Abstract
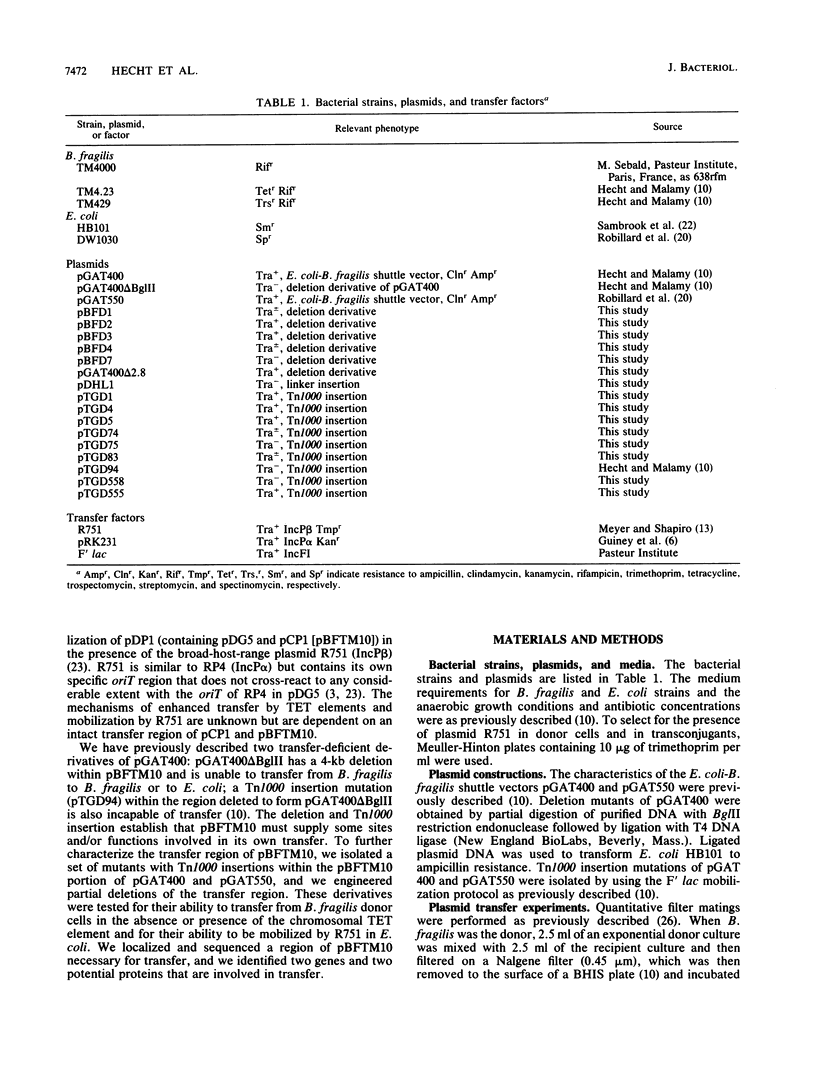
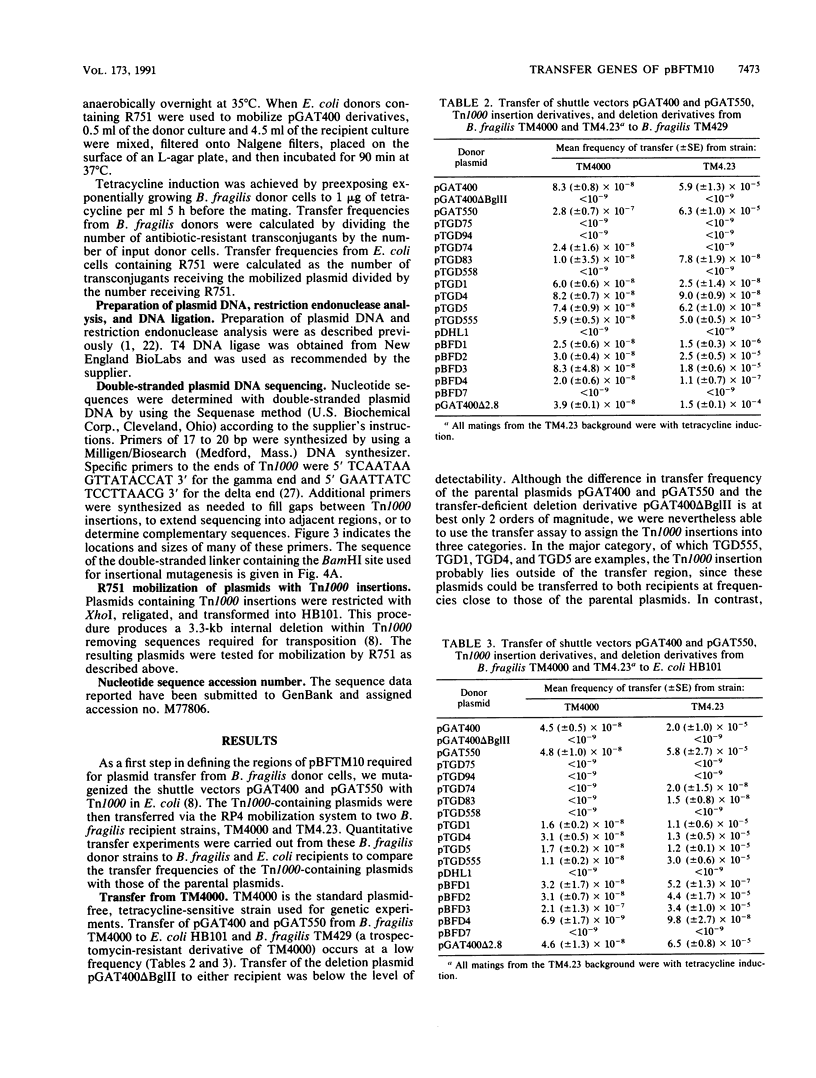
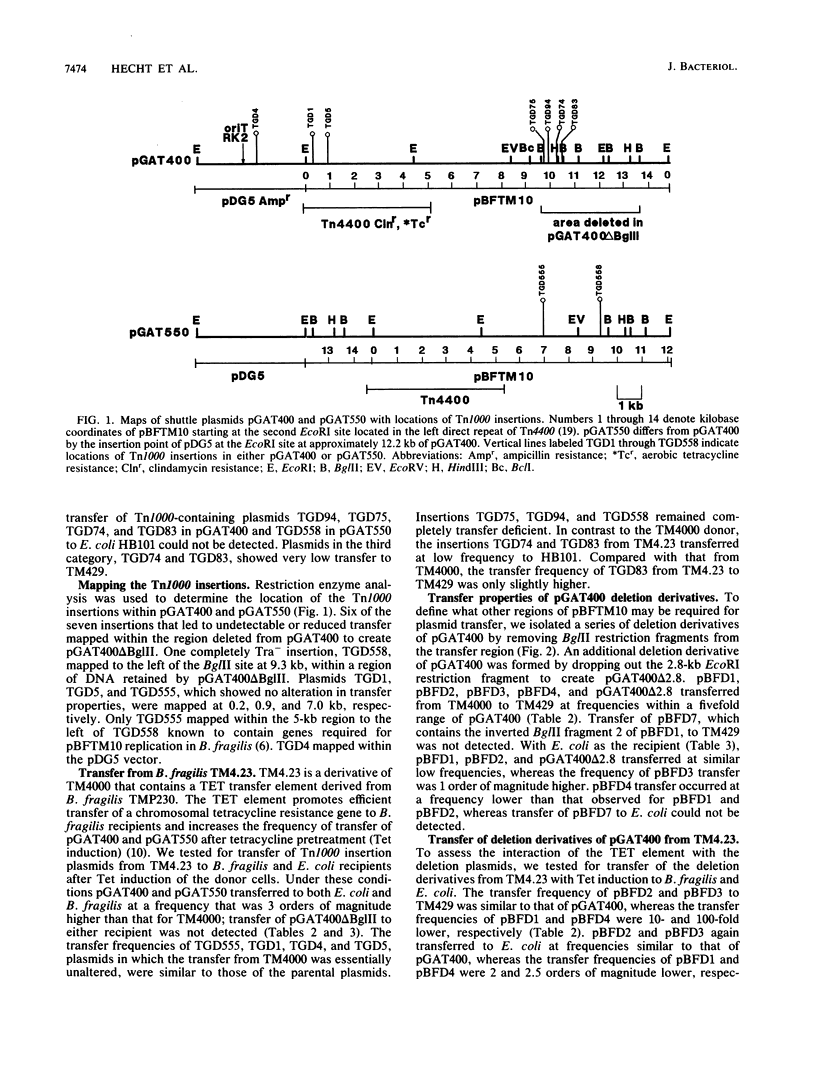
Transferable plasmids play an important role in the dissemination of clindamycin-erythromycin resistance in Bacteroides fragilis. We previously described the isolation and properties of pBFTM10, a 14.9-kb ClnR transfer factor from B. fragilis TMP10. We also reported the isolation of a transfer-deficient deletion derivative of pBFTM10 contained in the B. fragilis-Escherichia coli shuttle vector pGAT400. In the present study we used pGAT400 and a similar shuttle vector, pGAT550, to characterize and sequence a region of pBFTM10 required for its transfer from B. fragilis to B. fragilis or E. coli recipients and for its mobilization by the broad-host-range plasmid R751 from E. coli donors to E. coli recipients. Deletion of certain BglII restriction fragments from pBFTM10 resulted in partial or complete loss of transfer ability. Tn1000 insertions into this same region also resulted in altered transfer properties. We used the sites of Tn1000 insertions to determine the DNA sequence of the transfer region. Two potential open reading frames encoding proteins of 23.2 and 33.8 kDa, corresponding to two genes, btgA or btgB, were identified in the sequence. Tn1000 insertions within btgA or btgB or deletion of all or portions of btgA or btgB resulted in either a transfer deficiency or greatly reduced transfer from B. fragilis donors and alterations in mobilization by R751 in E. coli. A potential oriT sequence showing similarity in organization to the oriT regions of the IncP plasmids was also detected. Thus, pBFTM10 encodes and requires at least two proteins necessary for efficient transfer from B. fragilis. These same functions are expressed in E. coli and are required for mobilization by R751.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuchural G. J., Jr, Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Aldridge K., Cleary T., Finegold S. M., Hill G., Iannini P., O'Keefe J. P., Pierson C. Susceptibility of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United States: analysis by site of isolation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):717–722. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Ziegelin G., Kröger M., Lanka E. Conjugative transfer of promiscuous IncP plasmids: interaction of plasmid-encoded products with the transfer origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1771–1775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Deiss C., Simnad V. Location of the relaxation complex nick site within the minimal origin of transfer region of RK2. Plasmid. 1988 Nov;20(3):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Deiss C., Simnad V., Yee L., Pansegrau W., Lanka E. Mutagenesis of the Tra1 core region of RK2 by using Tn5: identification of plasmid-specific transfer genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4100–4103. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4100-4103.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Hasegawa P., Davis C. E. Plasmid transfer from Escherichia coli to Bacteroides fragilis: differential expression of antibiotic resistance phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7203–7206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyer M. S. The gamma delta sequence of F is an insertion sequence. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):347–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C., Aggarwal A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:933–969. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht D. W., Malamy M. H. Tn4399, a conjugal mobilizing transposon of Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3603–3608. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3603-3608.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamy M. H., Tally F. P. Mechanisms of drug-resistance transfer in Bacteroides fragilis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl 500):59–75. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_d.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh P. K., Malamy M. H., Shimell M. J., Tally F. P. Sequence homology of clindamycin resistance determinants in clinical isolates of Bacteroides spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):726–730. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. J., Shapiro J. A. Genetic organization of the broad-host-range IncP-1 plasmid R751. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1362–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1362-1373.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odelson D. A., Rasmussen J. L., Smith C. J., Macrina F. L. Extrachromosomal systems and gene transmission in anaerobic bacteria. Plasmid. 1987 Mar;17(2):87–109. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansegrau W., Lanka E. Common sequence motifs in DNA relaxases and nick regions from a variety of DNA transfer systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3455–3455. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansegrau W., Ziegelin G., Lanka E. Covalent association of the traI gene product of plasmid RP4 with the 5'-terminal nucleotide at the relaxation nick site. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10637–10644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privitera G., Dublanchet A., Sebald M. Transfer of multiple antibiotic resistance between subspecies of Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):97–101. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashtchian A., Dubes G. R., Booth S. J. Transferable resistance to cefoxitin in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):701–703. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen J. L., Odelson D. A., Macrina F. L. Complete nucleotide sequence of insertion element IS4351 from Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3573–3580. