Abstract
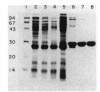
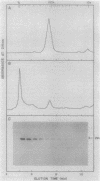
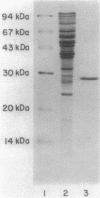
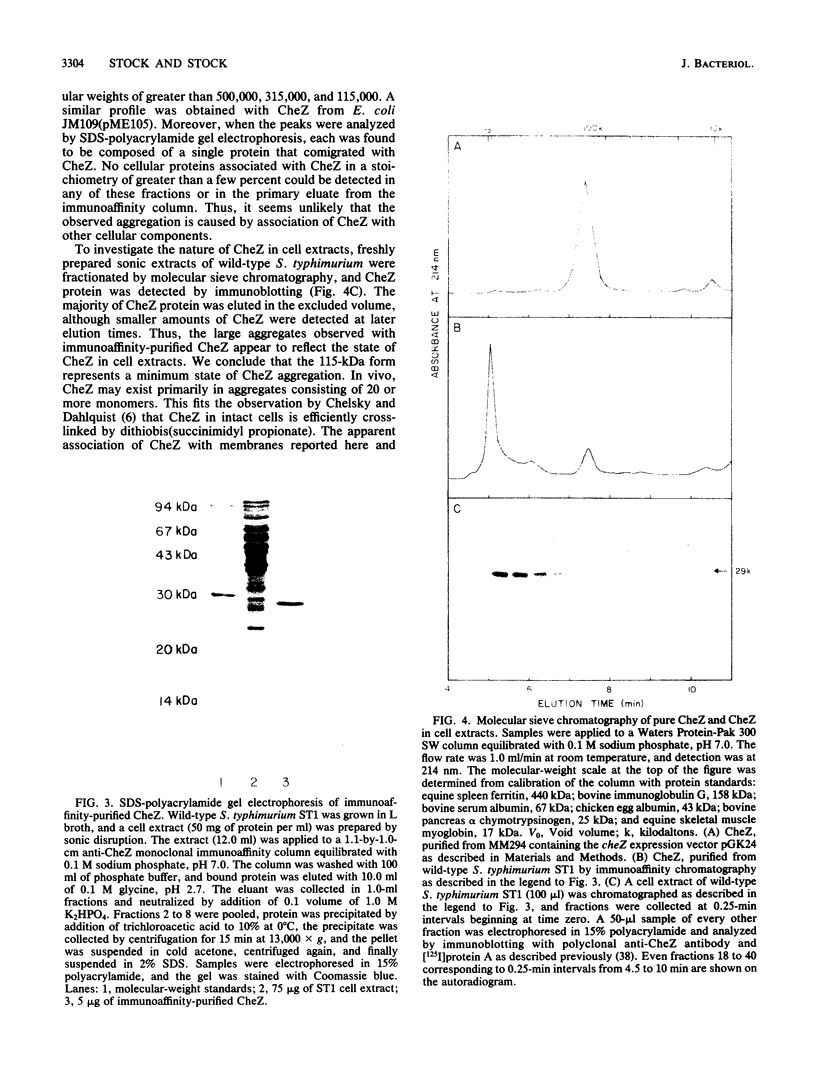
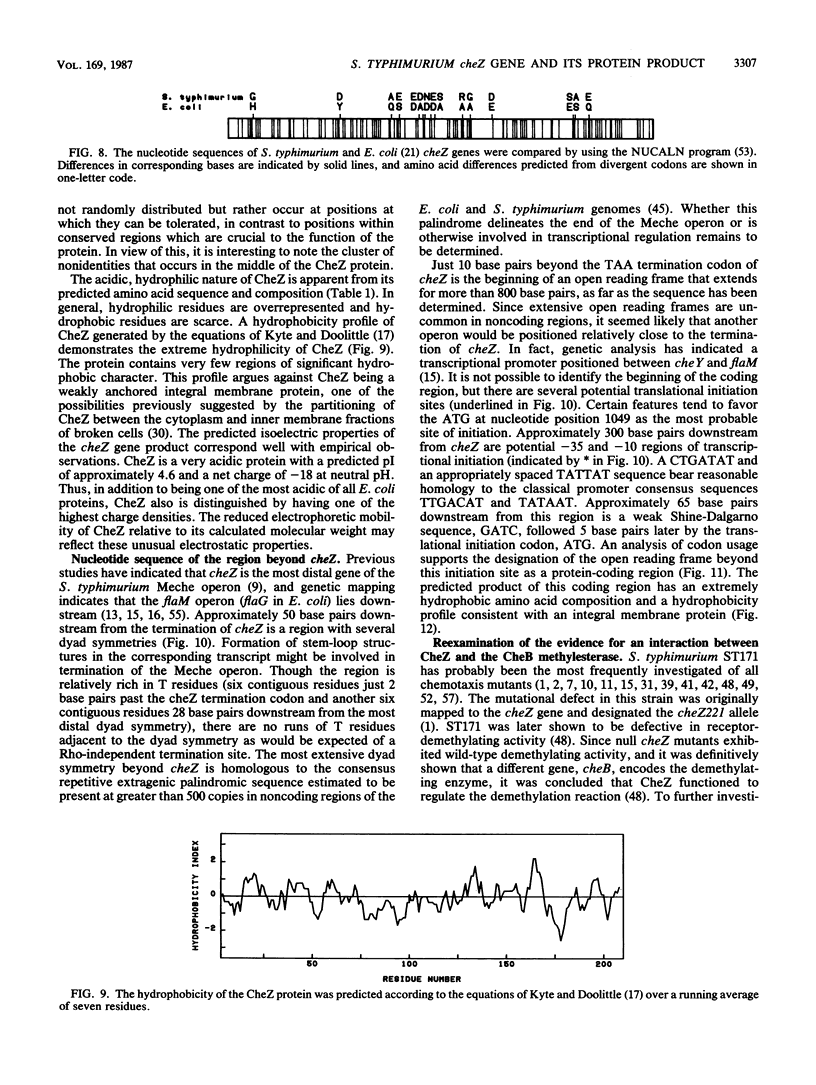
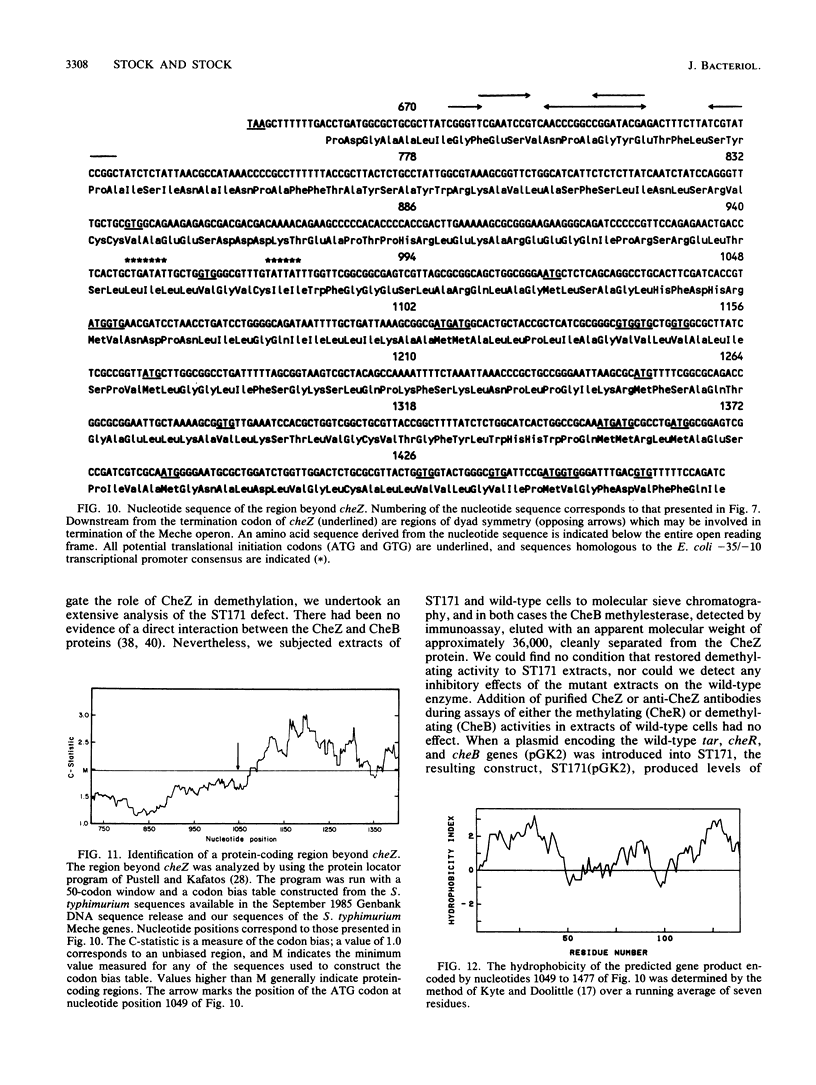
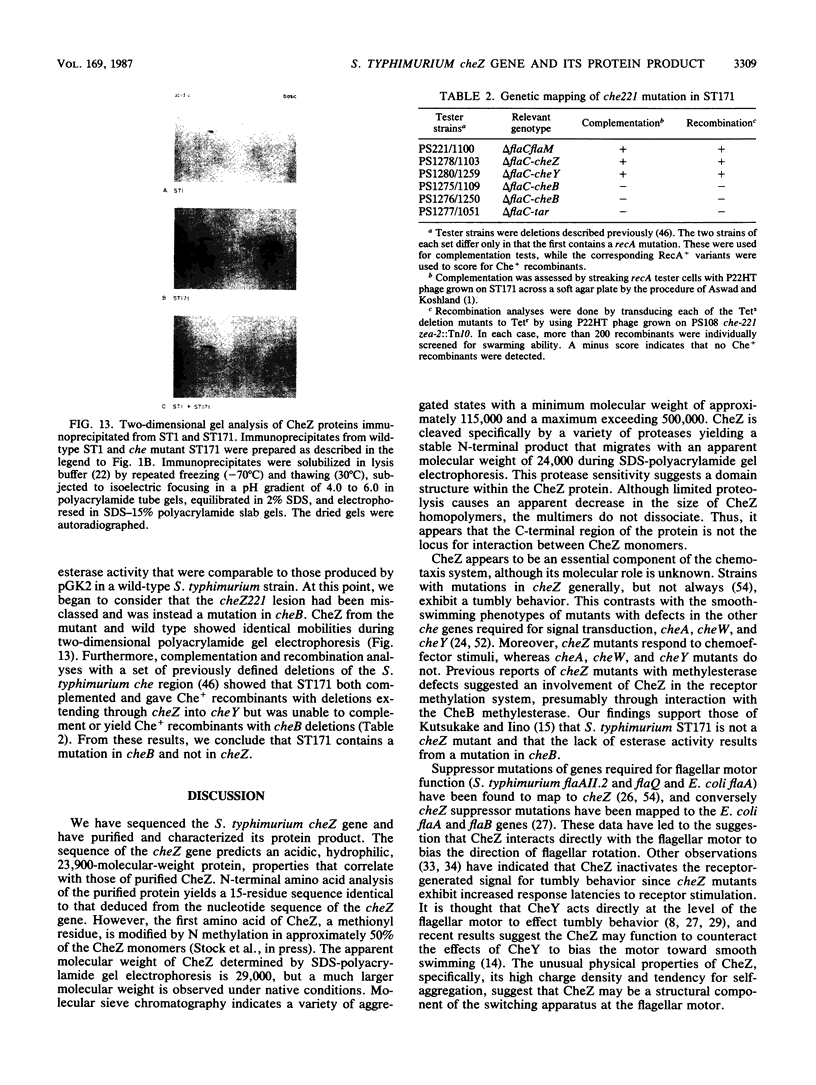
The cheZ gene is the most distal of five genes that comprise the Meche operon of the Salmonella typhimurium chemotaxis system. We have determined the sequence of the cheZ gene along with an 800-nucleotide flanking region at its 3' end. The flanking sequence contains an open reading frame that probably corresponds to the 5' end of flaM. The cheZ coding sequence predicts an extremely acidic, hydrophilic protein with a molecular weight of 23,900. We have purified and characterized this protein. N-terminal analysis of pure CheZ yields an amino acid sequence identical to that predicted by the nucleotide sequence except that the amino-terminal methionine residue is modified by N methylation. The purified CheZ protein exhibits a native molecular weight of 115,000, but in cell extracts the majority of CheZ exists as a much larger aggregate (Mr greater than 500,000). Under these conditions, CheZ appears to be a homopolymer composed of at least 20 monomeric subunits.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aswad D. W., Koshland D. E., Jr Evidence for an S-adenosylmethionine requirement in the chemotactic behavior of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):207–223. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswad D., Koshland D. E., Jr Isolation, characterization and complementation of Salmonella typhimurium chemotaxis mutants. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Simon M. Bacterial chemotaxis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:501–517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruck C., Portetelle D., Glineur C., Bollen A. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascitic fluid by DEAE Affi-Gel blue chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelsky D., Dahlquist F. W. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli: associations of protein components. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 30;19(20):4633–4639. doi: 10.1021/bi00561a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Koshland D. E., Jr Membrane receptors for aspartate and serine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9695–9702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg D. O., Koshland D. E., Jr The role of a signaling protein in bacterial sensing: behavioral effects of increased gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Molecular cloning of chemotaxis genes and overproduction of gene products in the bacterial sensing system. