Abstract
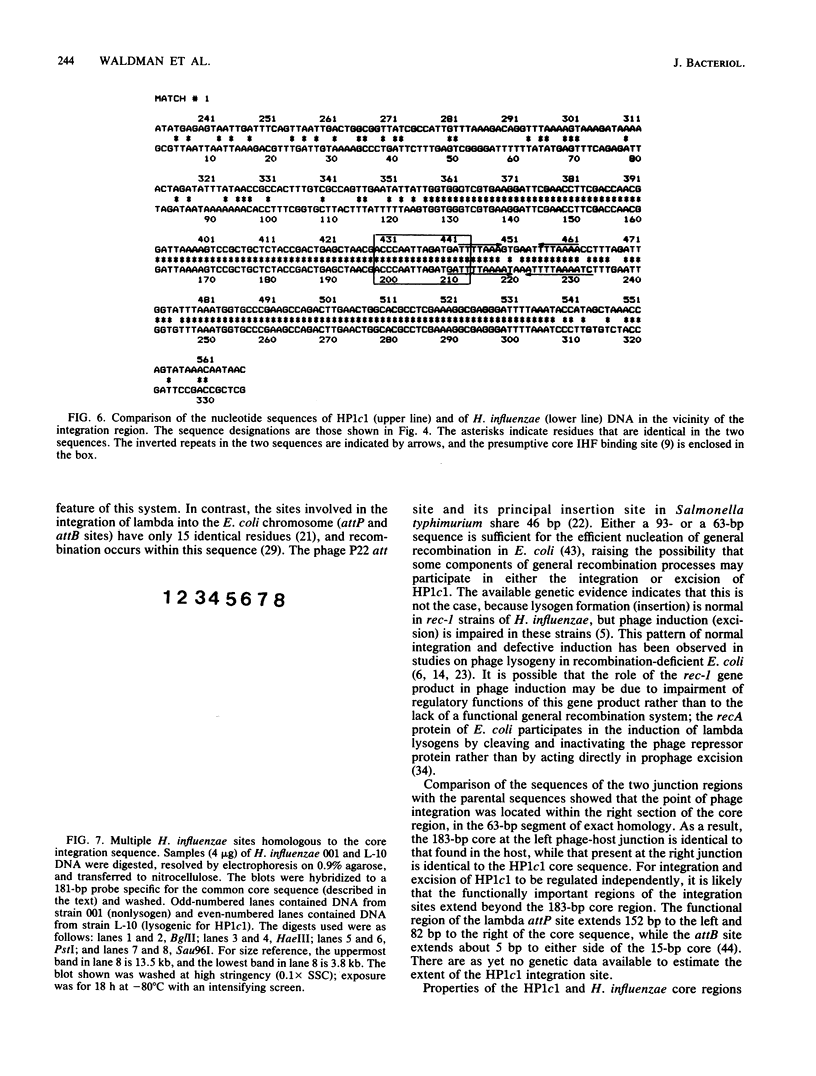
Bacteriophage HP1c1 lysogenizes its host Haemophilus influenzae Rd by inserting its genome into the bacterial chromosome. The DNA segments corresponding to the integration regions on the phage and host chromosomes and the two junctions formed between phage and host sequences on lysogenic insertion were isolated and propagated in Escherichia coli HB101 as hybrid plasmids by using pBR322 as the vector. The nucleotide sequences in the vicinity of the point of recombinational insertion were determined. Phage and host DNA shared an extensive, nearly identical, segment that was 183 base pairs long. This segment consisted of 93 identical residues and a 27-residue portion containing 6 mismatches, followed by 63 identical residues. Recombinational insertion occurred within the 63-residue identical segment and involved neither duplication nor deletion of any residues. Short inverted repeats consisting of clustered A-T base pairs were present within the two 27-residue segments. Two additional sites on the host chromosome showed significant hybridization to the phage-host homology region.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abremski K., Hoess R. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. Purification and properties of the Cre recombinase protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1509–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin S., Ziese M., Sternberg N. A novel role for site-specific recombination in maintenance of bacterial replicons. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Morrow J. F., Berg P. Cleavage of circular, superhelical simian virus 40 DNA to a linear duplex by S1 nuclease. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1303–1313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1303-1313.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin R. C., Fitzmaurice W. P., Huang P. C., Scocca J. J. Nucleotide sequence of cloned DNA segments of the Haemophilus influenzae bacteriophage HP1c1. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boling M. E., Setlow J. K. Dependence of Vegetative Recombination Among Haemophilus influenzae Bacteriophage on the Host Cell. J Virol. 1969 Sep;4(3):240–243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.3.240-243.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks K., Clark A. J. Behavior of lambda bacteriophage in a recombination deficienct strain of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):283–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.283-293.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calendar R., Lindahl G. Attachment of prophage P2: gene order at different host chromosomal sites. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):867–881. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. E. coli integration host factor binds to specific sites in DNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90478-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzmaurice W. P., Scocca J. J. Restriction map and location of mutations on the genome of bacteriophage Hp1c1 of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Gene. 1983 Sep;24(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzmaurice W. P., Waldman A. S., Benjamin R. C., Huang P. C., Scocca J. J. Nucleotide sequence and properties of the cohesive DNA termini from bacteriophage HP1c1 of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARM W., RUPERT C. S. INFECTION OF TRANSFORMABLE CELLS OF HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE BY BACTERIOPHAGE AND BACTERIOPHAGE DNA. Z Vererbungsl. 1963 Dec 30;94:336–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00897593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertman I., Luria S. E. Transduction studies on the role of a rec+ gene in the ultraviolet induction of prophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jan 28;23(2):117–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Ziese M., Sternberg N. P1 site-specific recombination: nucleotide sequence of the recombining sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3398–3402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Landy A. Resolution of synthetic att-site Holliday structures by the integrase protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):721–726. doi: 10.1038/311721a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLY B. Localization of P2 prophage in two strains of Escherichia coli. Virology. 