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3573-3580.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Tally F. P., Malamy M. H. Tn4400, a compound transposon isolated from Bacteroides fragilis, functions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1248–1255. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1248-1255.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Shoemaker N. B., Guthrie E. P. Recent advances in Bacteroides genetics. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(1):49–71. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Getty C., Guthrie E. P., Salyers A. A. Regions in Bacteroides plasmids pBFTM10 and pB8-51 that allow Escherichia coli-Bacteroides shuttle vectors to be mobilized by IncP plasmids and by a conjugative Bacteroides tetracycline resistance element. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):959–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.959-965.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Macrina F. L. Large transmissible clindamycin resistance plasmid in Bacteroides ovatus. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):739–741. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.739-741.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Cuchural G. J., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L., Aldridge K. E., Cleary T. J., Finegold S. M., Hill G. B., Iannini P. B., McCloskey R. V. Susceptibility of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United States in 1981. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):536–540. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Snydman D. R., Gorbach S. L., Malamy M. H. Plasmid-mediated, transferable resistance to clindamycin and erythromycin in Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):83–88. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Malamy M. H. Sequencing the gene for an imipenem-cefoxitin-hydrolyzing enzyme (CfiA) from Bacteroides fragilis TAL2480 reveals strong similarity between CfiA and Bacillus cereus beta-lactamase II. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2584–2593. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2584-2593.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters V. L., Hirata K. H., Pansegrau W., Lanka E., Guiney D. G. Sequence identity in the nick regions of IncP plasmid transfer origins and T-DNA borders of Agrobacterium Ti plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1456–1460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Jones K. R., Macrina F. L. Transferable lincosamide-macrolide resistance in Bacteroides. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegelin G., Fürste J. P., Lanka E. TraJ protein of plasmid RP4 binds to a 19-base pair invert sequence repetition within the transfer origin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11989–11994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



