Abstract
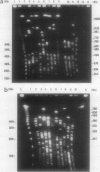
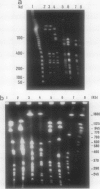
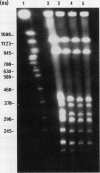
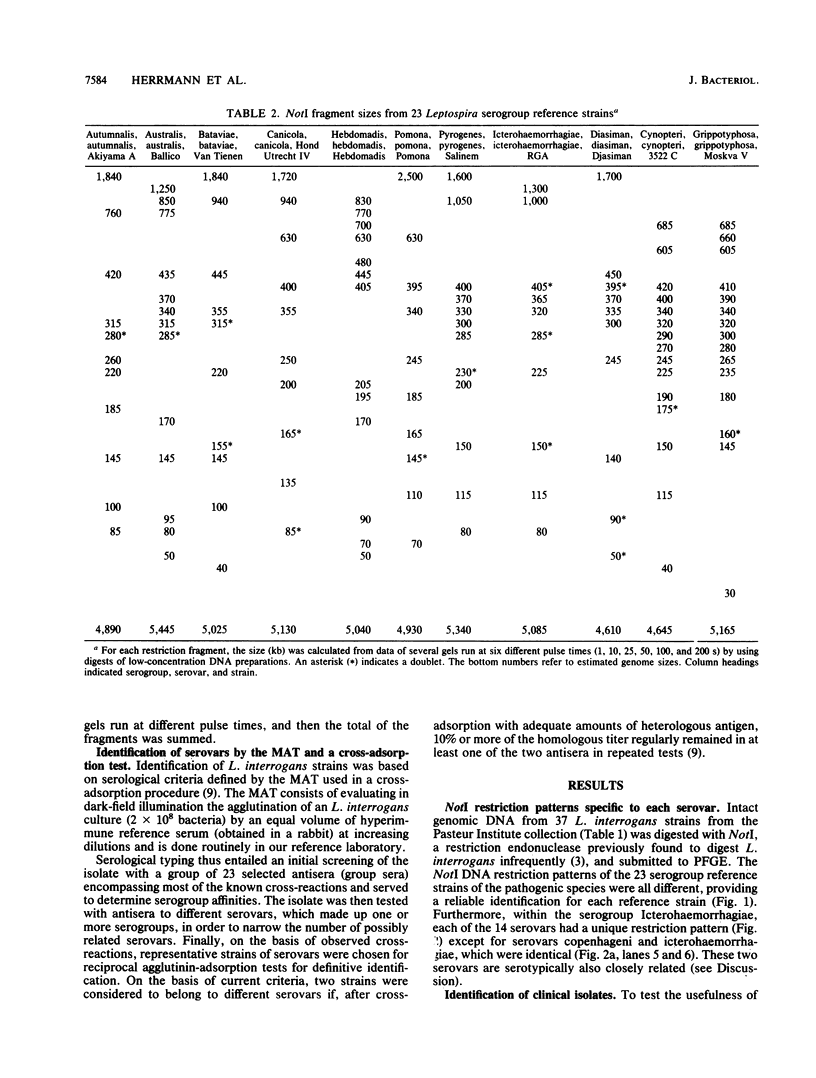
Reference strains for each of the 23 serogroups of Leptospira interrogans yielded different pulsed-field gel electrophoresis patterns of NotI digestion products. This was also the case for the 14 serovars belonging to serogroup Icterohaemorrhagiae (with one exception). The NotI restriction patterns of 45 clinical leptospiral isolates belonging to serovar icterohaemorrhagiae were analyzed and compared with those of type strains. No differences were observed between isolates from countries of different continents, namely, France, French Guiana, New Caledonia, and Tahiti. The pattern was indistinguishable from that of the reference strain of serovar icterohaemorrhagiae.
