Abstract
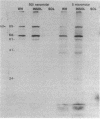
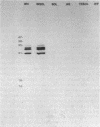
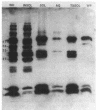
The effects of the nonionic detergent Triton X-114 on the ultrastructure of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum are presented in this study. Treatment of Percoll-purified motile T. pallidum with a 1% concentration of Triton X-114 resulted in cell surface blebbing followed by lysis of blebs and a decrease in diameter from 0.25-0.35 micron to 0.1-0.15 micron. Examination of thin sections of untreated Percoll-purified T. pallidum showed integrity of outer and cytoplasmic membranes. In contrast, thin sections of Triton X-114-treated treponemes showed integrity of the cytoplasmic membrane but loss of the outer membrane. The cytoplasmic cylinders generated by detergent treatment retained their periplasmic flagella, as judged by electron microscopy and immunoblotting. Recently identified T. pallidum penicillin-binding proteins also remained associated with the cytoplasmic cylinders. Proteins released by Triton X-114 at 4 degrees C were divided into aqueous and hydrophobic phases after incubation at 37 degrees C. The hydrophobic phase had major polypeptide constituents of 57, 47, 38, 33-35, 23, 16, and 14 kilodaltons (kDa) which were reactive with syphilitic serum. The 47-kDa polypeptide was reactive with a monoclonal antibody which has been previously shown to identify a surface-associated T. pallidum antigen. The aqueous phase contained the 190-kDa ordered ring molecule, 4D, which has been associated with the surface of the organisms. Full release of the 47- and 190-kDa molecules was dependent on the presence of a reducing agent. These results indicate that 1% Triton X-114 selectively solubilizes the T. pallidum outer membrane and associated proteins of likely outer membrane location.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface characterization of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):814–823. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.814-823.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop N. H., Miller J. N. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis. II. The relationship of neutralizing factors in immune serum to acquired resistance. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):197–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Champion C. I., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Antigenic and structural characterization of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) endoflagella. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):168–175. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.168-175.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Radolf J. D., Lovett M. A., Miller J. N. The antigenic interrelationship between the endoflagella of Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter and Treponema pallidum Nichols strain. I. Treponemicidal activity of cross-reactive endoflagellar antibodies against T. pallidum. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2973–2979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein L. A., Radolf J. D., Fehniger T. E., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Immunization of rabbits with recombinant Treponema pallidum surface antigen 4D alters the course of experimental syphilis. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2415–2421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Identification of Treponema pallidum penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5298–5300. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5298-5300.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehniger T. E., Radolf J. D., Lovett M. A. Properties of an ordered ring structure formed by recombinant Treponema pallidum surface antigen 4D. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):732–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.732-739.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehniger T. E., Radolf J. D., Walfield A. M., Cunningham T. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Native surface association of a recombinant 38-kilodalton Treponema pallidum antigen isolated from the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):586–593. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.586-593.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehniger T. E., Walfield A. M., Cunningham T. M., Radolf J. D., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Purification and characterization of a cloned protease-resistant Treponema pallidum-specific antigen. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):598–607. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.598-607.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDY P. H., Jr, NELL E. E. Study of the antigenic structure of Treponema pallidum by specific agglutination. Am J Hyg. 1957 Sep;66(2):160–172. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Norris S. J., Lovett M. A., Miller J. N. Purification of Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Oct-Dec;11(4):275–286. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198410000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K., Birch-Andersen A., Nielsen H. A. Electron microscopy of treponemes subjected to the Treponema pallidum immobilization (TPI) test. II. Immunoelectron microscopy. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1979 Aug;87C(4):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K., Nielsen H. A., Birch-Andersen A. Electron microscopy of treponemes subjected to the Treponema pallidum immobilization (TPI) test. I. Comparison of immunoimmobilized cells and control cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1979 Jun;87C(3):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. A., Marchitto K. S., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody with hemagglutination, immobilization, and neutralization activities defines an immunodominant, 47,000 mol wt, surface-exposed immunogen of Treponema pallidum (Nichols). J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1404–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METZGER M., RUCZKOWSKA J. INFLUENCE OF LYSOZYME UPON THE REACTIVITY OF TREPONEMA PALLIDUM IN THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY REACTION. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1964;12:702–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Chamberlain N. R., Swancutt M. A., Goldberg M. S. Cloning and expression of the major 47-kilodalton surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):500–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.500-506.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Cockayne A., Bailey M. J. The outer membrane of Treponema pallidum: biological significance and biochemical properties. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2349–2357. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Rhodes J. G. Surface-associated antigens of Treponema pallidum concealed by an inert outer layer. Immunology. 1982 May;46(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Antigenic interrelationship between endoflagella of Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter and Treponema pallidum (Nichols): molecular characterization of endoflagellar proteins. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):626–634. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.626-634.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Borenstein L. A., Kim J. Y., Fehniger T. E., Lovett M. A. Role of disulfide bonds in the oligomeric structure and protease resistance of recombinant and native Treponema pallidum surface antigen 4D. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1365–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1365-1371.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Chamberlain N. R., Clausell A., Norgard M. V. Identification and localization of integral membrane proteins of virulent Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by phase partitioning with the nonionic detergent triton X-114. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):490–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.490-498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Fehniger T. E., Silverblatt F. J., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. The surface of virulent Treponema pallidum: resistance to antibody binding in the absence of complement and surface association of recombinant antigen 4D. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):579–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.579-585.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riethman H. C., Boyer M. J., Wise K. S. Triton X-114 phase fractionation of an integral membrane surface protein mediating monoclonal antibody killing of Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1094–1100. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1094-1100.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Hodinka R. L., Wyrick P. B., Bassford P. J., Jr Changes in the cell surface properties of Treponema pallidum that occur during in vitro incubation of freshly extracted organisms. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2255–2261. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2255-2261.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins in bacteria. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Apr;96(4):502–504. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-4-502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]