Abstract
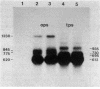
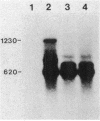
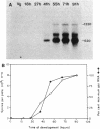
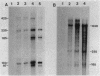
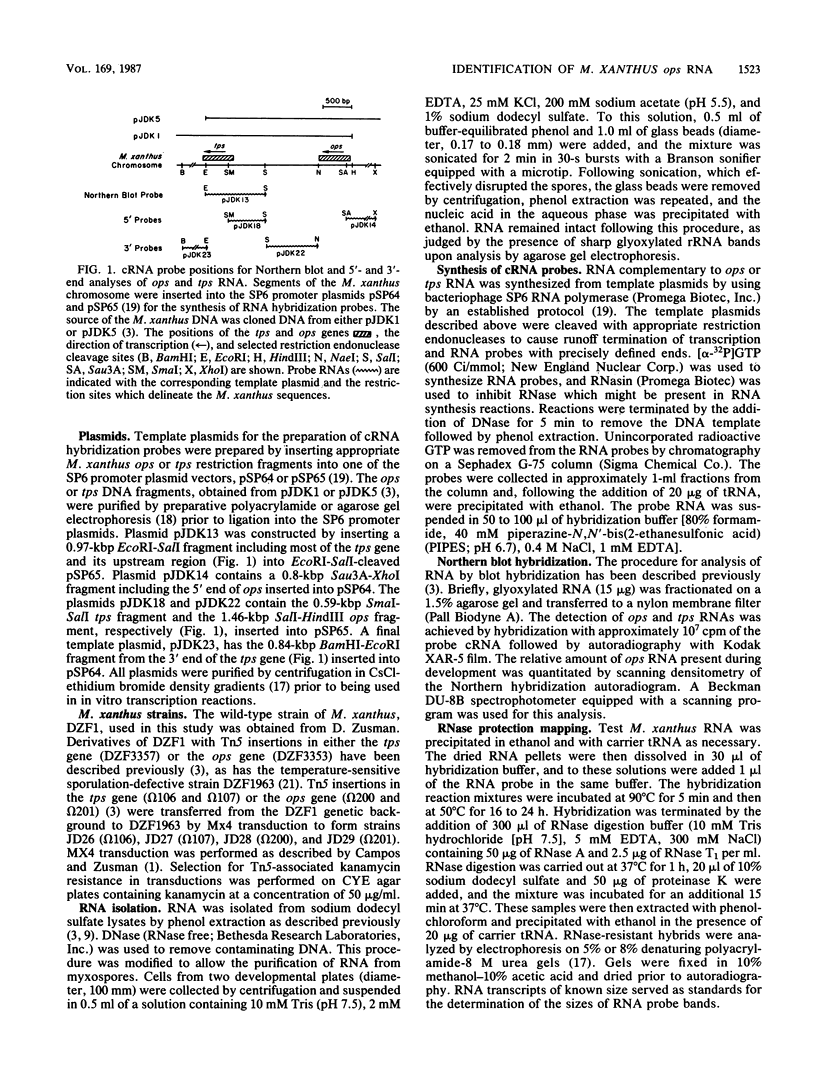
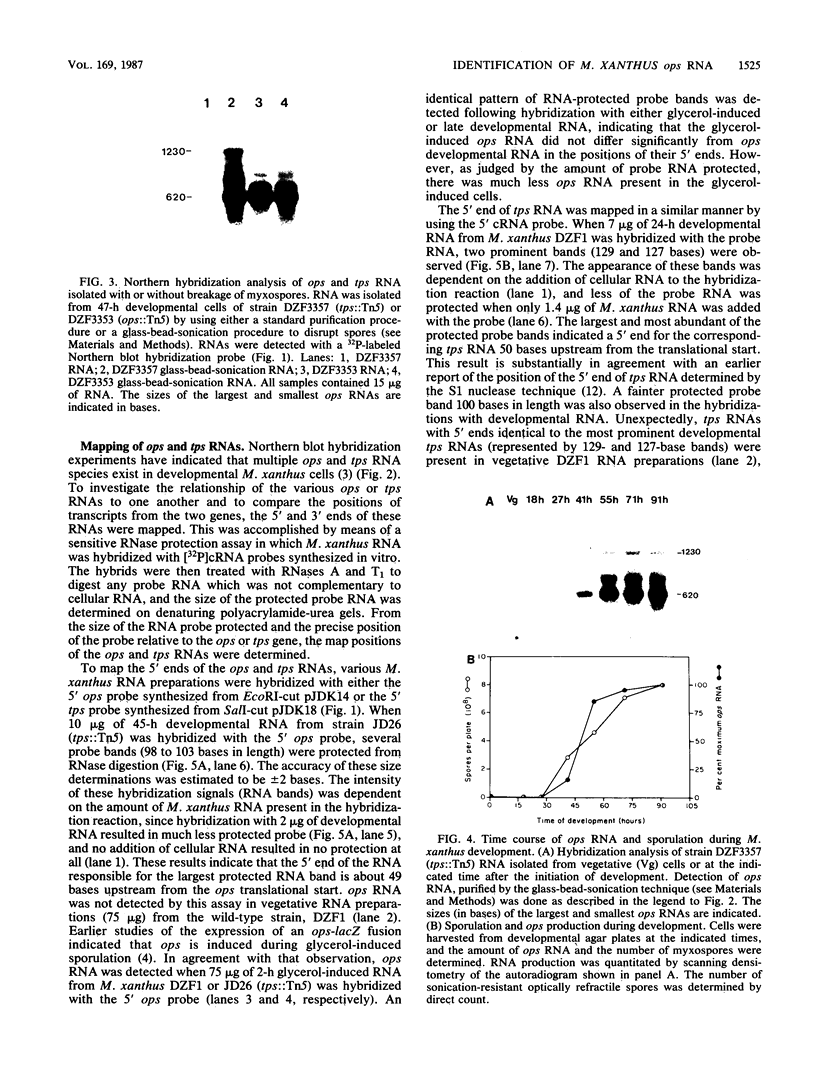
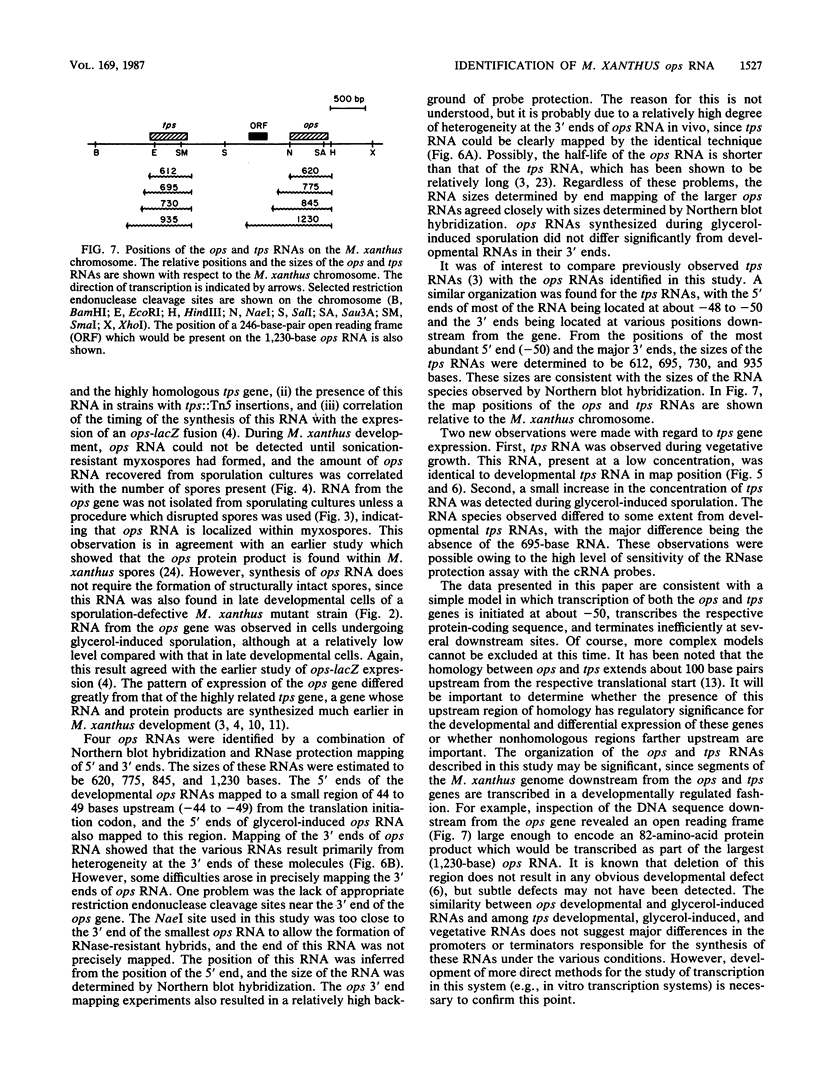
The expression of the ops gene, like that of the highly homologous and closely linked tps gene, is induced during development of the fruiting bacterium Myxococcus xanthus. The RNA products of the ops gene have been identified and compared with tps RNA. The ops RNA was observed in developmental cells only after spore formation had commenced, and it was necessary to use a sporulation-defective mutant strain or to disrupt spores to isolate this RNA. RNA from the ops gene was not observed in vegetative cells but was readily detected in cells subjected to glycerol-induced sporulation. In contrast, a large amount of developmental tps RNA was observed in cells well before sporulation had occurred; low levels of tps RNA were observed in vegetative cells; and only a slight increase in tps RNA was found during glycerol-induced sporulation. Several ops and tps RNAs were observed in this study, and the positions of these RNAs were mapped on the M. xanthus genome. The 5' ends of both the ops and tps RNAs mapped predominantly to positions about 50 bases upstream from the respective translational initiation sites. The 3' ends of RNAs from both genes were heterogeneous. The four ops RNAs were 620, 775, 845, and 1,230 bases in length, while the tps RNAs were 612, 695, 730, and 935 bases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campos J. M., Geisselsoder J., Zusman D. R. Isolation of bacteriophage MX4, a generalized transducing phage for Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M., Zusman D. R. Myxobacterial hemagglutinin: a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5505–5509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., GIBSON S. M. A SYSTEM FOR STUDYING MICROBIAL MORPHOGENESIS: RAPID FORMATION OF MICROCYSTS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. Science. 