Full text
PDF

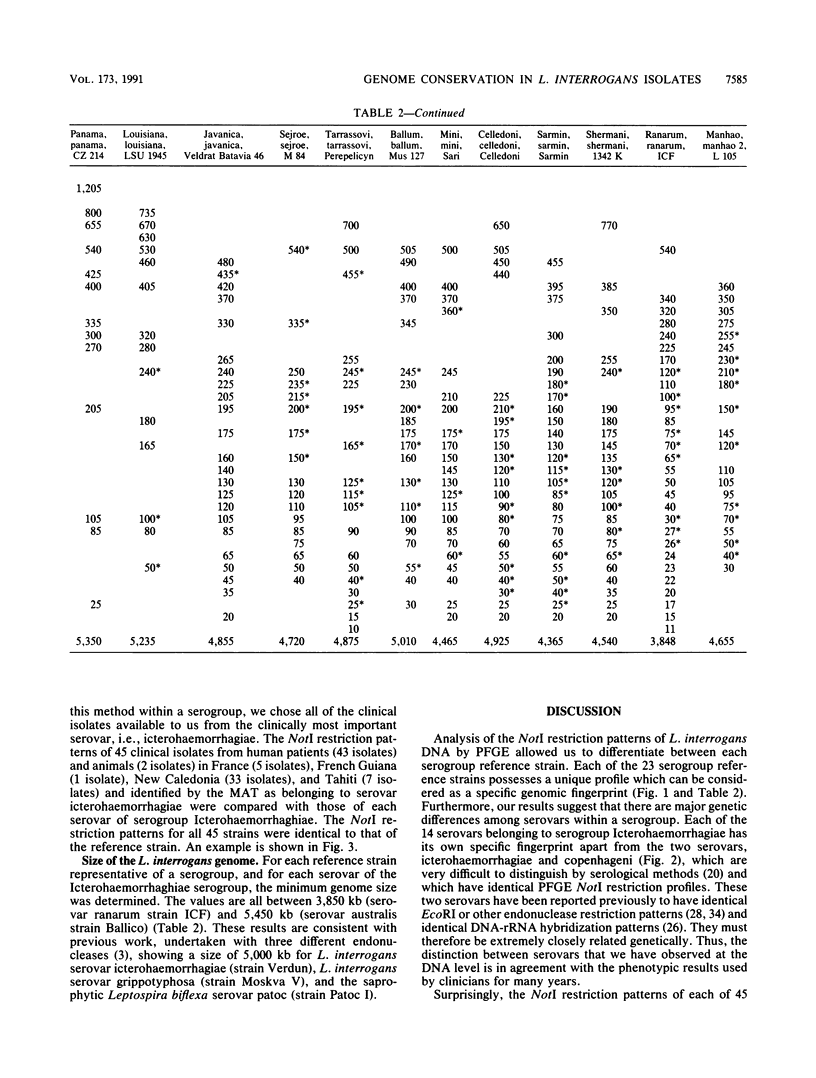
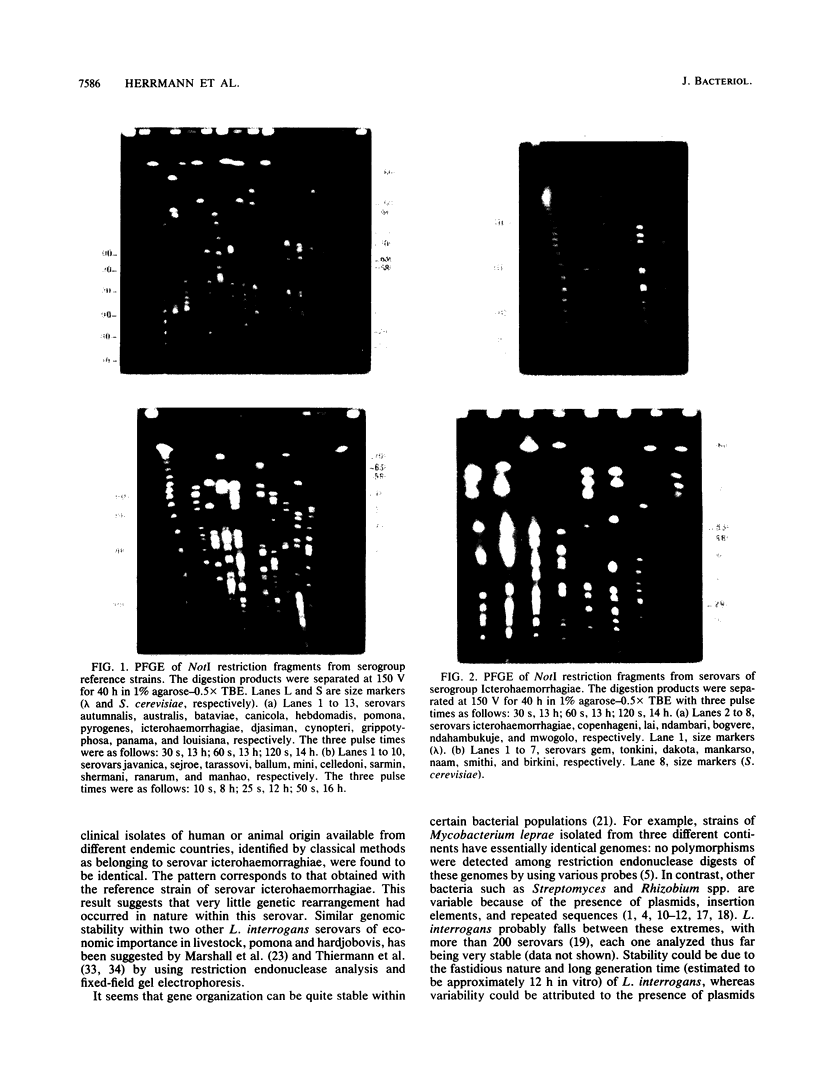


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenbuchner J., Cullum J. DNA amplification and an unstable arginine gene in Streptomyces lividans 66. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):134–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00332735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baril C., Richaud C., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. S. Linear chromosome of Borrelia burgdorferi. Res Microbiol. 1989 Oct;140(8):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry J. O., Atherly A. G. Induced plasmid-genome rearrangements in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):218–224. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.218-224.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Walsh G. P. Conservation of genomic sequences among isolates of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4844–4851. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4844-4851.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLINGHAUSEN H. C., Jr, MCCULLOUGH W. G. NUTRITION OF LEPTOSPIRA POMONA AND GROWTH OF 13 OTHER SEROTYPES: FRACTIONATION OF OLEIC ALBUMIN COMPLEX AND A MEDIUM OF BOVINE ALBUMIN AND POLYSORBATE 80. Am J Vet Res. 1965 Jan;26:45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. A., Montgomery J. M., Thiermann A. B. Restriction endonuclease analysis as a taxonomic tool in the study of pig isolates belonging to the Australis serogroup of Leptospira interrogans. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):957–961. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.957-961.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Brom S., Martínez E., Piñero D., Romero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Reiterated DNA sequences in Rhizobium and Agrobacterium spp. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5782–5788. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5782-5788.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Pardo M. A., Leija A., Martínez E., Romero D., Piñero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Genomic instability in Rhizobium phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1191–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1191-1196.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa M., Hintermann G., Simonet J. M., Crameri R., Piret J., Hütter R. Certain chromosomal regions in Streptomyces glaucescens tend to carry amplifications and deletions. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(3):375–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00425720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway S. C., Marshall R. B., Little T. W., Headlam S. A., Winter P. J. Differentiation of reference strains of leptospires of the Pomona serogroup by cross-agglutination absorption and restriction endonuclease analysis. Res Vet Sci. 1985 Sep;39(2):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hookey J. V. The detection of genetic variation in Leptospira interrogans serogroup ICTEROHAEMORRHAGIAE by ribosomal RNA gene restriction fragment patterns. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Nov;60(3):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90326-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Differentiation of pathogenic and saprophytic letospires. I. Growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.27-31.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza K., Hahn M., Hennecke H. Repeated sequences similar to insertion elements clustered around the nif region of the Rhizobium japonicum genome. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):535–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.535-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinashi H., Shimaji M., Sakai A. Giant linear plasmids in Streptomyces which code for antibiotic biosynthesis genes. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):454–456. doi: 10.1038/328454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Tamai T., Oyama T., Hasegawa H., Sada E., Kusaba T., Hamaji M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against etiological agents of Weil's disease. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(3):359–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawiec S., Riley M. Organization of the bacterial chromosome. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):502–539. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.502-539.