Abstract
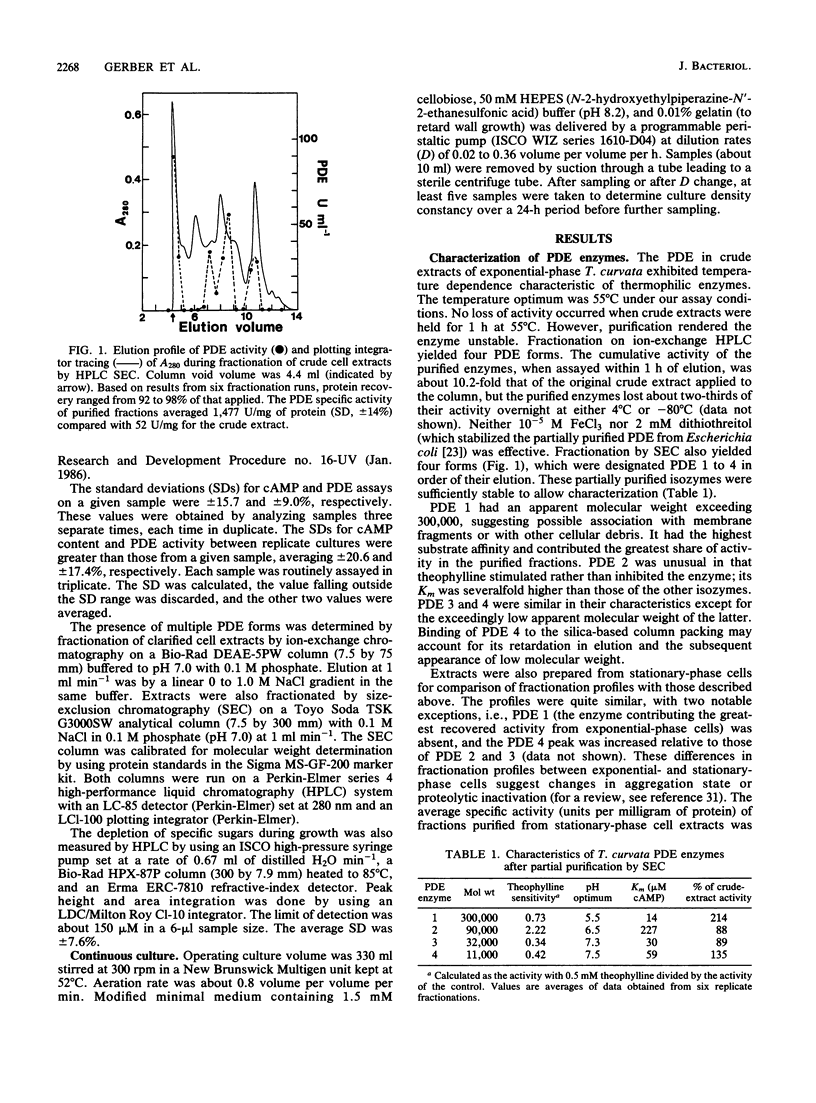
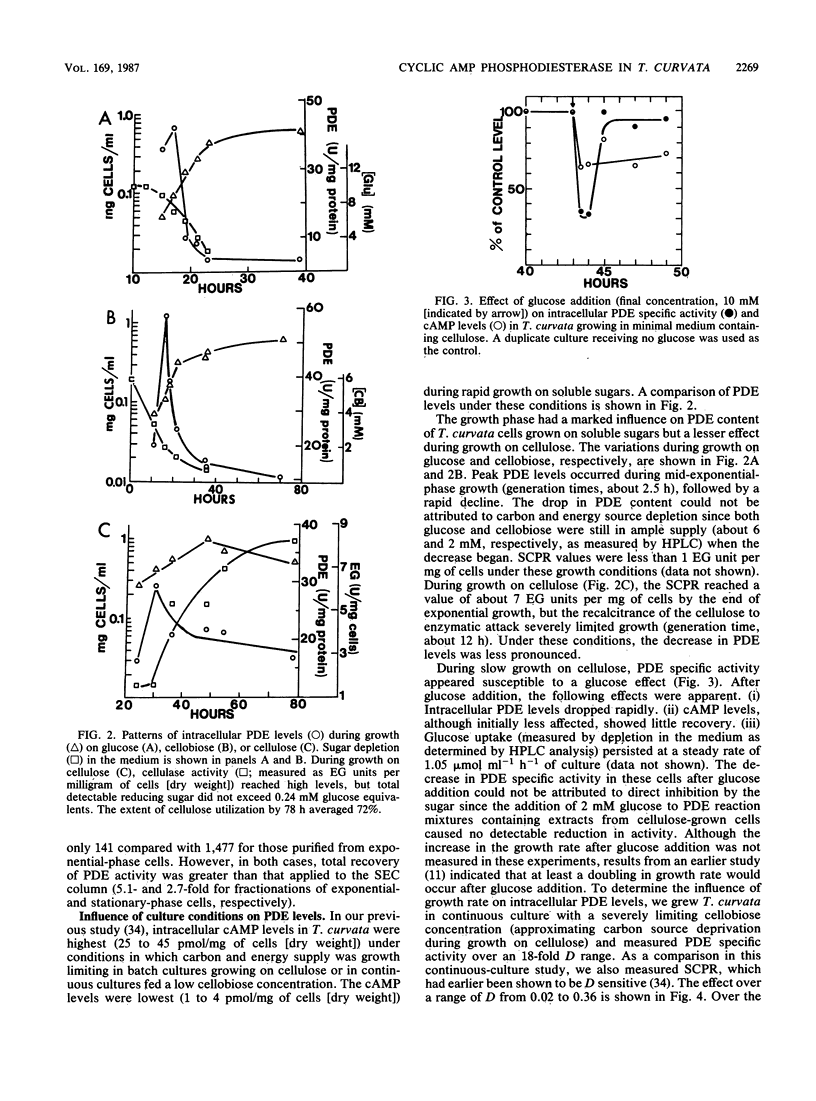
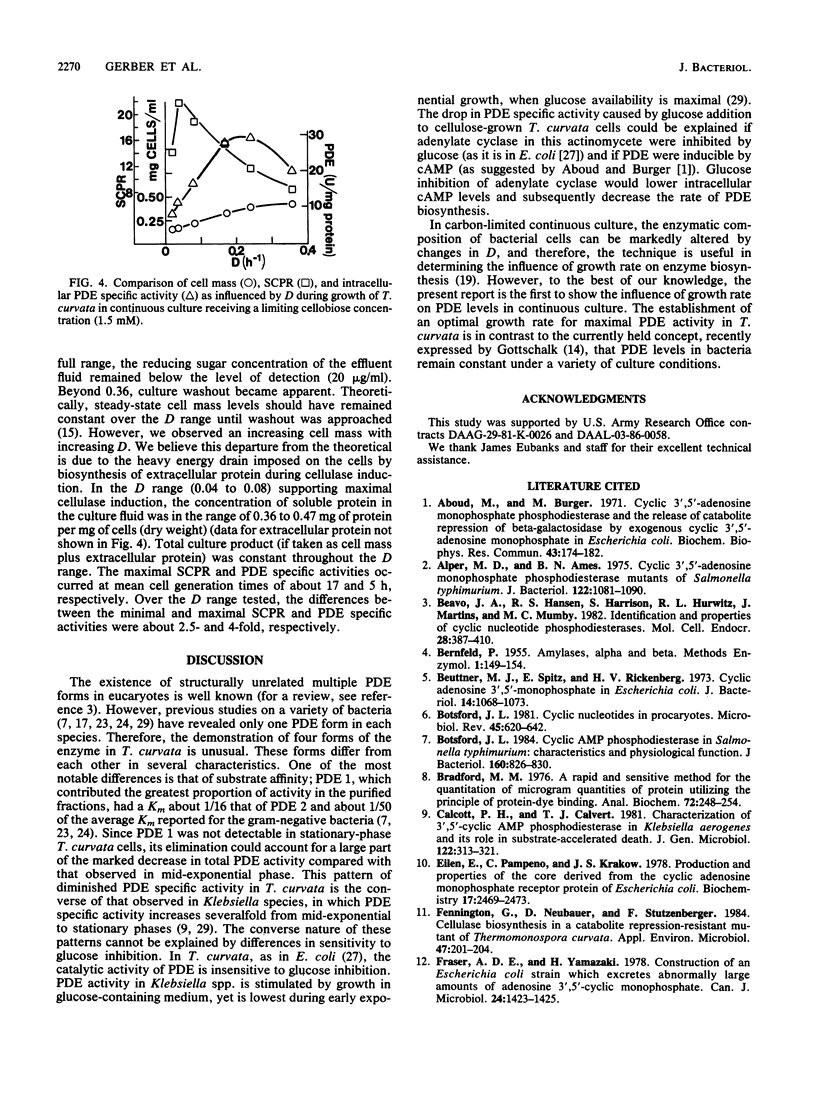
Cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase (PDE; EC 3.1.4.17) in Thermomonospora curvata was purified and characterized. Fractionation of cell extracts by ion-exchange and size-exclusion chromatography revealed four PDE isozymes, which differed markedly in molecular weight, theophylline sensitivity, pH optima, and substrate affinity. Although the enzyme was labile after purification, total recovery of PDE activity was fivefold that of the crude extract. PDE biosynthesis appeared sensitive to the growth phase, growth rate, and carbon source. PDE levels in batch cultures peaked and declined rapidly during mid-exponential-phase growth. In continuous culture, maximal PDE and cellulase production occurred at dilution rates yielding mean cell generation times of about 5 and 17 h, respectively. The addition of glucose to cellulose-grown cells caused declines in both cyclic AMP and PDE levels, suggesting that the enzyme was subject to, rather than the agent of, catabolite repression.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboud M., Burger M. Cyclic 3';5' adenosine monophosphate-phosphodiesterase and the release of catabolite repression of beta-galactosidase by exogenous cyclic 3';5' adenosine monophosphate in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 2;43(1):174–182. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper M. D., Ames B. N. Cyclic 3', 5'-adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1081–1090. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1081-1090.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botsford J. L. Cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Salmonella typhimurium: characteristics and physiological function. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):826–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.826-830.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botsford J. L. Cyclic nucleotides in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Dec;45(4):620–642. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.4.620-642.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buettner M. J., Spitz E., Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1068–1073. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1068-1073.