Abstract
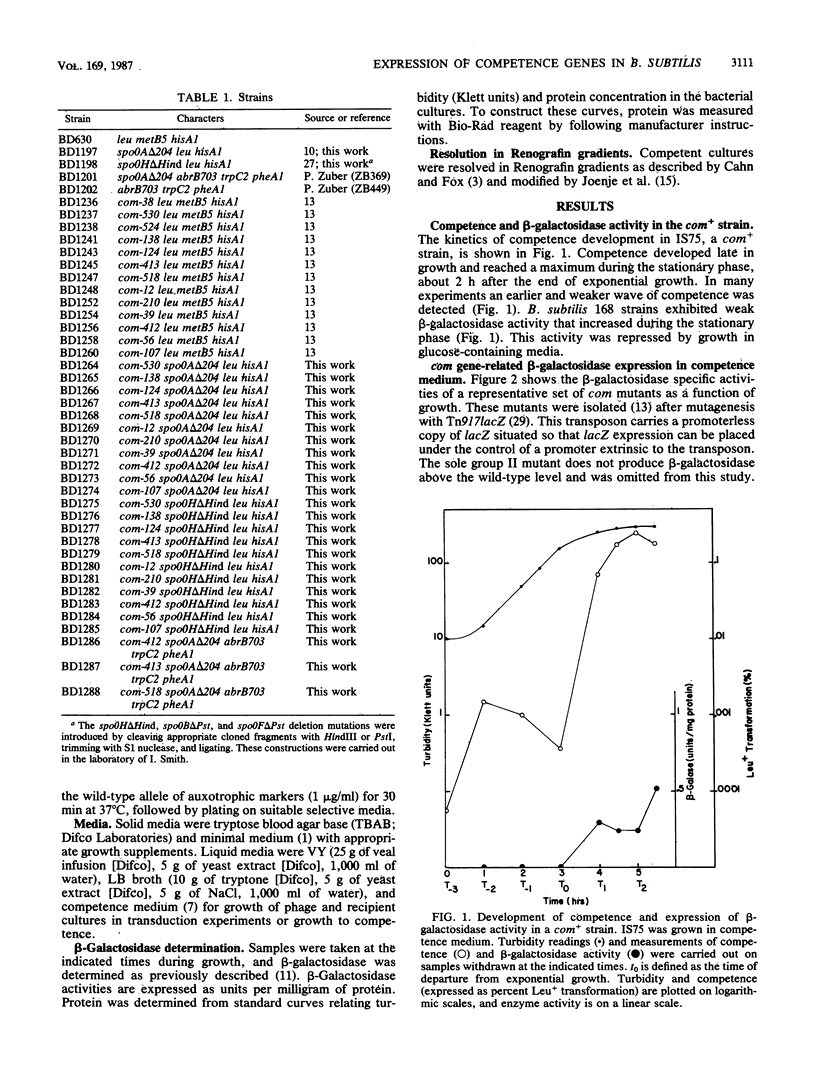
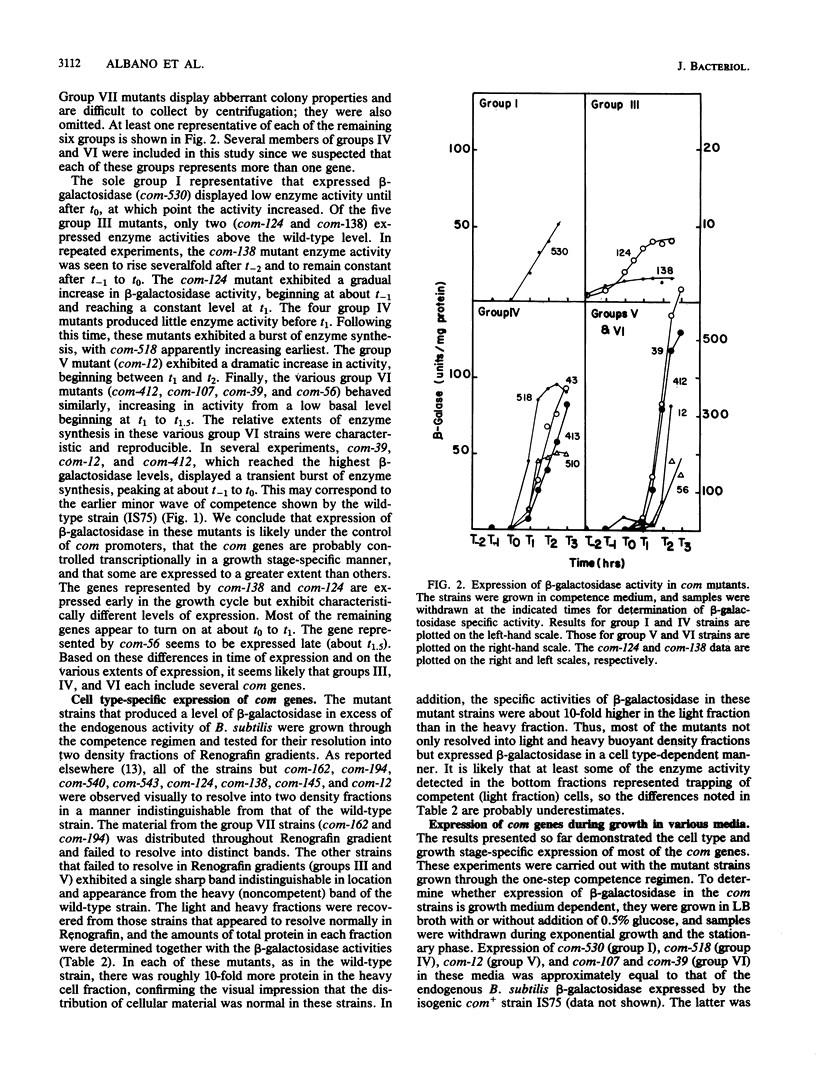
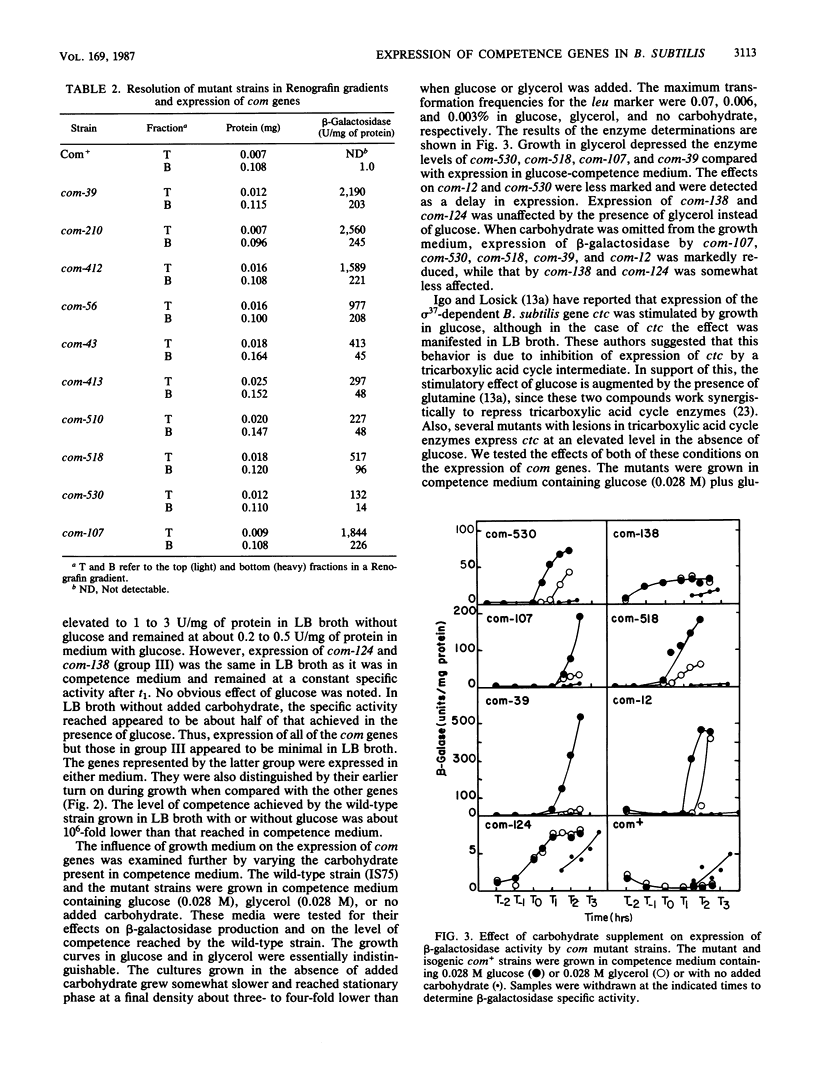
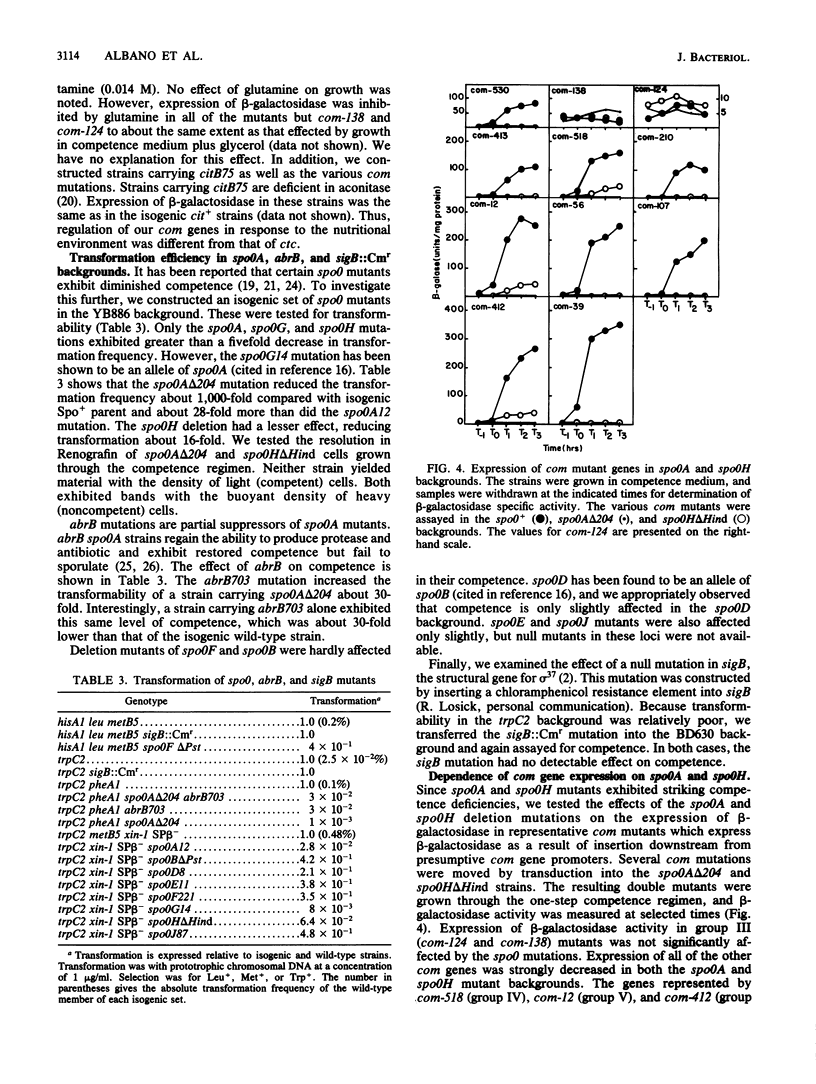
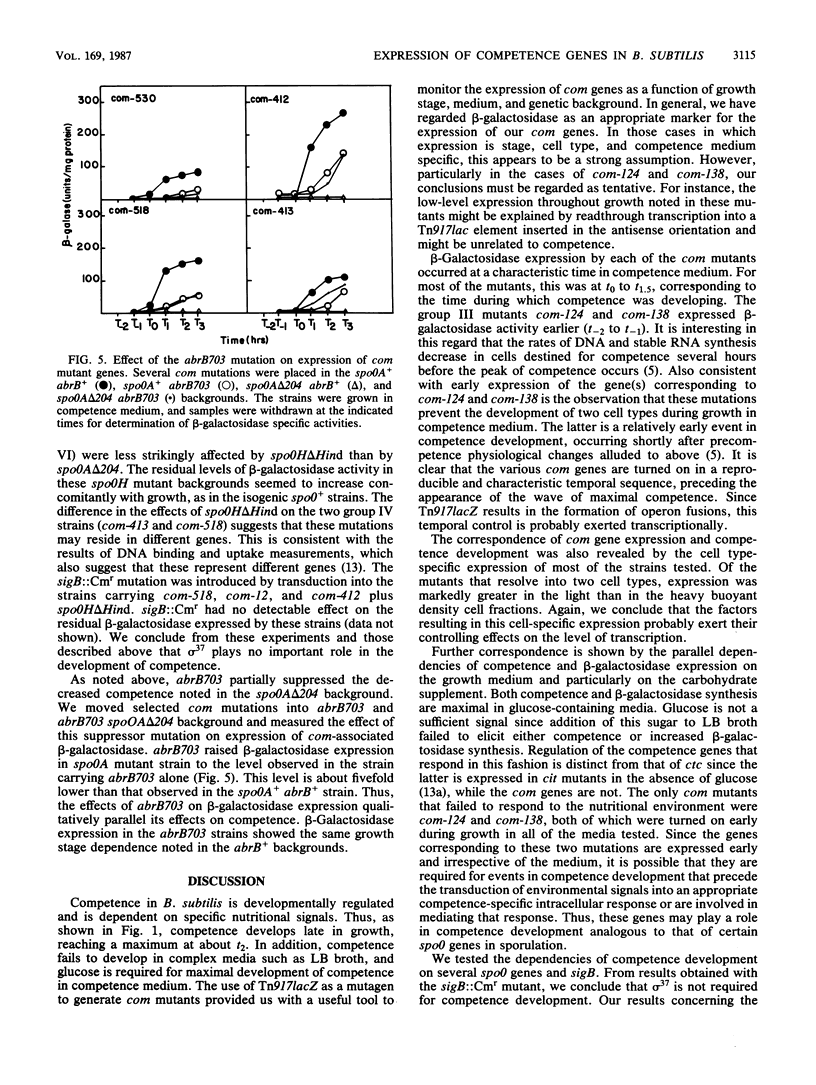
A set of competence (com) mutants of Bacillus subtilis was constructed by using Tn917lacZ as a mutagen. In about half of the mutants, the promoterless lacZ element on the transposon was placed under control of putative com promoters. Expression of the mutant com genes was studied by using the beta-galactosidase tag. Two of the mutant genes (those represented by com-124 and com-138) were expressed early in the growth cycle in all of the media tested and were not dependent on the spo0A or spo0H product for expression. The remaining mutants, which represented a minimum of four additional genes, expressed beta-galactosidase in stationary phase during the period in which competence developed. We conclude that expression of com genes is probably regulated transcriptionally and in a growth stage-specific manner. Expression of these genes was also dependent on growth in competence medium and, like competence development, required the presence of glucose and was dependent on the spo0H products. The dependence on the spo0A gene product was partially bypassed by the abrB703 mutation. These effects were qualitatively equivalent to those on competence development. The latter was dependent on spo0A and spo0H, and the spo0A dependency was partially suppressed by abrB703. Several of the mutants were still capable of resolution into light and heavy buoyant density cell fractions when grown in competence medium. All of these expressed beta-galactosidase to a greater extent in the light fraction, showing that expression of these com genes was cell type specific. Development of competence was not markedly affected by mutations in spo0B, spo0E, spo0F, spo0J, or sigB, the structural gene of sigma 37.