Abstract
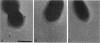
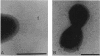
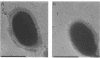
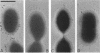
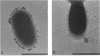
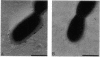
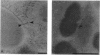
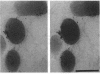
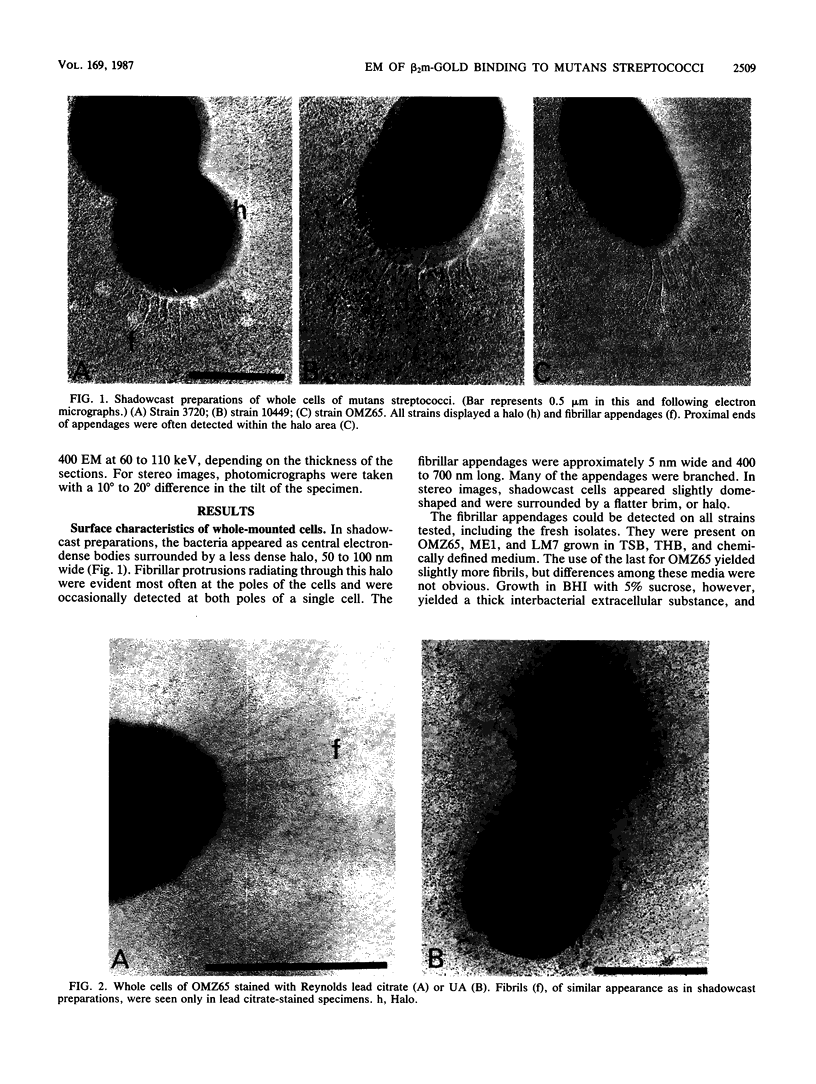
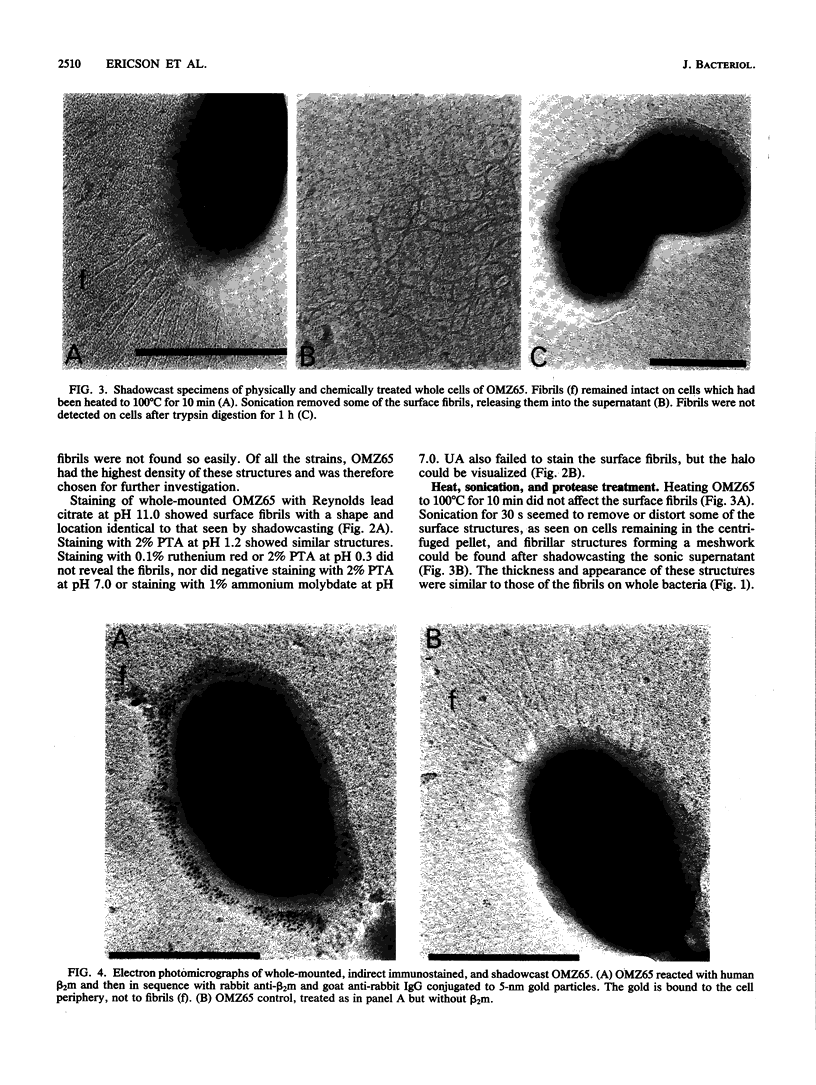
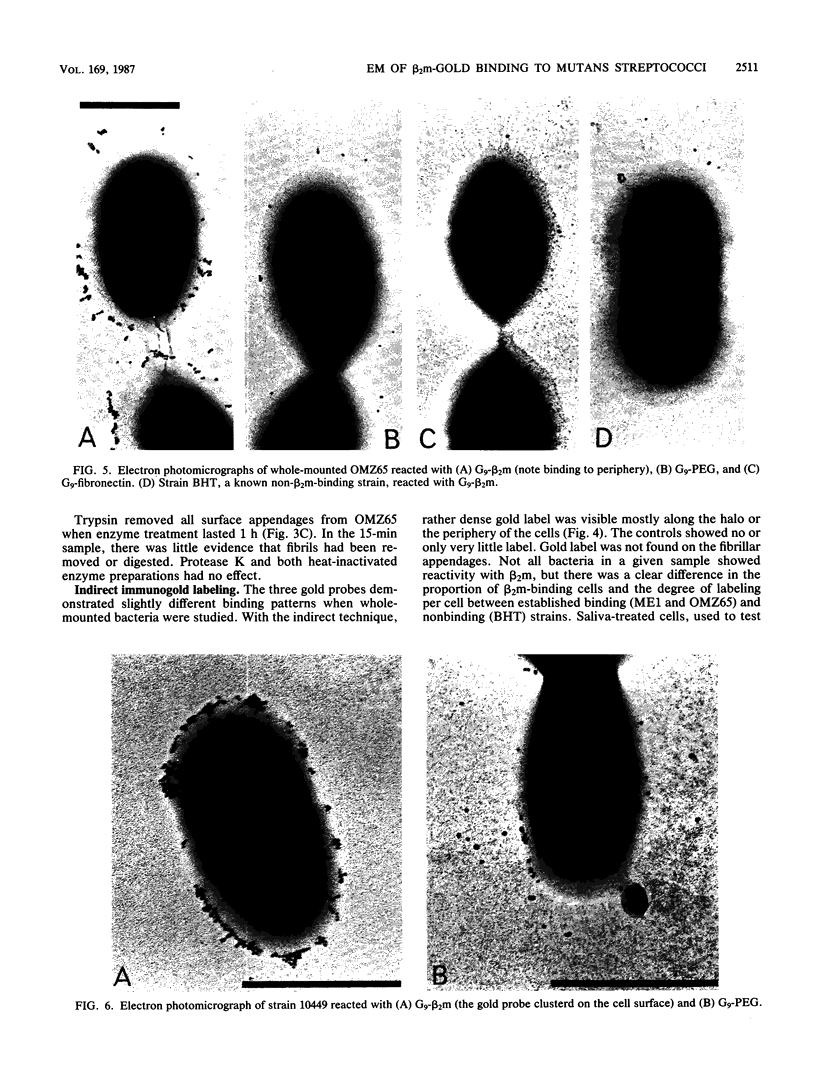
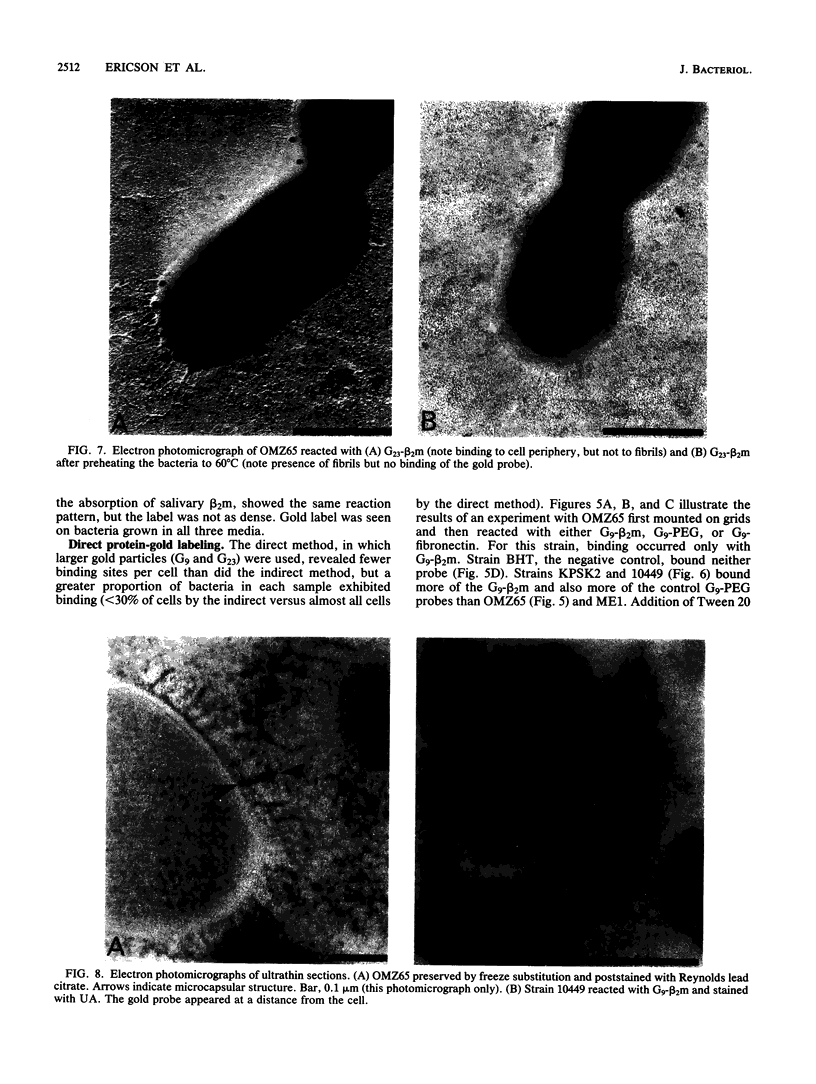
As little detail is known about the surface structure of streptococci in the mutans group and the relationship of surface structure to host ligand-binding functions, the twofold purpose of this investigation was to examine in detail, by a range of electron microscopic techniques, the surface structures of streptococci in the different species of the mutans group and to investigate the distribution of beta 2-microglobulin (beta 2m)-binding sites on such structures. Strains representing Streptococcus mutans, S. cricetus, S. rattus, S. sobrinus, and four fresh isolates were studied by shadowcasting and histochemical staining of whole-mounted cells as well as by ultrathin and thick sectioning of embedded specimens. beta 2m-binding site distribution was visualized by indirect immunogold electron microscopy and by direct bacterial binding of beta 2m-conjugated gold probes. Shadowcast preparations revealed binding of gold probes to the cell surface of known beta 2m-binding strains but not to their polar fibrillar appendages. These long fibrils, common to all strains, were trypsin and sonication sensitive and stained with lead citrate but not with uranyl acetate or ruthenium red. More gold particles were bound by the indirect technique. For grid-mounted bacteria, the gold was mostly bound in clusters at the periphery of the cells. When gold probes were reacted in suspension with bacteria before mounting onto grids, a more even distribution of the gold was seen, but the bacteria were aggregated. Heating the bacteria eliminated beta 2m-gold binding but had no effect on the morphology of the fibrils. Thick sections of embedded bacteria prereacted with beta 2m-conjugated gold probes were analyzed by stereo imaging. A wispy, uranyl acetate-stained fuzzy layer, distinct from the fibrils seen by shadowcasting and extending up to one cell diameter from the cell wall, contained the