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):390–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.390-400.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Parkinson J. S., Koshland D. E., Jr Functional homology of chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):107–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.107-114.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway R. J., Taylor B. L. Histidine starvation and adenosine 5'-triphosphate depletion in chemotaxis of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1068–1075. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1068-1075.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Suzuki H., Ishidsu J. I., Iino T. The role of cAMP in flagellation of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Dec 31;142(4):289–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00271253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Koshland D. E., Jr Roles of cheY and cheZ gene products in controlling flagellar rotation in bacterial chemotaxis of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1307–1314. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1307-1314.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Iino T., Komeda Y., Yamaguchi S. Functional homology of fla genes between Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):59–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00267213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsukake K., Iino T. Refined genetic analysis of the region II che mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(3):406–409. doi: 10.1007/BF00330750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M., Yuan R. DNA restriction enzyme from E. coli. Nature. 1968 Mar 23;217(5134):1110–1114. doi: 10.1038/2171110a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh N., Simon M. I. Nucleotide sequence corresponding to five chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):161–166. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.161-166.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Complementation analysis and deletion mapping of Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.45-53.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Parker S. R. Interaction of the cheC and cheZ gene products is required for chemotactic behavior in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2390–2394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Parker S. R., Talbert P. B., Houts S. E. Interactions between chemotaxis genes and flagellar genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.265-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A convenient and adaptable package of computer programs for DNA and protein sequence management, analysis and homology determination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):643–655. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid S., Matsumura P., Eisenbach M. Restoration of flagellar clockwise rotation in bacterial envelopes by insertion of the chemotaxis protein CheY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway H. G., Silverman M., Simon M. I. Localization of proteins controlling motility and chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):657–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.657-665.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubik B. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Potentiation, desensitization, and inversion of response in bacterial sensing of chemical stimuli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2820–2824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Ishihara A., Berg H. C. Chemotactic signaling in filamentous cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):51–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.51-59.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Manson M. D., Berg H. C. Signal processing times in bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1982 Apr 29;296(5860):855–857. doi: 10.1038/296855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli: methylation of che gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Identification of polypeptides necessary for chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1317–1325. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1317-1325.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simms S. A., Keane M. G., Stock J. Multiple forms of the CheB methylesterase in bacterial chemosensing. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10161–10168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of the esterase peptide and its interaction with the cheZ peptide in bacterial sensing. Biochimie. 1981 Feb;63(2):113–117. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Stock J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr Carboxylmethyl esterase of bacterial chemotaxis. Methods Enzymol. 1984;106:321–330. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)06032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. R., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of a protein methyltransferase as the cheR gene product in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):533–537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Quantitation of the sensory response in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):710–713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. J., Ames G. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Higgins C. F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: a major component of the bacterial genome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr A protein methylesterase involved in bacterial sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Borczuk A., Chiou F., Burchenal J. E. Compensatory mutations in receptor function: a reevaluation of the role of methylation in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8364–8368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Kersulis G., Koshland D. E., Jr Neither methylating nor demethylating enzymes are required for bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):683–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Intrinsic and extrinsic light responses of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):557–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.557-569.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J. L. Production of antisera with small doses of immunogen: multiple intradermal injections. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrick H. M., Taylor B. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Chemotactic mechanism of Salmonella typhimurium: preliminary mapping and characterization of mutants. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):223–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.223-231.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Aizawa S., Kihara M., Isomura M., Jones C. J., Macnab R. M. Genetic evidence for a switching and energy-transducing complex in the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1172–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1172-1179.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Iino T., Horiguchi T., Ota K. Genetic analysis of fla and mot cistrons closely linked to H1 in Salmonella abortusequi and its derivatives. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Apr;70(1):59–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Koshland D. E., Jr Mg2+, Ca2+-dependent adenosine triphosphatase as receptor for divalent cations in bacterial sensing. Science. 1976 Jul 30;193(4251):405–408. doi: 10.1126/science.132702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]