Abstract
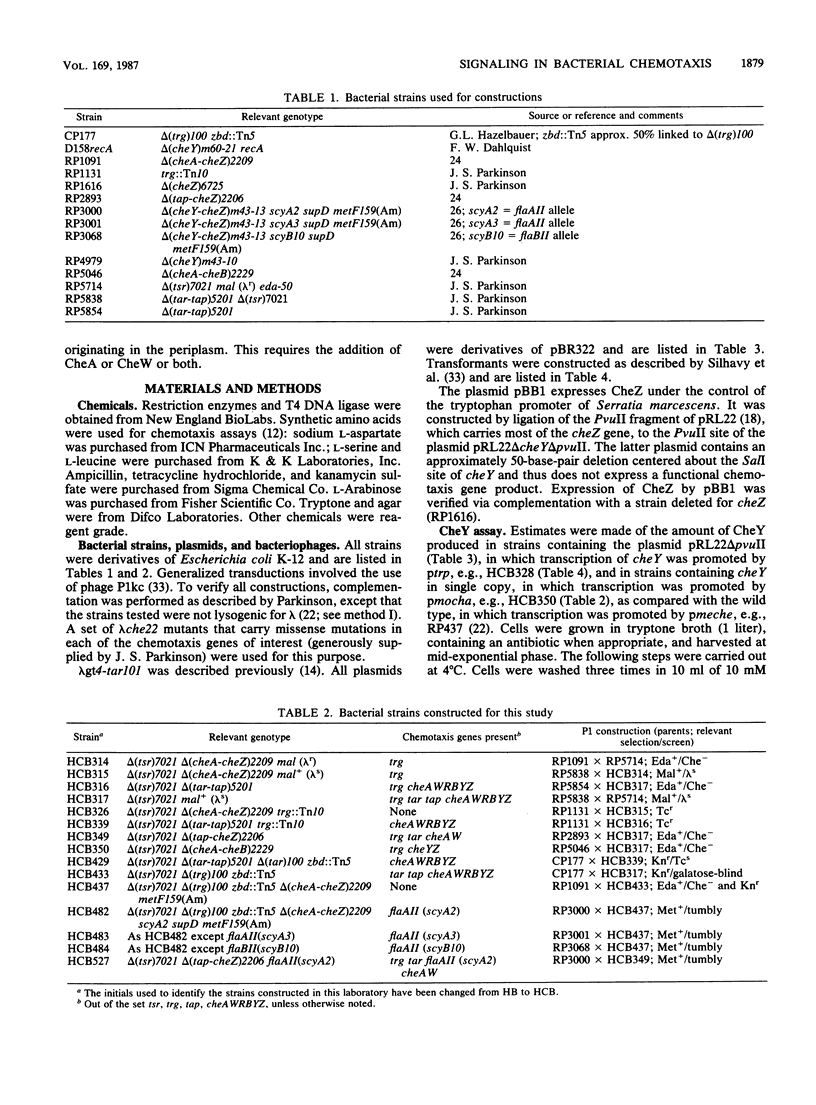
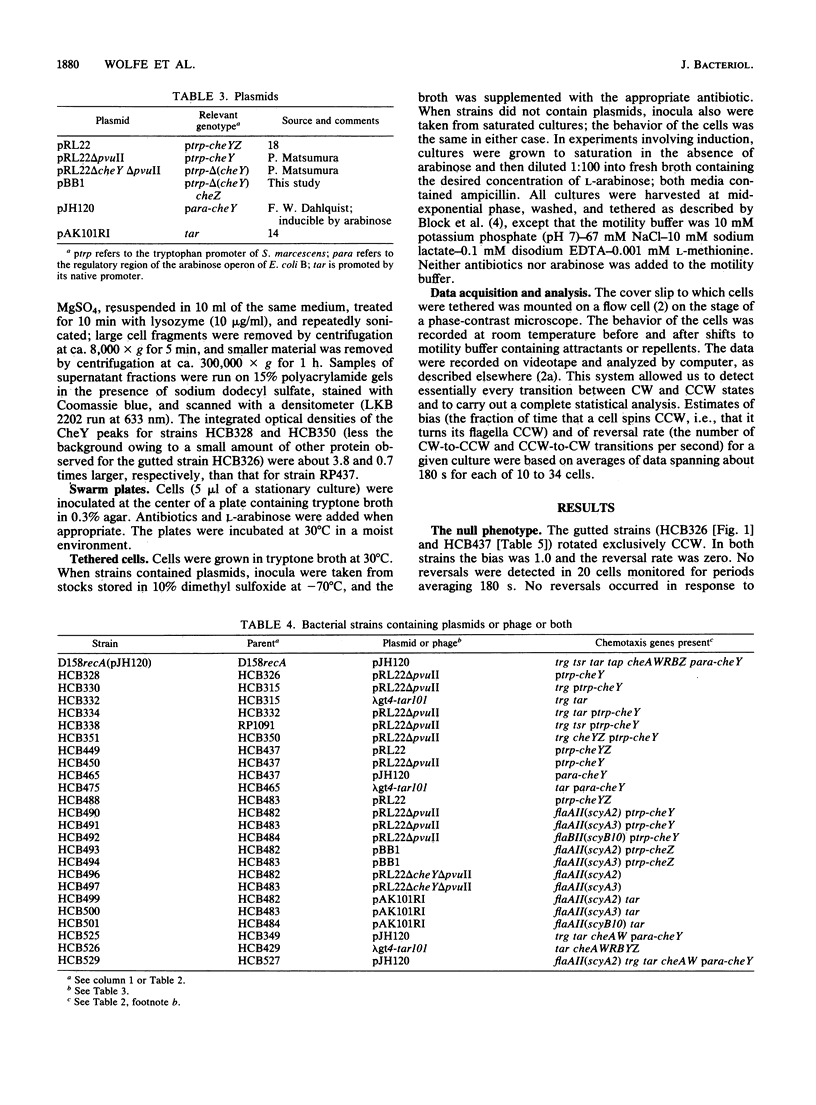
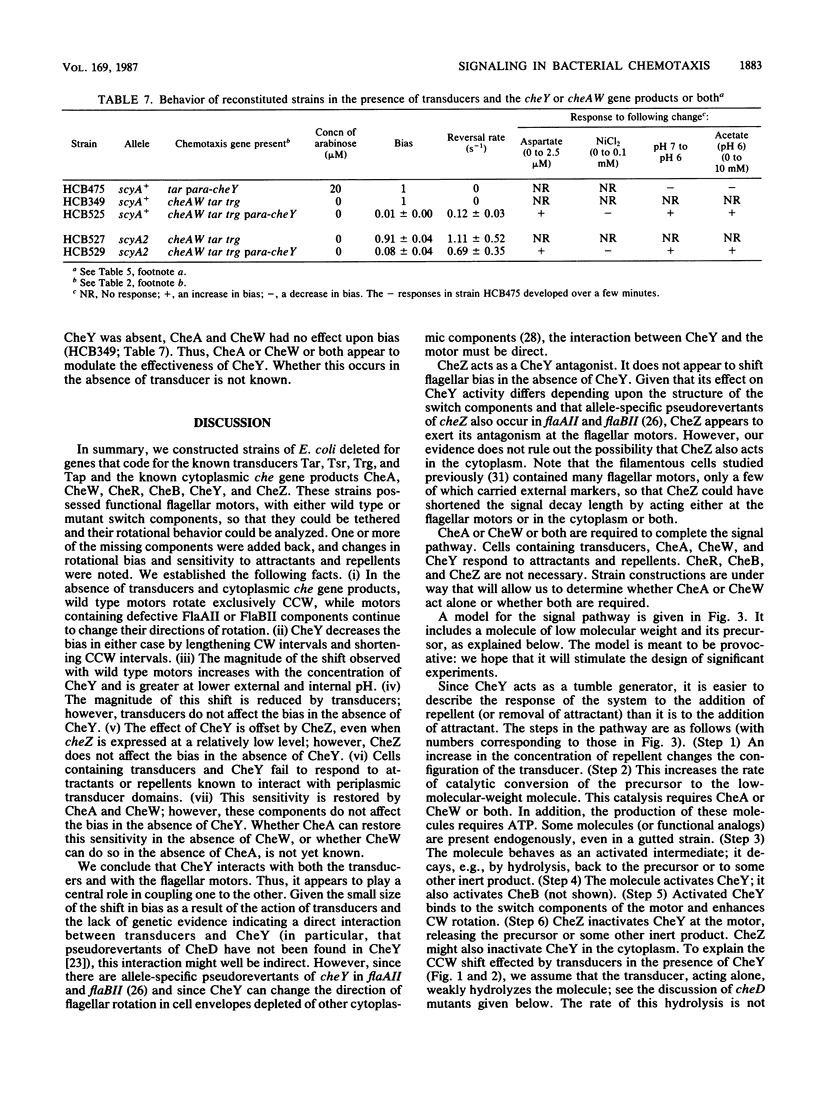
Strains missing several genes required for chemotaxis toward amino acids, peptides, and certain sugars were tethered and their rotational behavior was analyzed. Null strains (called gutted) were deleted for genes that code for the transducers Tsr, Tar, Tap, and Trg and for the cytoplasmic proteins CheA, CheW, CheR, CheB, CheY, and CheZ. Motor switch components were wild type, flaAII(cheC), or flaBII(cheV). Gutted cells with wild-type motors spun exclusively counterclockwise, while those with mutant motors changed their directions of rotation. CheY reduced the bias (the fraction of time that cells spun counterclockwise) in either case. CheZ offset the effect of CheY to an extent that varied with switch allele but did not change the bias when tested alone. Transducers also increased the bias in the presence of CheY but not when tested alone. However, cells containing transducers and CheY failed to respond to attractants or repellents normally detected in the periplasm. This sensitivity was restored by addition of CheA and CheW. Thus, CheY both enhances clockwise rotation and couples the transducers to the flagella. CheZ acts, at the level of the motor, as a CheY antagonist. CheA or CheW or both are required to complete the signal pathway. A model is presented that explains these results and is consistent with other data found in the literature.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. Chemoreceptors in bacteria. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1588–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Block S. M. A miniature flow cell designed for rapid exchange of media under high-power microscope objectives. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Nov;130(11):2915–2920. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-11-2915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. M., Segall J. E., Berg H. C. Adaptation kinetics in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):312–323. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.312-323.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. M., Segall J. E., Berg H. C. Impulse responses in bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90421-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan A. M., Parkinson J. S. Genetics of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli: cheD mutations affect the structure and function of the Tsr transducer. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):96–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.96-104.