Abstract
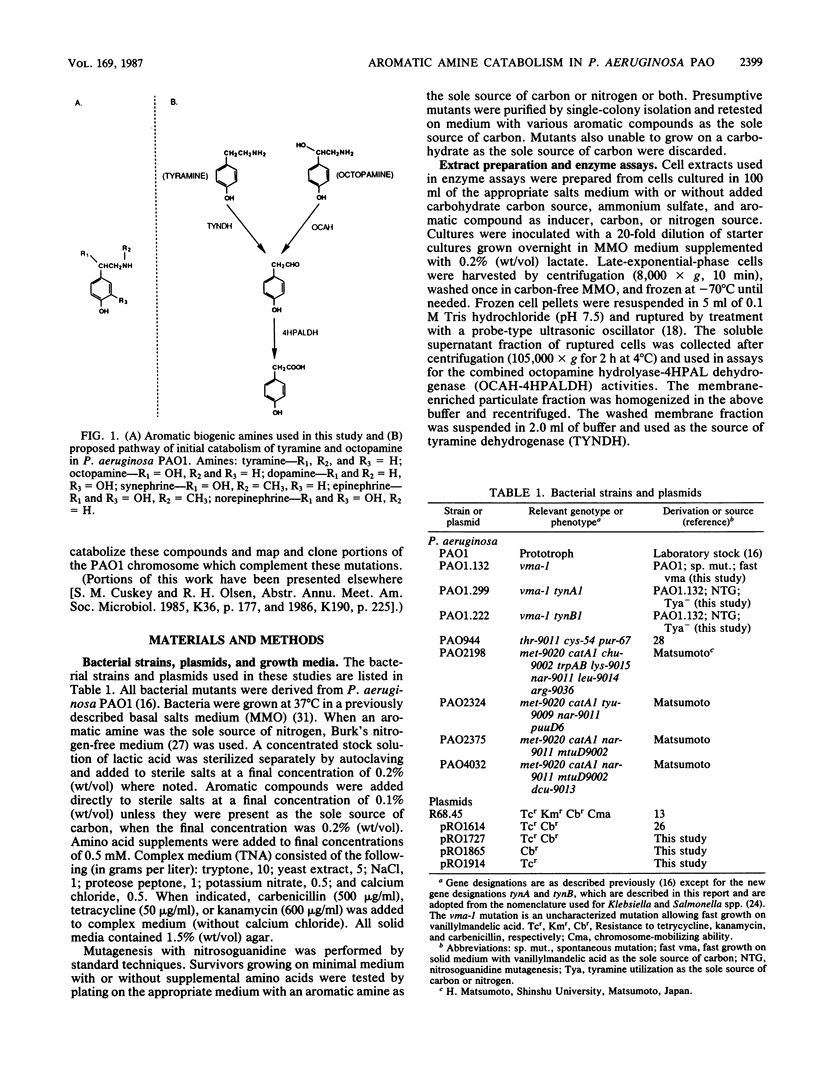
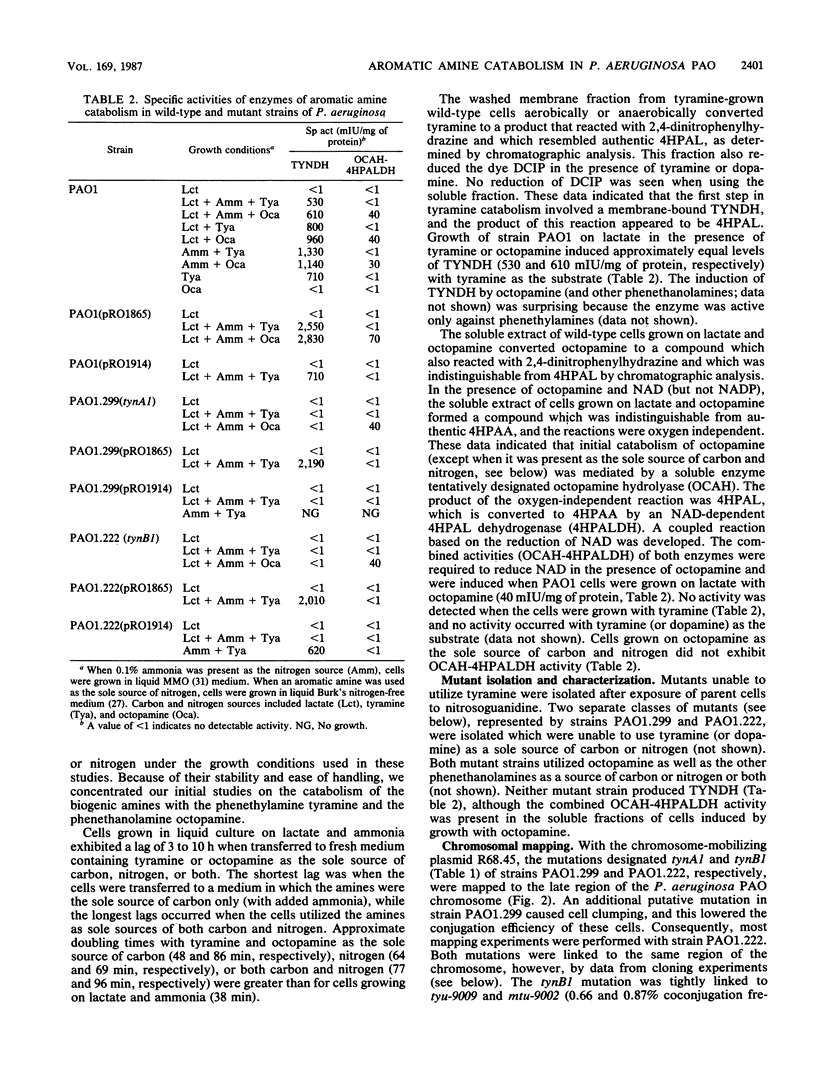
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 was able to utilize several aromatic biogenic amines as sole sources of carbon or nitrogen. These included the phenethylamines tyramine and dopamine and the phenethanolamines octopamine, synephrine, and norepinephrine. Initial catabolism of the phenethylamines was mediated by a membrane-bound tyramine dehydrogenase which produced 4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (4HPAL) with tyramine as the substrate. The enzyme was induced by growth with both classes of amines. Initial catabolism of octopamine (except when present as the sole source of carbon and nitrogen) was mediated by a soluble enzyme with activity against the phenethanolamines but not against tyramine or dopamine. The product of the reaction with octopamine as substrate was also 4HPAL. Addition of NAD to reaction mixtures yielded 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid and NADH. These activities, octopamine hydrolyase and 4-HPAL dehydrogenase (measured as a combined activity, OCAH-4HPALDH), were only induced by growth with phenethanolamines. However, the combined activities were not observed in extracts from cells grown with octopamine as the sole source of carbon and nitrogen, suggesting that an alternate pathway is used under this growth condition. Two independently isolated mutant strains were unable to utilize tyramine as a sole source of carbon or nitrogen. These mutants were also unable to utilize dopamine but grew at wild-type rates on the phenethanolamines. The mutations were mapped at about 70 min on the PAO1 chromosome with the chromosome-mobilizing plasmid R68.45, and both were linked to the catA1, mtu-9002, tyu-9009, and puuE mutations. DNA complementing both of the mutations was cloned on a single BamHI fragment approximately 13.8 kilobase pairs in length. Analysis of a subcloned fragment showed that the two mutations were in different genes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG J. M. THE MOLAR EXTINCTION COEFFICIENT OF 2,6-DICHLOROPHENOL INDOPHENOL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 4;86:194–197. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakley E. R. Microbial conversion of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid to homogentisic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Aug;18(8):1247–1255. doi: 10.1139/m72-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Skinner M. A. Catabolism of 3- and 4-hydroxyphenylacetate by the 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):302–306. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.302-306.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuskey S. M., Wolff J. A., Phibbs P. V., Jr, Olsen R. H. Cloning of genes specifying carbohydrate catabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):865–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.865-871.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi N. A., Kutty R. K., Vasantharajan V. N., Subba RAO P. V. Microbial metabolism of phenolic amines: degradation of dl-synephrine by an unidentified arthrobacter. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):866–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.866-873.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham D. R., Perry J. J. Purification and characterization of a heme-containing amine dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):837–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.837-843.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D. Genetic aspects of biodegradation by pseudomonads. Experientia. 1983 Nov 15;39(11):1199–1213. doi: 10.1007/BF01990357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Holloway B. W. R factor variants with enhanced sex factor activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 30;144(3):243–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00341722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Matsumoto H., Moretti P., Stalon V., Mercenier A. Arginine degradation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants blocked in two arginine catabolic pathways. