Abstract
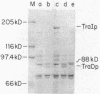
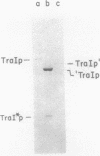
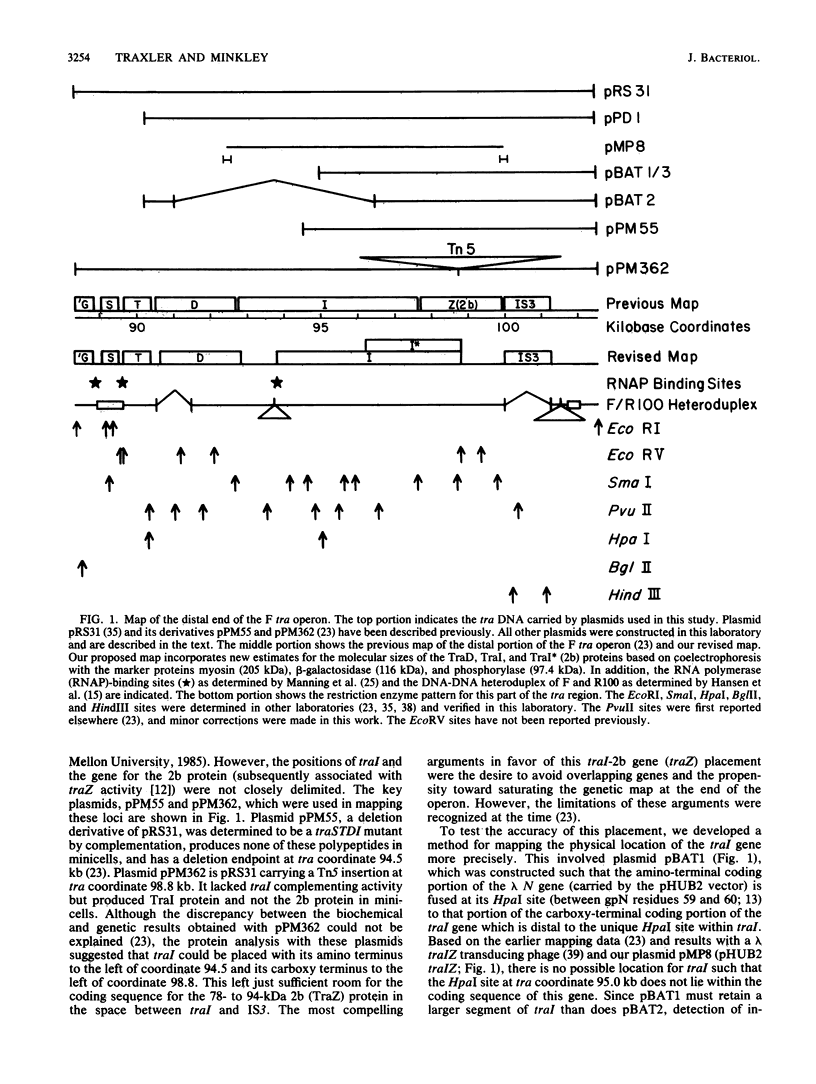
The DNA transfer stage of conjugation requires the products of the F sex factor genes traMYDIZ and the cis-acting site oriT. Previous interpretation of genetic and protein analyses suggested that traD, traI, and traZ mapped as contiguous genes at the distal end of the transfer operon and saturated this portion of the F transfer region (which ends with an IS3 element). Using antibodies prepared against the purified TraD and TraI proteins, we analyzed the products encoded by a collection of chimeric plasmids constructed with various segments of traDIZ DNA. We found the traI gene to be located 1 kilobase to the right of the position suggested on previous maps. This creates an unsaturated space between traD and traI where unidentified tra genes may be located and leaves insufficient space between traI and IS3 for coding the 94-kilodalton protein previously thought to be the product of traZ. We found that the 94-kilodalton protein arose from a translational restart and corresponds to the carboxy terminus of traI; we named it TraI*. The precise physical location of the traZ gene and the identity of its product are unknown. The oriT nicking activity known as TraZ may stem from unassigned regions between traD and traI and between traI and IS3, but a more interesting possibility is that it is actually a function of traI. On our revised map, the position of a previously detected RNA polymerase-binding site corresponds to a site at the amino terminus of traI rather than a location 1 kilobase into the coding region of the gene. Furthermore, the physical and genetic comparison of the F traD and traI genes with those of the closely related F-like conjugative plasmids R1 and R100 is greatly simplified. The translational organization we found for traI, together with its identity as the structural gene for DNA helicase I, suggests a possible functional link to several other genes from which translational restart polypeptides are expressed. These include the primases of the conjugative plasmids ColI and R16, the primase-helicase of bacteriophage T7, and the cisA product (nickase) of phage phi X174.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Monem M., Dürwald H., Hoffmann-Berling H. Enzymic unwinding of DNA. 2. Chain separation by an ATP-dependent DNA unwinding enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):441–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Monem M., Hoffmann-Berling H. Enzymic unwinding of DNA. 1. Purification and characterization of a DNA-dependent ATPase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):431–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Monem M., Taucher-Scholz G., Klinkert M. Q. Identification of Escherichia coli DNA helicase I as the traI gene product of the F sex factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4659–4663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M., Skurray R. A., Thompson R., Helmuth R., Hall S., Beutin L., Clark A. J. Assignment of tra cistrons to EcoRI fragments of F sex factor DNA. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1383–1392. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1383-1392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro G., Willetts N. The relationship between the transfer systems of some bacterial plasmids. Genet Res. 1972 Dec;20(3):279–289. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300013811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Helinski D. R. Use of the lambda phage promoter PL to promote gene expression in hybrid plasmid cloning vehicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:482–492. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Wilkins B. M., Lanka E. Overlapping genes at the DNA primase locus of the large plasmid ColI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):855–869. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. C., Skurray R. The F plasmid carries an IS3 insertion within finO. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Dec;132(12):3269–3275. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-12-3269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple B. P., Williams P. H. Analysis of the R16 plasmid primase gene. Plasmid. 1984 Nov;12(3):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Nucleotide sequence from the genetic left end of bacteriophage T7 DNA to the beginning of gene 4. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):303–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Griffith J., Kornberg A. phiX174 cistron A protein is a multifunctional enzyme in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R., Willetts N. Characterisation of an in vivo system for nicking at the origin of conjugal DNA transfer of the sex factor F. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 15;136(2):129–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90309-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C., Bennett G. N. The N protein of bacteriophage lambda, defined by its DNA sequence, is highly basic. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):107–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Adhya S., Das A. Transcription antitermination by bacteriophage lambda N gene product. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):57–75. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen B. S., Manning P. A., Achtman M. Promoter-distal region of the tra operon of F-like sex factor R100 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):89–99. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.89-99.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Achtman M. Operon structure of DNA transfer cistrons on the F sex factor. Nature. 1975 Oct 23;257(5528):652–656. doi: 10.1038/257652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ippen-Ihler K., Achtman M., Willetts N. Deletion map of the Escherichia coli K-12 sex factor F: the order of eleven transfer cistrons. