Abstract
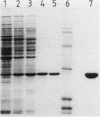
The haloacid dehalogenase of the 1,2-dichloroethane-utilizing bacterium Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10 was purified from a mutant with an eightfold increase in expression of the enzyme. The mutant was obtained by selecting for enhanced resistance to monobromoacetate. The enzyme was purified through (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, DEAE-cellulose chromatography, and hydroxylapatite chromatography. The molecular mass of the protein was 28 kDa as determined with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and 36 kDa as determined with gel filtration on Superose 12 fast protein liquid chromatography. The enzyme was active with 2-halogenated carboxylic acids and converted only the L-isomer of 2-chloropropionic acid with inversion of configuration to produce D-lactate. The activity of the enzyme was not readily influenced by thiol reagents. The gene encoding the haloacid dehalogenase (dhlB) was cloned and could be allocated to a 6.5-kb EcoRI-BglII fragment. Part of this fragment was sequenced, and the dhlB open reading frame was identified by comparison with the N-terminal amino acid sequence of the protein. The gene was found to encode a protein of 27,433 Da that showed considerable homology (60.5 and 61.0% similarity) with the two other haloacid dehalogenases sequenced to date but not with the haloalkane dehalogenase from X. autotrophicus GJ10.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franken S. M., Rozeboom H. J., Kalk K. H., Dijkstra B. W. Crystal structure of haloalkane dehalogenase: an enzyme to detoxify halogenated alkanes. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1297–1302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07647.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman P., Milne G. W., Keister D. B. Carbon-halogen bond cleavage. 3. Studies on bacterial halidohrolases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 25;243(2):428–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen D. B., Pries F., van der Ploeg J., Kazemier B., Terpstra P., Witholt B. Cloning of 1,2-dichloroethane degradation genes of Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10 and expression and sequencing of the dhlA gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6791–6799. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6791-6799.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen D. B., Scheper A., Dijkhuizen L., Witholt B. Degradation of halogenated aliphatic compounds by Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):673–677. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.673-677.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keuning S., Janssen D. B., Witholt B. Purification and characterization of hydrolytic haloalkane dehalogenase from Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):635–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.635-639.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klages U., Krauss S., Lingens F. 2-Haloacid dehalogenase from a 4-chlorobenzoate-degrading Pseudomonas spec. CBS 3. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 May;364(5):529–535. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.1.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little M., Williams P. A. A bacterial halidohydrolase. Its purification, some properties and its modification by specific amino acid reagents. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 15;21(1):99–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01445.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Jr, Nguyen N. Y., Liu T. Y. Reproducible high yield sequencing of proteins electrophoretically separated and transferred to an inert support. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6005–6008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motosugi K., Esaki N., Soda K. Purification and properties of a new enzyme, DL-2-haloacid dehalogenase, from Pseudomonas sp. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):522–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.522-527.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozeboom H. J., Kingma J., Janssen D. B., Dijkstra B. W. Crystallization of haloalkane dehalogenase from Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):611–612. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90548-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B., Müller R., Frank R., Lingens F. Complete nucleotide sequences and comparison of the structural genes of two 2-haloalkanoic acid dehalogenases from Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1530–1535. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1530-1535.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. H., Weightman A. J., Hall B. G. Dehalogenase genes of Pseudomonas putida PP3 on chromosomally located transposable elements. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Nov;2(6):557–567. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Harrison K., Colby J. Purification and characterization of D-2-haloacid dehalogenase from Pseudomonas putida strain AJ1/23. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 May;136(5):881–886. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-5-881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staskawicz B., Dahlbeck D., Keen N., Napoli C. Molecular characterization of cloned avirulence genes from race 0 and race 1 of Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5789–5794. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5789-5794.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardif G., Greer C. W., Labbé D., Lau P. C. Involvement of a large plasmid in the degradation of 1,2-dichloroethane by Xanthobacter autotrophicus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1853–1857. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1853-1857.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weightman A. J., Weightman A. L., Slater J. H. Stereospecificity of 2-monochloropropionate dehalogenation by the two dehalogenases of Pseudomonas putida PP3: evidence for two different dehalogenation mechanisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Aug;128(8):1755–1762. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-8-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weightman A. J., Weightman A. L., Slater J. H. Toxic effects of chlorinated and brominated alkanoic acids on Pseudomonas putida PP3: selection at high frequencies of mutations in genes encoding dehalogenases. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1494–1501. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1494-1501.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Wijngaard A. J., Reuvekamp P. T., Janssen D. B. Purification and characterization of haloalcohol dehalogenase from Arthrobacter sp. strain AD2. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.124-129.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]