Abstract
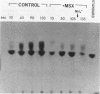
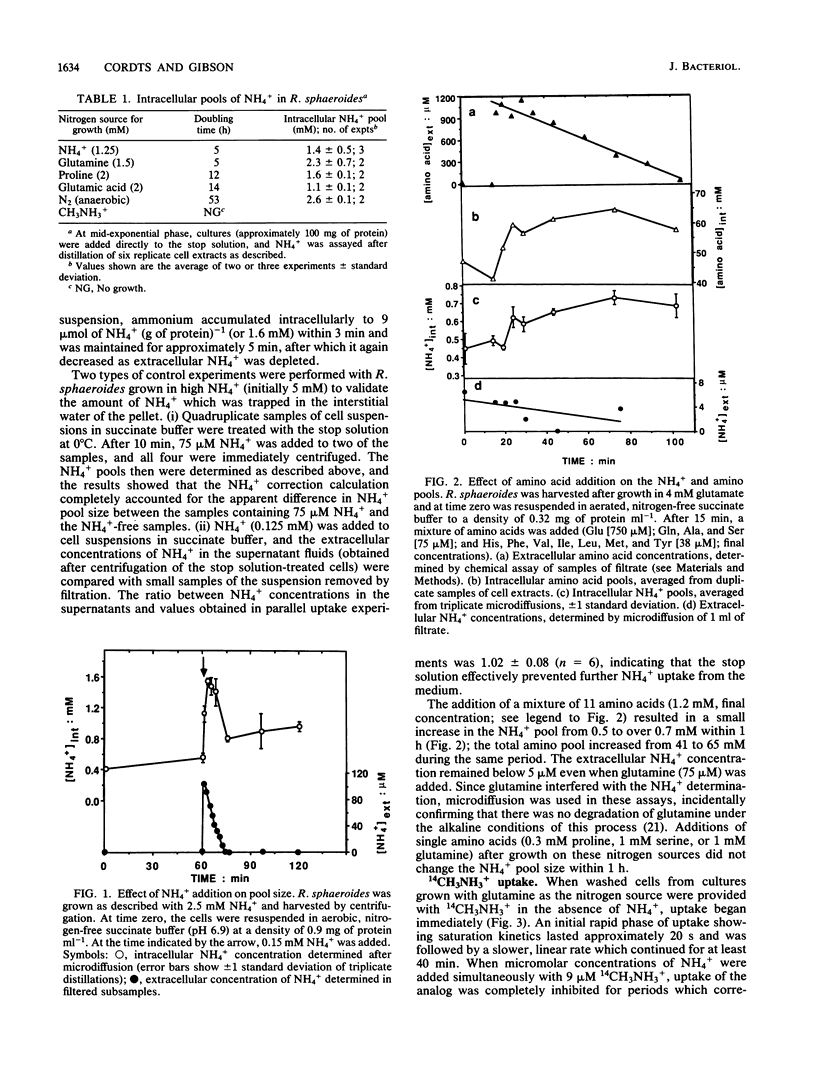
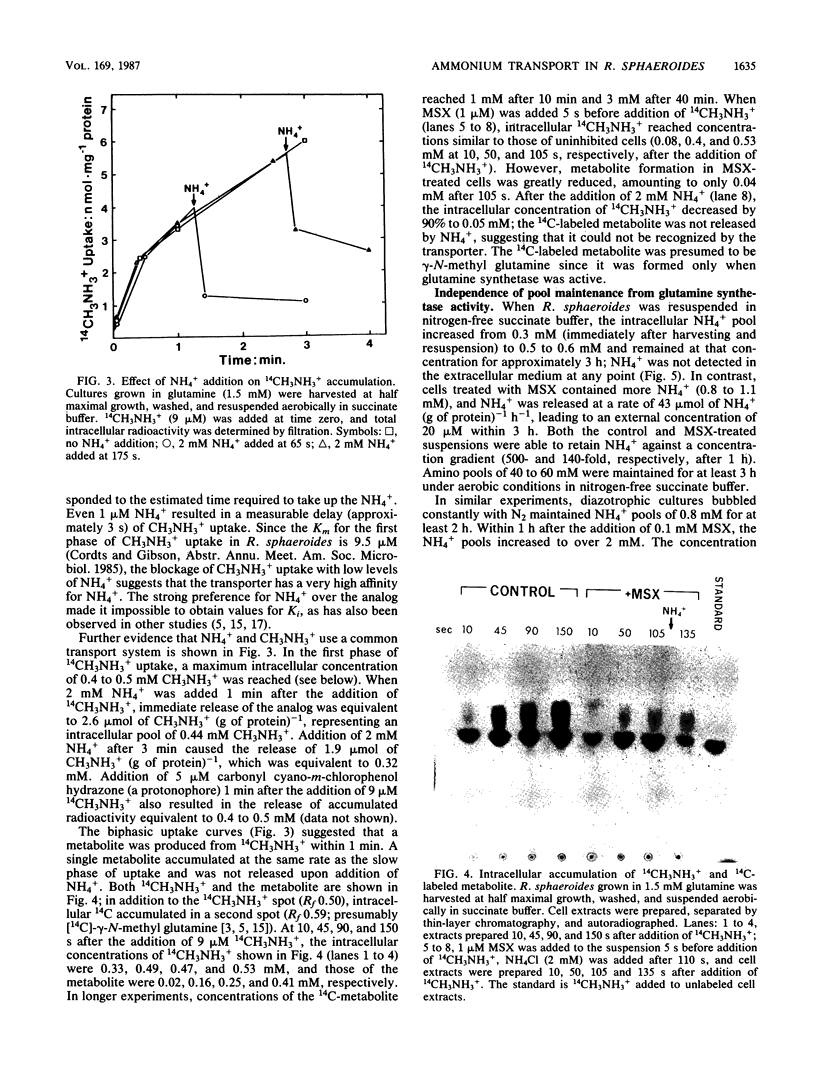
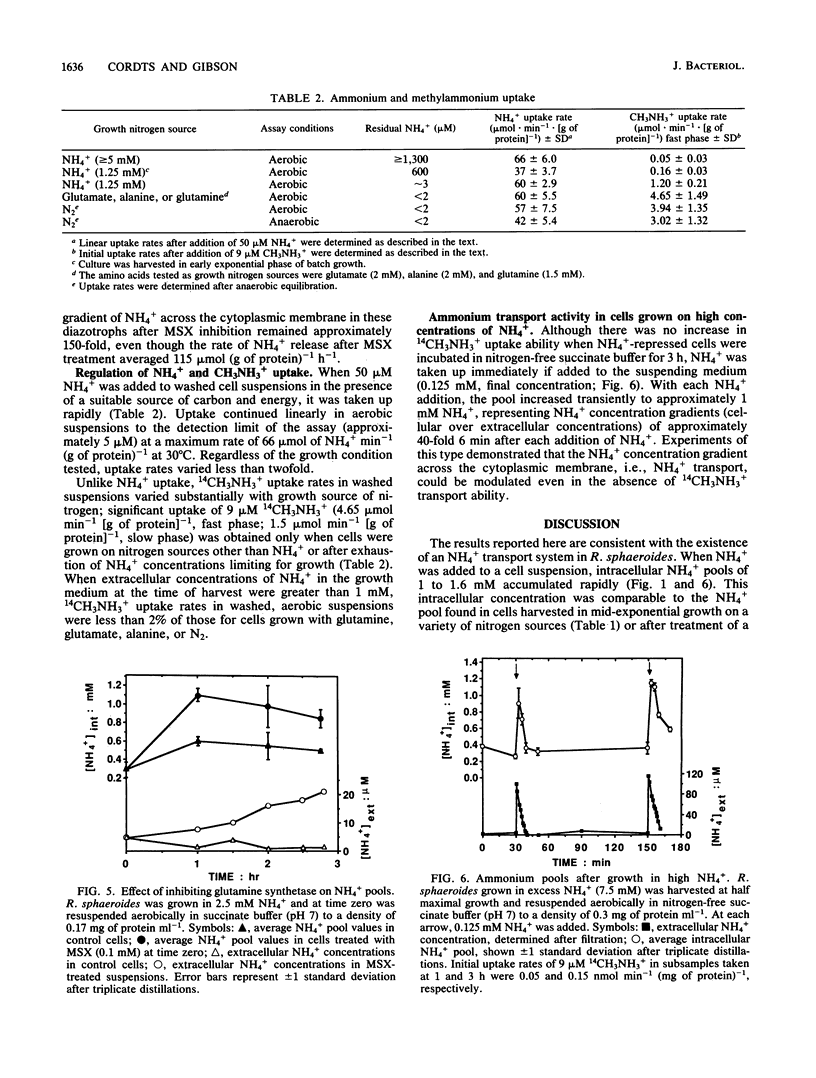
Rhodobacter sphaeroides maintained intracellular ammonium pools of 1.1 to 2.6 mM during growth in several fixed nitrogen sources as well as during diazotrophic growth. Addition of 0.15 mM NH4+ to washed, nitrogen-free cell suspensions was followed by linear uptake of NH4+ from the medium and transient formation of intracellular pools of 0.9 to 1.5 mM NH4+. Transport of NH4+ was shown to be independent of assimilation by glutamine synthetase because intracellular pools of over 1 mM represented NH4+ concentration gradients of at least 100-fold across the cytoplasmic membrane. Ammonium pools of over 1 mM were also found in non-growing cell suspensions in nitrogen-free medium after glutamine synthetase was inhibited with methionine sulfoximine. In NH4+-free cell suspensions, methylammonium (14CH3NH3+) was taken up rapidly, and intracellular concentrations of 0.4 to 0.5 mM were maintained. The 14CH3NH3+ pool was not affected by methionine sulfoximine. Unlike NH4+ uptake, 14CH3NH3+ uptake in nitrogen-free cell suspensions was repressed by growth in NH4+. These results suggest that R. sphaeroides may produce an NH4+-specific transport system in addition to the NH4+/14CH3NH3+ transporter. This second transporter is able to produce normal-size NH4+ pools but has very little affinity for 14CH3NH3+ and is not repressed by growth in high concentrations of NH4+.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Zimniak P., Jayakumar A. Role of glutamine synthetase in the uptake and metabolism of methylammonium by Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):752–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.752-757.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Zimniak P. Transport of ammonium and methylammonium ions by Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):512–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.512-516.