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calcott P. H., Calvert T. J. Characterization of 3': 5' -cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Klebsiella aerogenes and its role in substrate-accelerated death. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Feb;122(2):313–321. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilen E., Pampeno C., Krakow J. S. Production and properties of the alpha core derived from the cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2469–2473. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennington G., Neubauer D., Stutzenberger F. Cellulase biosynthesis in a catabolite repression-resistant mutant of Thermomonospora curvata. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):201–204. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.201-204.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser A. D., Yamazaki H. Effect of carbon sources on the rates of cyclic AMP synthesis, excretion, and degradation, and the ability to produce beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli. Can J Biochem. 1979 Aug;57(8):1073–1079. doi: 10.1139/o79-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. E., Yamazaki H. Construction of an Escherichia coli strain which excretes abnormally large amounts of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Nov;24(11):1423–1425. doi: 10.1139/m78-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S. A., Murthy N. S., Krakow J. S. Ligand-induced change in the radius of gyration of cAMP receptor protein from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 1;109(1):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN R. S., SUTHERLAND E. W. ADENOSINE 3',5'-PHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1309–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Grootjans A., Hogenhuis H. Influence of dilution rate on enzymes of intermediary metabolism in two freshwater bacteria grown in continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jun;94(2):323–332. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-2-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Matin M. K. Cellular levels, excretion, and synthesis rates of cyclic AMP in Escherichia coli grown in continuous culture. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):801–807. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.801-807.