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Koshland D. E., Jr Membrane receptors for aspartate and serine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9695–9702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg D. O., Koshland D. E., Jr The role of a signaling protein in bacterial sensing: behavioral effects of increased gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Molecular cloning of chemotaxis genes and overproduction of gene products in the bacterial sensing system. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):390–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.390-400.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S. Sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;81:33–70. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedblom M. L., Adler J. Chemotactic response of Escherichia coli to chemically synthesized amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1463–1466. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1463-1466.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M. R., Doak T. G., Dahlquist F. W. Aberrant regulation of methylesterase activity in cheD chemotaxis mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):105–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.105-112.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Conley M. P., Boyd A., Berg H. C., Simon M. I. Chimeric chemosensory transducers of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1326–1330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Ornston M. K. Normal-to-curly flagellar transitions and their role in bacterial tumbling. Stabilization of an alternative quaternary structure by mechanical force. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 5;112(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Blank V., Brade G., Higgins C. F. Peptide chemotaxis in E. coli involves the Tap signal transducer and the dipeptide permease. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):253–256. doi: 10.1038/321253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Kort E. N., Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Attraction by repellents: an error in sensory information processing by bacterial mutants. Science. 1978 Jul 7;201(4350):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.351803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh N., Oosawa K., Simon M. I. Characterization of Escherichia coli chemotaxis receptor mutants with null phenotypes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):992–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.992-998.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Complementation analysis and deletion mapping of Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.45-53.