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellion E., Wayland L. Methylamine uptake in Pseudomonas species strain MA: utilization of methylamine as the sole nitrogen source. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):395–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.395-398.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boussiba S., Dilling W., Gibson J. Methylammonium transport in Anacystis nidulans R-2. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):204–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.204-210.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drozd J. W., Tubb R. S., Postgate J. R. A chemostat study of the effect of fixed nitrogen sources on nitrogen fixation, membranes and free amino acids in Azotobacter chroococcum. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(2):221–232. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensslen R. E., McCarty R. E. Determination of solute accumulation in chloroplasts by rapid centrifugal transfer through silicone fluid layers. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):504–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Kashket E. R. Methylammonium uptake by Rhizobium sp. strain 32H1. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1196–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1196-1201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. K., Moore R. A. Ammonium and methylammonium transport by the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):435–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.435-442.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar A., Epstein W., Barnes E. M., Jr Characterization of ammonium (methylammonium)/potassium antiport in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7528–7532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Donohue T. J., Corrigan M. G., Bernlohr R. W. A new and specific assay for ammonia and glutamine sensitive to 100 pmol. Anal Biochem. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D., Alef K., Hartmann A. Uptake of methionine sulfoximine by some N2 fixing bacteria, and its effect on ammonium transport. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. Ammonium uptake by nitrogen fixing bacteria I. Azotobacter vinelandii. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 22;104(2):163–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00447319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. Energy expenditure for cyclic retention of NH3/NH4+ during N2 fixation by Klebsiella pneumoniae. FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 5;187(2):237–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H. Second system for potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):506–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.506-511.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN H. A modified ninhydrin colorimetric analysis for amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. A requirement for sodium in the growth of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Jun;22:778–785. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-3-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier H. J., Smith T. M., Bernlohr R. W. Regulation of nitrogen catabolic enzymes in Bacillus spp. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):971–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.971-975.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turpin D. H., Edie S. A., Canvin D. T. In Vivo Nitrogenase Regulation by Ammonium and Methylamine and the Effect of MSX on Ammonium Transport in Anabaena flos-aquae. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):701–704. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]