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D., Janecek J., Rickenberg H. V. The enzymic degradation of 3',5' cyclic AMP in strains of E. Coli sensitive and resistant to catobolite repression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 May 22;35(4):584–591. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90388-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen L. D., Monard D., Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):857–866. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.857-866.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabayashi T., Ide M. Cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase of Serratia marcescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 14;220(1):116–123. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pall M. L. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in fungi. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):462–480. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.462-480.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Gazdar C. Glucose inhibition of adenylate cyclase in intact cells of Escherichia coli B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2324–2328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter K., Chaloner-Larsson G., Yamazaki H. Abnormally high rate of cyclic AMP excretion from an Escherichia coli mutant deficient in cyclic AMP receptor protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 25;57(2):379–385. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90941-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutzenberger F. J. Cellulolytic activity of Thermomonospora curvata: nutritional requirments for cellulase production. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jul;24(1):77–82. doi: 10.1128/am.24.1.77-82.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer R. L. The inactivation of microbial enzymes in vivo. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:135–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Brooker G., Appleman M. M. Assay of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases with radioactive substrates. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:205–212. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. E., Neubauer D. G., Stutzenberger F. J. Cyclic AMP levels during induction and repression of cellulase biosynthesis in Thermomonospora curvata. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1047–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1047-1054.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