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Houts S. E. Isolation and behavior of Escherichia coli deletion mutants lacking chemotaxis functions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Parker S. R. Interaction of the cheC and cheZ gene products is required for chemotactic behavior in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2390–2394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Parker S. R., Talbert P. B., Houts S. E. Interactions between chemotaxis genes and flagellar genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.265-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. cheA, cheB, and cheC genes of Escherichia coli and their role in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):758–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.758-770.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Eisenbach M. Direction of flagellar rotation in bacterial cell envelopes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):222–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.222-230.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Matsumura P., Eisenbach M. Restoration of flagellar clockwise rotation in bacterial envelopes by insertion of the chemotaxis protein CheY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reader R. W., Tso W. W., Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Pleiotropic aspartate taxis and serine taxis mutants of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Apr;111(2):363–374. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-2-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Block S. M., Berg H. C. Temporal comparisons in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8987–8991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Ishihara A., Berg H. C. Chemotactic signaling in filamentous cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):51–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.51-59.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioi J. I., Galloway R. J., Niwano M., Chinnock R. E., Taylor B. L. Requirement of ATP in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7969–7975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simms S. A., Keane M. G., Stock J. Multiple forms of the CheB methylesterase in bacterial chemosensing. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10161–10168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Parkinson J. S. Overlapping genes at the cheA locus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5370–5374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Zanolari B. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: regulation of the demethylation rate by the CheA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5061–5065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A., Koshland D. E., Jr, Stock J. Homologies between the Salmonella typhimurium CheY protein and proteins involved in the regulation of chemotaxis, membrane protein synthesis, and sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7989–7993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Receptor structure in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