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Febvre R. B., Thiermann A. B. DNA homology studies of leptospires of serogroups Sejroe and Pomona from cattle and swine. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Apr;47(4):959–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. B., Wilton B. E., Robinson A. J. Identification of Leptospira serovars by restriction-endonuclease analysis. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):163–166. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. N., Armstrong C. H., Nielsen N. C. Relationship among selected Leptospira interrogans serogroups as determined by nucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2724–2729. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2724-2729.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérolat P., Grimont F., Regnault B., Grimont P. A., Fournié E., Thevenet H., Baranton G. rRNA gene restriction patterns of Leptospira: a molecular typing system. Res Microbiol. 1990 Feb;141(2):159–171. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90025-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. J., Ramadass P., Lee A., Marshall R. B. Differentiation of subtypes within Leptospira interrogans serovars Hardjo, Balcanica and Tarassovi, by bacterial restriction-endonuclease DNA analysis (BRENDA). J Med Microbiol. 1982 Aug;15(3):331–338. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-3-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai T., Sada E., Kobayashi Y. Restriction endonuclease DNA analysis of Leptospira interrogans serovars Icterohaemorrhagiae and Copenhageni. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(9):887–894. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Barbour A. G., Thomas D. D. Pulsed-field gel electrophoretic analysis of leptospiral DNA. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):323–329. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.323-329.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpstra W. J., Korver H., Schoone G. J., von Leeuwen J., Schönemann C. E., de Jonge-Aglibut S., Kolk A. H. Comparative classification of Leptospira serovars of the Pomona group by monoclonal antibodies and restriction-endonuclease analysis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Oct;266(3-4):412–421. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpstra W. J., Schoone G. J., ter Schegget J. Detection of leptospiral DNA by nucleic acid hybridisation with 32P- and biotin-labelled probes. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Aug;22(1):23–28. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Foley J. W., White F. H., Kingscote B. F. Reclassification of North American leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroups Mini and Sejroe by restriction endonuclease analysis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;47(1):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Moseley S. L., Kingscote B. New method for classification of leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroup pomona by restriction endonuclease analysis: serovar kennewicki. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.585-587.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eys G. J., Gerritsen M. J., Korver H., Schoone G. J., Kroon C. C., Terpstra W. J. Characterization of serovars of the genus Leptospira by DNA hybridization with hardjobovis and icterohaemorrhagiae recombinant probes with special attention to serogroup sejroe. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):1042–1048. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.1042-1048.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eys G. J., Zaal J., Schoone G. J., Terpstra W. J. DNA hybridization with hardjobovis-specific recombinant probes as a method for type discrimination of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):567–574. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-3-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Bolin C. A. Nucleic acid probe characterizes Leptospira interrogans serovars by restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Sep;24(3-4):355–366. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90183-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Bolin C. A. Repetitive sequence element cloned from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo type hardjo-bovis provides a sensitive diagnostic probe for bovine leptospirosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2495–2500. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2495-2500.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]