Abstract
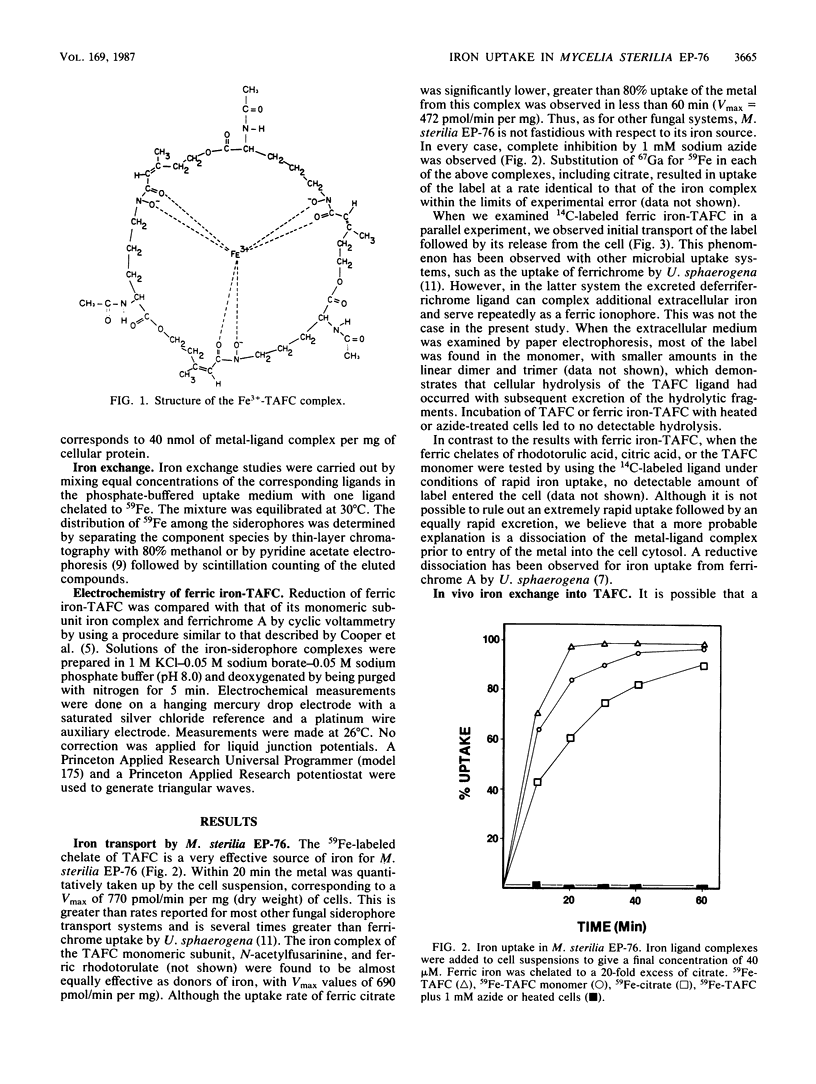
The cyclic trihydroxamic acid, N,N',N''-triacetylfusarinine C, produced by Mycelia sterilia EP-76, was shown to be a ferric ionophore for this organism. The logarithm of the association constant k for the ferric triacetylfusarinine C chelate was determined to be 31.8. Other iron-chelating agents, such as rhodotorulic acid, citric acid, and the monomeric subunit of triacetylfusarinine C, N-acetylfusarinine, delivered iron to the cells by an indirect mechanism involving iron exchange into triacetylfusarinine C. In vitro ferric ion exchange was found to be rapid with triacetylfusarinine C. Gallium uptake rates comparable to those of iron were observed with the chelating agents that transport iron into the cell. Ferrichrome, but not ferrichrome A, was also capable of delivering iron and gallium to this organism, but not by an exchange mechanism. Unlike triacetylfusarinine C, the 14C-ligand of ferrichrome was retained by the cell. A midpoint potential of -690 mV with respect to the saturated silver chloride electrode was obtained for the ferric triacetylfusarinine C complex, indicating that an unfavorable reduction potential was not the reason for the use of a hydrolytic mechanism of intracellular iron release from the ferric triacetylfusarinine C chelate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anke H. Metabolic products of microoorganisms. 163. Desferritriacetylfusigen, an antibiotic from Aspergillus deflectus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Feb;30(2):125–128. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkin C. L., Neilands J. B. Rhodotorulic acid, a diketopiperazine dihydroxamic acid with growth-factor activity. I. Isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3734–3739. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrano C. J., Raymond K. N. Coordination chemistry of microbial iron transport compounds: rhodotorulic acid and iron uptake in Rhodotorula pilimanae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):69–74. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.69-74.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. R., McArdle J. V., Raymond K. N. Siderophore electrochemistry: relation to intracellular iron release mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3551–3554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann H., Zähner H. Konstitution von Fusigen und dessen Abbau zu delta-2-Anhydromevalonsäurelacton. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Dec;3(2):213–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker D. J., Lancaster J. R., Jr, Emery T. Siderophore iron transport followed by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8623–8626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker D. J., Passavant C. W., Emery T. Role of two siderophores in Ustilago sphaerogena. Regulation of biosynthesis and uptake mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 8;720(3):242–249. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery T. F. Initial steps in the biosynthesis of ferrichrome. Incorporation of delta-N-hydroxyornithine and delta-N-acetyl-delta-N-hydroxyornithine. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3694–3701. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery T. Fungal ornithine esterases: relationship to iron transport. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2723–2728. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery T., Hoffer P. B. Siderophore-mediated mechanism of gallium uptake demonstrated in the microorganism Ustilago sphaerogena. J Nucl Med. 1980 Oct;21(10):935–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery T. Isolation, characterization, and properties of fusarinine, a delta-hydroxamic acid derivative of ornithine. Biochemistry. 1965 Jul;4(7):1410–1417. doi: 10.1021/bi00883a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery T. Role of ferrichrome as a ferric ionophore in Ustilago sphaerogena. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1483–1488. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. K., Moore R. A. Ammonium and methylammonium transport by the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):435–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.435-442.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton A. J., Cole D. S., Macdonald K. D. A hydroxamic acid from Aspergillus nidulans with antibiotic activity against Proteus species. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Nov;31(11):1110–1115. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monzyk B., Crumbliss A. L. Factors that influence siderophoremediated iron bioavailability: catalysis of interligand iron (III) transfer from ferrioxamine B to EDTA by hydroxamic acids. J Inorg Biochem. 1983 Aug;19(1):19–39. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(83)85010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. E., Emery T. Nalpha-acetylfusarinines: isolation, characterization, and properties. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2719–2723. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien I. G., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Enterochelin hydrolysis and iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 22;237(3):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien I. G., Gibson F. The structure of enterochelin and related 2,3-dihydroxy-N-benzoylserine conjugates from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 14;215(2):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. R., Neilands J. B. Enterobactin, an iron transport compound from Salmonella typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 12;38(5):989–992. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90819-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayer J. M., Emery T. F. Structures of the naturally occurring hydroxamic acids, fusarinines A and B. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):184–190. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmann G., Zähner H. Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen. 115. Eisenaufnahme bei Neurospora crassa. I. Zur Spezifität des Eisentransportes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;88(1):49–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