1963 Jan;19:32–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Nash H. A. The bacteriophage lambda int gene product. A filter assay for genetic recombination, purification of int, and specific binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7149–7157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Ross W. Viral integration and excision: structure of the lambda att sites. Science. 1977 Sep 16;197(4309):1147–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.331474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Nunes-Düby S., Lesser C. F., Youderian P., Susskind M. M., Landy A. The phi 80 and P22 attachment sites. Primary structure and interaction with Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4468–4477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G. Multiple recombination mechanisms in bacteriophage P2. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):861–866. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens G., Hoffmann A., Blöcker H., Frank R., Kahmann R. Gin-mediated site-specific recombination in bacteriophage Mu DNA: overproduction of the protein and inversion in vitro. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2415–2421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Weisberg R., Enquist L., Mizuuchi M., Buraczynska M., Foeller C., Hsu P. L., Ross W., Landy A. Structure and function of the phage lambda att site: size, int-binding sites, and location of the crossover point. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):429–437. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda: the mechanism of conservation site specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:143–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkham J. L., Platt T., Enquist L. W., Weisberg R. A. The secondary attachment site for bacteriophage lambda in the proA/B gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 25;144(4):587–592. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Kanaar R., van de Putte P. A genetic switch in vitro: DNA inversion by Gin protein of phage Mu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2689–2692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W., Craig N. L. Escherichia coli recA gene product inactivates phage lambda repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4714–4718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Bacteriophage lambda int protein recognizes two classes of sequence in the phage att site: characterization of arm-type sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7724–7728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. Site-specific recombinases: changing partners and doing the twist. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.341-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scocca J. J., Poland R. L., Zoon K. C. Specificity in deoxyribonucleic acid uptake by transformable Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):369–373. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.369-373.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow J. K., Boling M. E., Beattie K. L., Kimball R. F. A complex of recombination and repair genes in Haemophilus influenzae. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 21;68(2):361–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuy J. H. Transfer of genetic information within a colony of Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.1-4.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman A. S., Fitzmaurice W. P., Scocca J. J. Integration of the bacteriophage HP1c1 genome into the Haemophilus influenzae Rd chromosome in the lysogenic state. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):297–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.297-300.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt V. M., Ingles C. J., Urdea M. S., Rutter W. J. Homology requirements for recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4768–4772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]