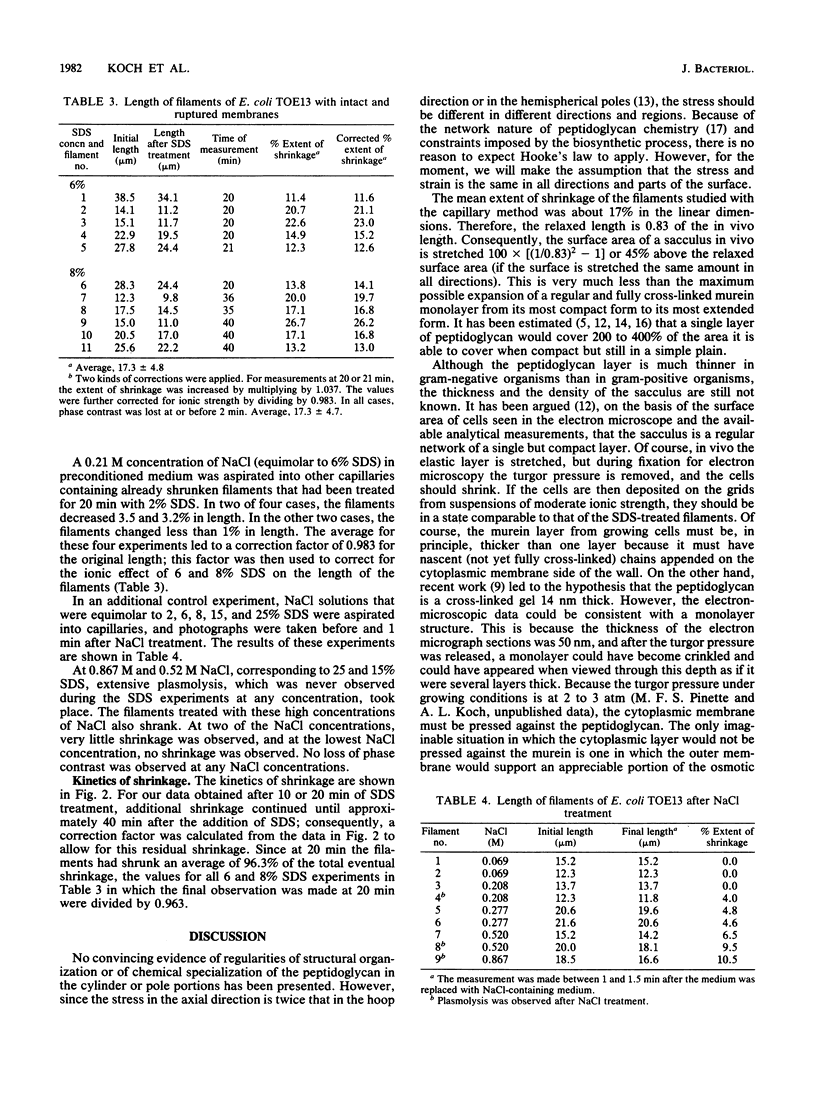
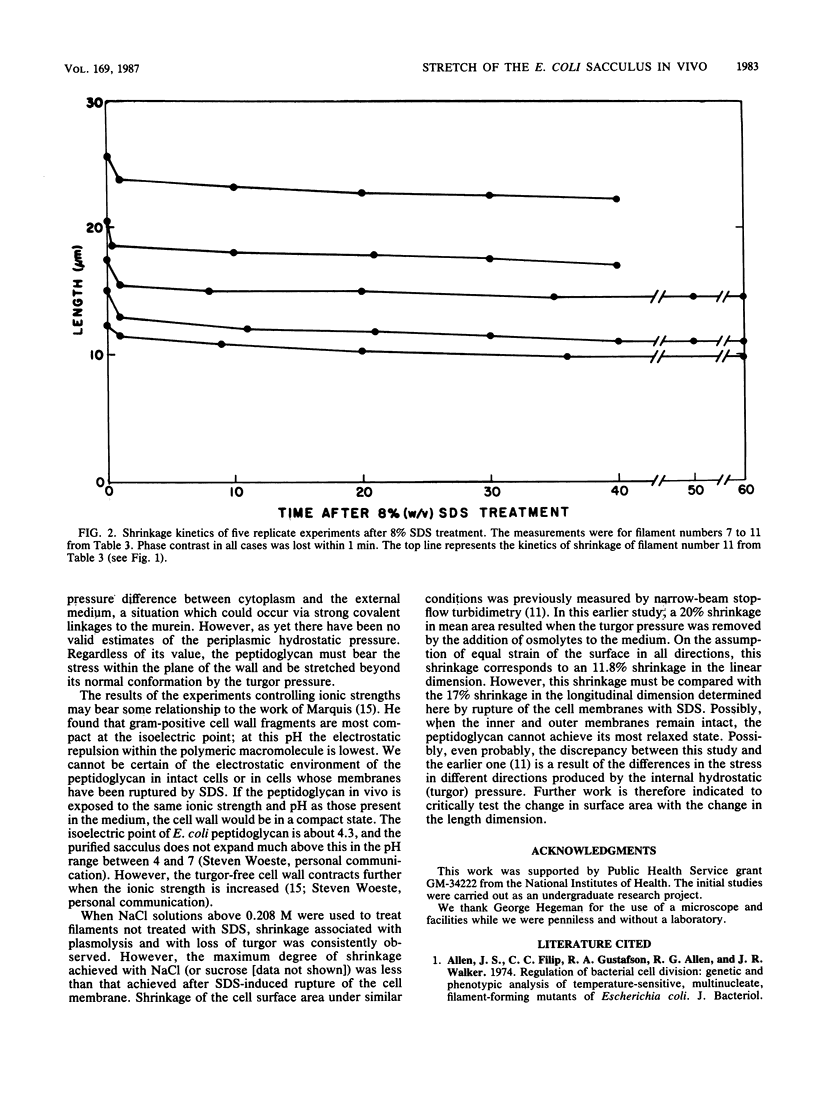
Abstract
The osmotic pressure within a living bacterium creates stresses in the peptidoglycan that stretch the sacculus. We measured the amount of stretch by monitoring the shrinkage of growing cells of Escherichia coli after removal of the osmotic pressure by disruption of the phospholipid membranes with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Because the rods of the wild type are so short, length changes of filaments of longer than 7 microns were measured on phase-contrast micrographs. The filaments were prepared by growing ftsA and ftsI strains under permissive conditions in rich medium and then shifting them to 42 degrees C for 40 to 180 min. During this time, the mutant cells became elongated but did not divide. The growing filaments were mounted on a glass surface that had been treated with poly-L-lysine or RNase. The filaments were photographed before being treated with sodium dodecyl sulfate. The filaments were rephotographed at the time when the first change in phase contrast was noted. Some filaments were also measured at 10-min time intervals from 0 to 60 min. The reduction in phase contrast signaled the leakage of solutes and the loss of turgor pressure. The average length of the filaments decreased 17%. If the circumference were stretched to the same degree, then the surface area in vivo would be 45% greater than in the relaxed state. For comparison, a fully cross-linked monolayer of E. coli peptidoglycan in its most compact conformation could stretch up to 300% in achieving the most extended conformation possible without splitting covalent bonds.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begg K. J., Donachie W. D. Cell shape and division in Escherichia coli: experiments with shape and division mutants. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):615–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.615-622.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begg K. J., Hatfull G. F., Donachie W. D. Identification of new genes in a cell envelope-cell division gene cluster of Escherichia coli: cell division gene ftsQ. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.435-437.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V. Covalent lipoprotein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 31;415(3):335–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Gnirke H., Henning U., Rehn K. Model for the structure of the shape-maintaining layer of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1264–1270. