on its expression in Escherichia coli and shown to be contained on a 1.8-kilobase DNA fragment. The identity of the pglA gene product and the 52-kDa polygalacturonase was demonstrated by immunoadsorption and isoelectric focusing experiments. The cloned pglA gene was apparently expressed from its own promoter in E. coli and its product was partially secreted into the periplasm. The pglA gene was insertionally inactivated in vitro and used to mutate the chromosomal pglA gene of P. solanacearum by marker exchange mutagenesis. The resulting mutant strain was deficient in production of the 52-kDa polygalacturonase and took twice as long to wilt and kill tomato plants as the wild-type parent in plant bioassay experiments. Complementation in trans with the wild-type cloned pglA gene restored virulence to near wild-type levels. The data indicate that the pglA gene is important, but not absolutely necessary, for pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andro T., Chambost J. P., Kotoujansky A., Cattaneo J., Bertheau Y., Barras F., Van Gijsegem F., Coleno A. Mutants of Erwinia chrysanthemi defective in secretion of pectinase and cellulase. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1199–1203. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1199-1203.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collmer A., Schoedel C., Roeder D. L., Ried J. L., Rissler J. F. Molecular cloning in Escherichia coli of Erwinia chrysanthemi genes encoding multiple forms of pectate lyase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):913–920. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.913-920.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Schmidhauser T., Yakobson E., Lu P., Liang X. W., Finlay D. R., Guiney D., Helinski D. R. Plasmids related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid. 1985 Mar;13(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobanputra R. S., Datta N. Trimethoprim R factors in enterobacteria from clinical specimens. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Tamaki S. Structure of two pectate lyase genes from Erwinia chrysanthemi EC16 and their high-level expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):595–606. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.595-606.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil M., Darvill A. G., Fry S. C., Albersheim P. Structure and function of the primary cell walls of plants. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:625–663. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran F., Nasuno S., Starr M. P. Extracellular and intracellular polygllacturonic acid trans-eliminases of Erwinia carotovora. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Feb;123(2):298–306. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Dressler D. A 'Southern Cross' method for the analysis of genome organization and the localization of transcription units. Gene. 1986;48(2-3):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ried J. L., Collmer A. Activity stain for rapid characterization of pectic enzymes in isoelectric focusing and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):615–622. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.615-622.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. P., Berman P. M., Allen C., Stromberg V. K., Lacy G. H., Mount M. S. Requirement for two or more Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora pectolytic gene products for maceration of potato tuber tissue by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):279–284. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.279-284.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. P., Denny T. P., Schell M. A. Cloning of the egl gene of Pseudomonas solanacearum and analysis of its role in phytopathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1445–1451. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1445-1451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A. Purification and Characterization of an Endoglucanase from Pseudomonas solanacearum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2237-2241.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A. Purification and Characterization of an Endoglucanase from Pseudomonas solanacearum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2237-2241.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staskawicz B., Dahlbeck D., Keen N., Napoli C. Molecular characterization of cloned avirulence genes from race 0 and race 1 of Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5789–5794. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5789-5794.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K. W., Keegstra K., Bauer W. D., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: I. The Macromolecular Components of the Walls of Suspension-cultured Sycamore Cells with a Detailed Analysis of the Pectic Polysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):158–173. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu P. L., Leong S., Sequeira L. Molecular cloning of genes that specify virulence in Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):617–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.617-622.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida N., Uozumi T., Beppu T. Specific excretion of Serratia marcescens protease through the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):937–944. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.937-944.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]