gold probes. These findings introduce a concept that binding sites for some salivary ligands on mutans streptococci may be clustered on very delicate, nonfibrillar structures extending much further from the cell wall than previously appreciated. As for beta 2m, which composes part of the human histocompatibility antigens, part of the bacterial surface would be coated at a distance from its body with a protein not necessarily recognized as foreign by the host.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björck L., Miörner H., Kühnemund O., Kronvall G., Sundler R. On the interaction between beta 2-microglobulin and group A streptococci. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Jul;20(1):69–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Fjellanger I., Gjeruldsen S. T. Adsorption of immunolgobulin A onto oral bacteria in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):242–249. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.242-249.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. W. The binding of human salivary alpha-amylase by oral strains of streptococcal bacteria. Arch Oral Biol. 1983;28(7):567–573. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(83)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Walker D. L., Chan K. H. Association of long surface appendages with adherence-related functions of the gram-positive species Actinomyces naeslundii. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1171–1175. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1171-1175.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson D. Agglutination of Streptococcus mutans by low-molecular-weight salivary components: effect of beta 2-microglobulin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):526–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.526-530.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson D., Björck L., Kronvall G. Further characteristics of beta2-microglobulin binding to oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):117–124. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.117-124.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson D., Bratthall D., Björck L., Myhre E., Kronvall G. Interactions between human serum proteins and oral streptococci reveal occurrence of receptors for aggregated beta 2-microglobulin. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):279–283. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.279-283.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson D., Tynelius-Bratthall G. Absorption of fibronectin from human saliva by strains of oral streptococci. Scand J Dent Res. 1986 Aug;94(4):377–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1986.tb01777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fives-Taylor P. M., Thompson D. W. Surface properties of Streptococcus sanguis FW213 mutants nonadherent to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):752–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.752-759.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J. Adherent interactions which may affect microbial ecology in the mouth. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):378–385. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630030401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Cohen L., Hay D. I. Strains of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus attach to different pellicle receptors. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):555–561. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.555-561.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Van Houte J., Liljemark W. F. Parameters that effect the adherence of Streptococcus salivarius to oral epithelial surfaces. J Dent Res. 1972 Mar-Apr;51(2):424–435. doi: 10.1177/00220345720510023101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Carter P. L., Fielding J. Streptococcus salivarius strains carry either fibrils or fimbriae on the cell surface. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):64–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.64-72.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Carter P. L., Wyatt J. E., Hesketh L. M. Surface structures (peritrichous fibrils and tufts of fibrils) found on Streptococcus sanguis strains may be related to their ability to coaggregate with other oral genera. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):217–227. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.217-227.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Comparative ultrastructure of selected oral streptococci: thin-sectioning and freeze-etching studies. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;22(4):475–485. doi: 10.1139/m76-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai S., Okahashi N., Koga T., Nisizawa T., Hamada S. Ability of various oral bacteria to bind human plasma fibronectin. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(8):863–871. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Myhre E. B., Björck L., Berggård I. Binding of aggregated human beta2-microglobulin to surface protein structure in group A, C, and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):136–142. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.136-142.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. B., Brown K. N., Lam J., Costerton J. W. Morphological stabilization of capsules of group B streptococci, types Ia, Ib, II, and III, with specific antibody. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.609-617.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbandian J., Freedman M. L., Tanzer J. M., Lovelace S. M. Ultrastructure of Mutants of Streptococcus mutans with Reference to Agglutination, Adhesion, and Extracellular Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1170–1179. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1170-1179.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S., Dzink J. L., Smith C. M. Chemically defined medium for oral microorganisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):303–305. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.303-305.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak L. A., Levine M. J., Mandel I. D., Ellison S. A. Role of salivary mucins in the protection of the oral cavity. J Oral Pathol. 1982 Feb;11(1):1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1982.tb00138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Wagner B., Kronvall G., Björck L. Electron microscopic localization of receptors for aggregated beta 2-microglobulin on the surface of beta-hemolytic streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):326–332. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.326-332.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Handley P. S., Baars A., Slot J. W. Negative staining and immunoelectron microscopy of adhesion-deficient mutants of Streptococcus salivarius reveal that the adhesive protein antigens are separate classes of cell surface fibril. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):746–755. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.746-755.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]