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):857–863. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.857-863.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy N., Beutin L., Achtman M., Skurray R., Rahmsdorf U., Herrlich P. Conjugation proteins encoded by the F sex factor. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):580–585. doi: 10.1038/270580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsman A., Willetts N. The requirements for conjugal DNA synthesis in the donor strain during flac transfer. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jul 5;122(3):287–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn B., Abdel-Monem M., Hoffmann-Berling H. DNA helicases. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):63–67. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanka E., Scherzinger E., Günther E., Schuster H. A DNA primase specified by I-like plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3632–3636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Hayashi M. Intragenic regulation of the synthesis of phi chi 174 gene A proteins. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):345–348. doi: 10.1038/249345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Kusecek B., Morelli G., Fisseau C., Achtman M. Analysis of the promoter-distal region of the tra operon of the F sex factor of Escherichia coli K-12 encoded by EcoRI restriction fragments f17, f19, and f2. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):76–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.76-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Morelli G. DNA homology of the promoter-distal regions of the tra operons of sex factors F and R100 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):389–394. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.389-394.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Morelli G., Fisseau C. RNA-polymerase binding sites within the tra region of the F factor of Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire S., Willetts N. Plasmid cointegrates of Flac and lambda prophage. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.184-192.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meynell E., Datta N. Mutant drug resistant factors of high transmissibility. Nature. 1967 May 27;214(5091):885–887. doi: 10.1038/214885a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkley E. G., Jr Purification and characterization of pro-TraTp, the signal sequence-containing precursor of a secreted protein encoded by the F sex factor. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):464–473. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.464-473.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkley E. G., Jr, Willetts N. S. Overproduction, purification and characterization of the F traT protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(2):225–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00328054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D., Sowa B. A., Ippen-Ihler K. A new activity in the Ftra operon which is required for F-pilin synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(3):459–464. doi: 10.1007/BF00330049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullineaux P., Willetts N. Promoters in the transfer region of plasmid F. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:605–614. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicker M. M., Minkley E. G., Jr DNA transfer occurs during a cell surface contact stage of F sex factor-mediated bacterial conjugation. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):584–590. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.584-590.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Cohen S. N., Davidson N. Electron microscope heteroduplex studies of sequence relations among plasmids of Escherichia coli. II. Structure of drug resistance (R) factors and F factors. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):235–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurray R. A., Nagaishi H., Clark A. J. Molecular cloning of DNA from F sex factor of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins B. M. Partial suppression of the phenotype of Escherichia coli K-12 dnaG mutants by some I-like conjugative plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):899–904. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.899-904.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Achtman M. Genetic analysis of transfer by the Escherichia coli sex factor F, using P1 transductional complementation. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):843–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.843-851.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Johnson G. R.SmaI cleavage map of the transfer region of the E. coli K12 sex factor F. Genet Res. 1979 Oct;34(2):195–202. doi: 10.1017/s001667230001942x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Maule J. Investigations of the F conjugation gene traI:traI mutants and lambdatraI transducing phages. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 1;169(3):325–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00382278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Maule J. Specificities of IncF plasmid conjugation genes. Genet Res. 1986 Feb;47(1):1–11. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300024447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Wilkins B. Processing of plasmid DNA during bacterial conjugation. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):24–41. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.24-41.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka Y., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Repressor gene finO in plasmids R100 and F: constitutive transfer of plasmid F is caused by insertion of IS3 into F finO. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):619–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.619-623.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]