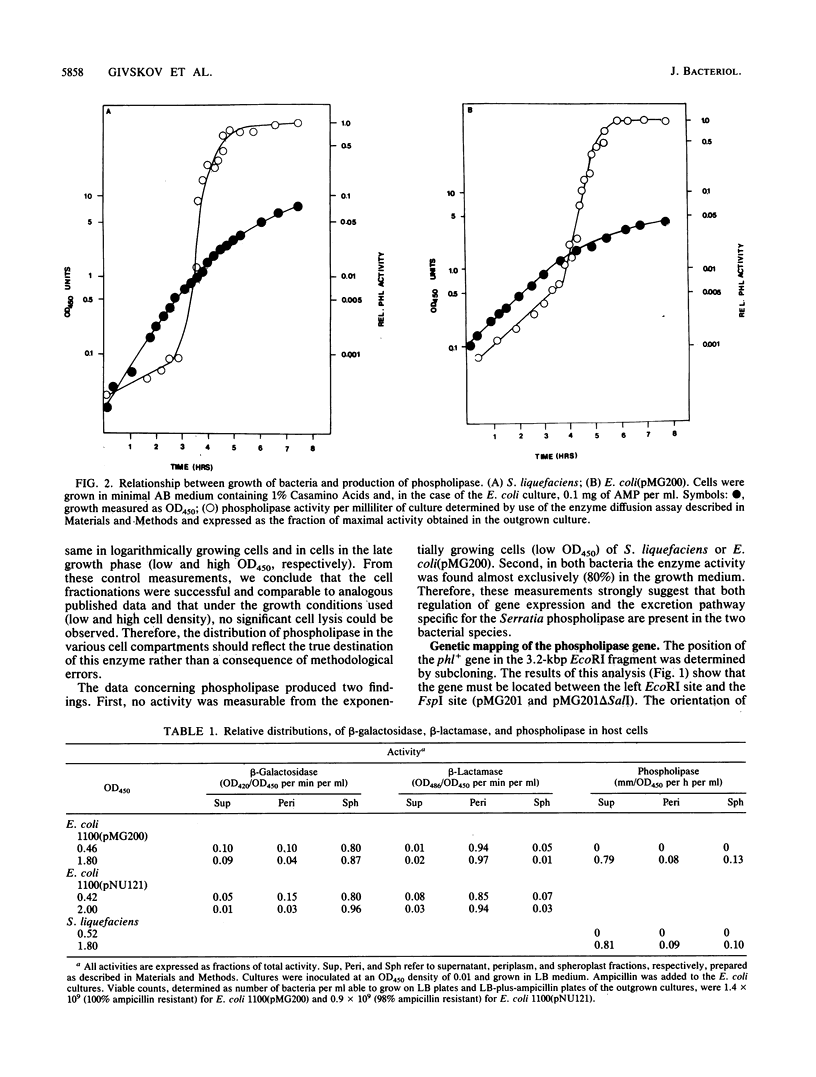
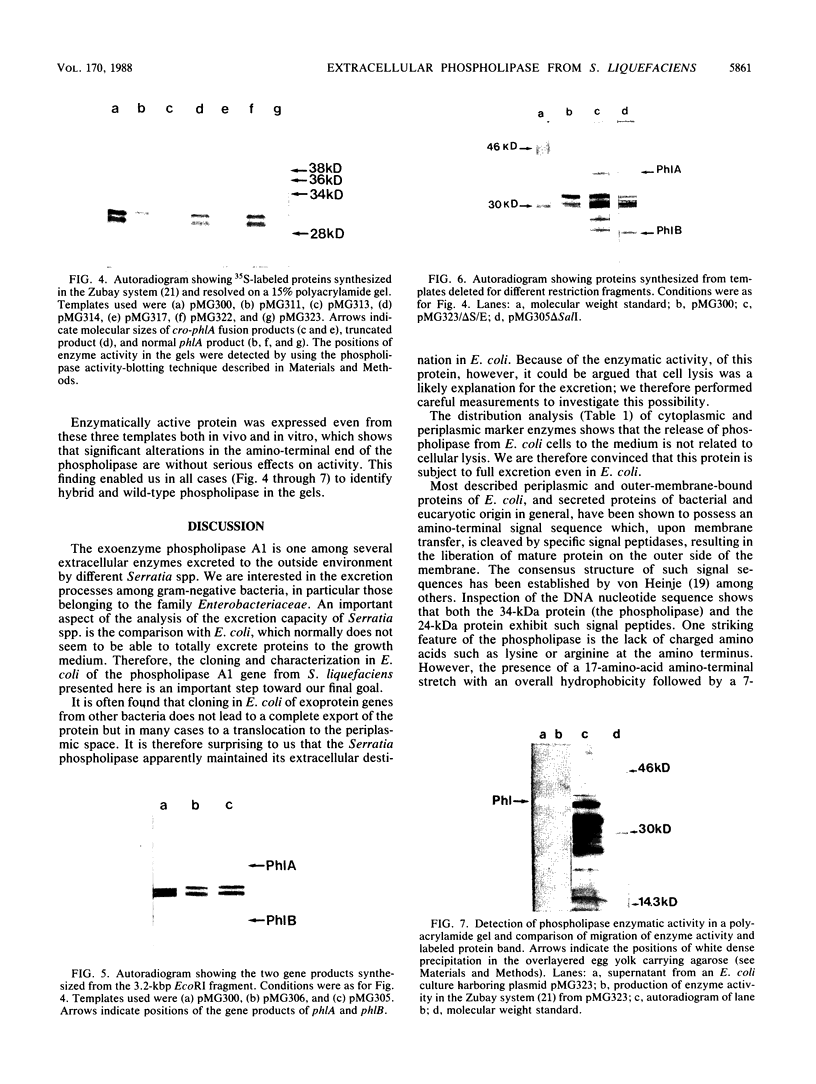
Abstract
From a genomic library of Serratia liquefaciens, a cloned DNA fragment comprising a two-gene operon was isolated and expressed in Escherichia coli. One of the gene products was identified as a phospholipase A1, and the enzyme was found to be excreted to the outer environment from S. liquefaciens as well as from E. coli. Both genes were sequenced, and the relationship between open reading frames in the DNA sequence and in vitro-expressed polypeptides was established. The length of the phospholipase polypeptide was found to be 319 amino acids. In the amino-terminal end of the coding sequence was a stretch of about 20 hydrophobic amino acids, but, in contrast to consensus signal peptides, no basic residues were present. The length of the second polypeptide was 227 amino acids. It was found that expression of the phospholipase gene in both E. coli and S. liquefaciens was growth phase regulated (late expression).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boros I., Pósfai G., Venetianer P. High-copy-number derivatives of the plasmid cloning vector pBR322. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell N., Han Z., Moreno F., Kolter R. An E. coli promoter induced by the cessation of growth. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):195–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Beckwith J. Mechanism of incorporation of cell envelope proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:435–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton N. P. Improved plasmid vectors for the isolation of translational lac gene fusions. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Uhlén M., Josephson S., Gatenbeck S., Philipson L. An improved positive selection plasmid vector constructed by oligonucleotide mediated mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):8019–8030. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.8019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. Regulation of a membrane component required for protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. D. A method for the rapid, automated filtration of protein hydrolyzates. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):91–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90161-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Strycharz G. D., Nomura M., Lewis H., Dennis P. P. Nucleotide sequence of the ribosomal protein gene cluster adjacent to the gene for RNA polymerase subunit beta in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1697–1701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Export of protein in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):290–298. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.290-298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Benson S. A., Emr S. D. Mechanisms of protein localization. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):313–344. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.313-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K., Stahl S., Gilbert W. Eukaryotic signal sequence transports insulin antigen in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3369–3373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler U. K., Stuckmann M. Glycogen, hyaluronate, and some other polysaccharides greatly enhance the formation of exolipase by Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):663–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.663-670.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G. In vitro synthesis of protein in microbial systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:267–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Geus P., Verheij H. M., Riegman N. H., Hoekstra W. P., de Haas G. H. The pro- and mature forms of the E. coli K-12 outer membrane phospholipase A are identical. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1799–1802. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02048.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]