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnie C., Lampe M., Losick R. Gene encoding the sigma 37 species of RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5943–5947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahn F. H., Fox M. S. Fractionation of transformable bacteria from ocompetent cultures of Bacillus subtilis on renografin gradients. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):867–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.867-875.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter H. L., 3rd, Moran C. P., Jr New RNA polymerase sigma factor under spo0 control in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9438–9442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley D. C., Hadden C. T., Nester E. W. Macromolecular synthesis in Bacillus subtilis during development of the competent state. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):668–679. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.668-679.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Davidoff-Abelson R. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. I. Formation and properties of the donor-recipient complex. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):209–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Davidoff-Abelson R., Smith I. Transformation and transduction in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for separate modes of recombinant formation. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):155–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau E. J., Cabane K., Smith I. Regulation of spo0H, an early sporulation gene in bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1182–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1182-1191.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari E., Howard S. M., Hoch J. A. Effect of stage 0 sporulation mutations on subtilisin expression. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):173–179. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.173-179.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Trach K., LeCoq D., Spence J., Ferrari E., Hoch J. A. Characterization of the spo0A locus and its deduced product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2647–2651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Israeli-Reches M., Dubnau D. Induction of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance requires ribosomes able to bind inducer. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(3):357–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00425544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden C., Nester E. W. Purification of competent cells in the Bacillus subtilis transformation system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):876–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.876-885.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J., Albano M., Dubnau D. Isolation and characterization of Tn917lac-generated competence mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3104–3109. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3104-3109.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M. M., Losick R. Regulation of a promoter that is utilized by minor forms of RNA polymerase holoenzyme in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90449-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionesco H., Michel J., Cami B., Schaeffer P. Symposium on bacterial spores: II. Genetics of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis Marburg. J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;33(1):13–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb05230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joenje H., Konings W. N., Venema G. Interactions between exogenous deoxyribonucleic acid and membrane vesicles isolated from competent and noncompetent Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):771–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.771-776.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Youngman P., Piggot P. J. Genetics of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:625–669. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marahiel M. A., Zuber P., Czekay G., Losick R. Identification of the promoter for a peptide antibiotic biosynthesis gene from Bacillus brevis and its regulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2215–2222. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2215-2222.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Coote J. G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):908–962. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.908-962.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg B., Hoch J. A. Citric acid cycle: gene-enzyme relationships in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):826–833. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.826-833.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadaie Y., Kada T. Formation of competent Bacillus subtilis cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):813–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.813-821.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Chen S. M., Hoch J. A. Genetic analysis of a class of polymyxin resistant partial revertants of stage O sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis: map of the chromosome region near the origin of replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 23;173(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00267691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J., Dubnau E., Ramakrishna N., Smith I. Bacillus subtilis spo0H gene. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):405–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.405-412.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Fields P. I., Andersen B. J. Properties of Bacillus subtilis 168 derivatives freed of their natural prophages. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman P., Zuber P., Perkins J. B., Sandman K., Igo M., Losick R. New ways to study developmental genes in spore-forming bacteria. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):285–291. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4697.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