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(3):437–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00382081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hareland W. A., Crawford R. L., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Metabolic function and properties of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 1-hydroxylase from Pseudomonas acidovorans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):272–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.272-285.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Independent regulation of hexose catabolizing enzymes and glucose transport activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1041–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90813-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki M., Yagi T., Horiike K., Saeki Y., Ushijima T., Nozaki M. Crystallization and properties of aromatic amine dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas sp. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jan;220(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutty R. K., Devi N. A., Veeraswamy M., Ramesh S., Rao P. V. Degradation of (+/-)-synephrine by Arthrobacter synephrinum. Oxidation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate to 2-hydroxy-5-carboxymethyl-muconate semialdehyde. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):163–170. doi: 10.1042/bj1670163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKI Y., ITSUNO Y., TAKESHITA M., MIYATA S., TANAKA S. STUDIES ON BACTERIAL MONOAMINE OXIDASE. Kumamoto Med J. 1964 Jun 30;17:90–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murooka Y., Doi N., Harada T. Distribution of membrane-bound monoamine oxidase in bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Oct;38(4):565–569. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.4.565-569.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murooka Y., Harada T. Regulation of derepressed synthesis of arylsulfatase by tyramine oxidase in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):796–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.796-802.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murooka Y., Higashiura T., Harada T. Genetic mapping of tyramine oxidase and arylsulfatase genes and their regulation in intergeneric hybrids of enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):714–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.714-722.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura H., Murooka Y., Harada T. Regulation of tyramine oxidase synthesis in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):24–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.24-31.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., DeBusscher G., McCombie W. R. Development of broad-host-range vectors and gene banks: self-cloning of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):60–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.60-69.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page W. J., Sadoff H. L. Physiological factors affecting transformation of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1080–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1080-1087.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royle P. L., Matsumoto H., Holloway B. W. Genetic circularity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):145–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.145-155.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparnins V. L., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Bacterial degradation of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid and homoprotocatechuic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):159–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.159-167.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veeraswamy M., Devi N. A., Kutty R. K., Rao P. V. Conversion of (+/-)-synephrine into p-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde by Arthrobacter synephrinum. A novel enzymic reaction. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):807–809. doi: 10.1042/bj1590807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelis L. The genetics of dissimilarity pathways in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:505–524. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