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1264-1270.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formanek H., Formanek S., Wawra H. A three-dimensional atomic model of the murein layer of bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 15;46(2):279–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Kellenberger E. Periplasmic gel: new concept resulting from the reinvestigation of bacterial cell envelope ultrastructure by new methods. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.143-152.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L., Burdett I. D. The variable T model for gram-negative morphology. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Sep;130(9):2325–2338. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-9-2325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L., Higgins M. L., Doyle R. J. The role of surface stress in the morphology of microbes. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 May;128(5):927–945. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-5-927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Shrinkage of growing Escherichia coli cells by osmotic challenge. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):919–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.919-924.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labischinski H., Barnickel G., Bradaczek H., Giesbrecht P. On the secondary and tertiary structure of murein. Low and medium-angle X-ray evidence against chitin-based conformations of bacterial peptidoglycan. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar 15;95(1):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis R. E. Salt-induced contraction of bacterial cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):775–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.775-781.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldmixon E. H., Glauser S., Higgins M. L. Two proposed general configurations for bacterial cell wall peptidoglycans shown by space-filling molecular models. Biopolymers. 1974;13(10):2037–2060. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360131008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. R., Kovarik A., Allen J. S., Gustafson R. A. Regulation of bacterial cell division: temperature-sensitive mutants of Escherichia coli that are defective in septum formation. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):693–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.693-703.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]