1964 Oct 9;146(3641):243–244. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3641.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Kupfer D., Zusman D. R. Gene expression during development of Myxococcus xanthus. Analysis of the genes for protein S. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 5;175(4):469–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downard J. S., Zusman D. R. Differential expression of protein S genes during Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1146–1155. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1146-1155.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Komano T., Inouye M., Inouye S. Functional complementation between the two homologous genes, ops and tps, during differentiation of Myxococcus xanthus. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(3):434–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00330755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R. E., Cull M. G. Control of developmental gene expression by cell-to-cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.341-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F., Young E. T. Regulation of synthesis of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme mRNA. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):231–241. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Gene expression during development of Myxococcus xanthus: pattern of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Franceschini T., Inouye M. Structural similarities between the development-specific protein S from a gram-negative bacterium, Myxococcus xanthus, and calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6829–6833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Harada W., Zusman D., Inouye M. Development-specific protein S of Myxococcus xanthus: purification and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):678–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.678-683.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S. Identification of a development-specific promoter of Myxococcus xanthus. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90367-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Ike Y., Inouye M. Tandem repeat of the genes for protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):38–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Manoil C., Dworkin M. Myxobacteria: cell interactions, genetics, and development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:595–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison C. E., Zusman D. R. Myxococcus xanthus mutants with temperature-sensitive, stage-specific defects: evidence for independent pathways in development. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1036–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1036-1042.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zusman D. R. Evidence for long-lived mRNA during fruiting body formation in myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1467–1471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zusman D. R. Transport and localization of protein S, a spore coat protein, during fruiting body formation by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):547–553. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.547-553.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teintze M., Thomas R., Furuichi T., Inouye M., Inouye S. Two homologous genes coding for spore-specific proteins are expressed at different times during development of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):121–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.121-125.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]