Abstract
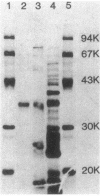
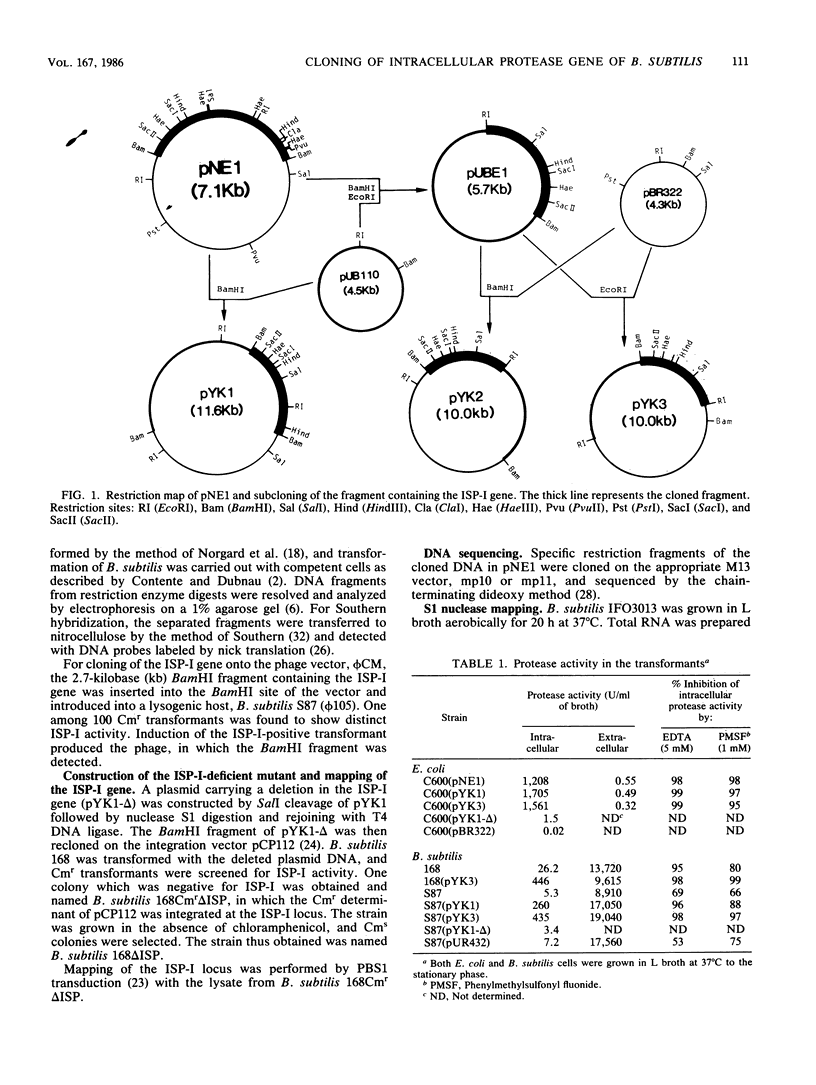
A Bacillus subtilis 2.7-kilobase DNA fragment containing an intracellular protease gene was cloned into Escherichia coli. The transformants produced an intracellular protease of approximately 35,000 Mr whose activity was inhibited by both phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride and EDTA. Introduction of the fragment on a multicopy vector, pUB110, into B. subtilis caused a marked increase in the level of the intracellular protease. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned fragment showed the presence of an open reading frame for a possible proenzyme of the major intracellular serine protease (ISP-I) of B. subtilis with an NH2-terminal 17- or 20-amino-acid extension. The total amino acid sequence of the protease deduced from the nucleotide sequence showed considerable homology with that of an extracellular serine protease, subtilisin. The transcriptional initiation site of the ISP-I gene was identified by nuclease S1 mapping. No typical conserved sequence for promoters was found upstream of the open reading frame. An ISP-I-negative mutant of B. subtilis was constructed by integration of artificially deleted gene into the chromosome. The mutant sporulated normally in a nutritionally rich medium but showed decreased sporulation in a synthetic medium. The chloramphenicol resistance determinant of a plasmid integrated at the ISP-I locus was mapped by PBS1 transduction and was found to be closely linked to metC (99.5%).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyagi T., Takeuchi T., Matsuzaki A., Kawamura K., Kondo S. Leupeptins, new protease inhibitors from Actinomycetes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Jun;22(6):283–286. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of plasmid transformation in Bacillus subtilis: kinetic properties and the effect of DNA conformation. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 2;167(3):251–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00267416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Vapnek D. A simple method of preparing large amounts of phiX174 RF 1 supercoiled DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):516–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman J. H., Carlton B. C. Effects of mutational loss of specific intracellular proteases on the sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):612–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.612-617.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Analysis of endonuclease R-EcoRI fragments of DNA from lambdoid bacteriophages and other viruses by agarose-gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1235–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1235-1244.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezawa H., Aoyagi T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Effect of protease inhibitors of actinomycetes on lysosomal peptide-hydrolases from swine liver. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Jul;24(7):488–490. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. C., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Two RNA polymerase sigma factors from Bacillus subtilis discriminate between overlapping promoters for a developmentally regulated gene. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):800–804. doi: 10.1038/302800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjan P., Keryer E., Szulmajster J. Characterization of a thermosensitive sporulation mutant of Bacillus subtilis affected in the structural gene of an intracellular protease. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):353–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurotsu T., Marahiel M. A., Müller K. D., Kleinkauf H. Characterization of an intracellular serine protease from sporulating cells of Bacillus brevis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1466–1472. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1466-1472.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtovaara P., Ulmanen I., Palva I. In vivo transcription initiation and termination sites of an alpha-amylase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens cloned in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelstam J., Waites W. M. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. The role of exoprotease. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):793–801. doi: 10.1042/bj1090793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz L., Sadaie Y., Doi R. H. Spore coat protein of Bacillus subtilis. Structure and precursor synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6694–6701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T., Munoz L. E., Sadaie Y., Doi R. H. Spore coat protein synthesis in cell-free systems from sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):952–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.952-960.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neway J. O., Switzer R. L. Degradation of ornithine transcarbamylase in sporulating Bacillus subtilis cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):522–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.522-530.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Keem K., Monahan J. J. Factors affecting the transformation of Escherichia coli strain chi1776 by pBR322 plasmid DNA. Gene. 1978 Jul;3(4):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi K., Kandala J. C., Freese E. Initiation of Bacillus subtilis sporulation by the stringent response to partial amino acid deprivation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6866–6875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulus T. J., Switzer R. L. Synthesis and inactivation of carbamyl phosphate synthetase isozymes of Bacillus subtilis during growth and sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):769–773. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.769-773.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestidge L., Gage V., Spizizen J. Protease activities during the course of sporulation on Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):815–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.815-823.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. W., Doi R. H. Genetic mapping of rpoD implicates the major sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase in sporulation initiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(1):88–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00397991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. W., Gitt M. A., Doi R. H. Isolation and physical mapping of the gene encoding the major sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4074–4078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reysset G., Millet J. Characterization of an intracellular protease in B. subtillus during sporulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry K. J., Srivastava O. P., Millet J., FitzJames P. C., Aronson A. I. Characterization of Bacillus subtilis mutants with a temperature-sensitive intracellular protease. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):511–519. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.511-519.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germaination. VII. Protein turnover during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4600–4605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava O. P., Aronson A. I. Isolation and characterization of a unique protease from sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis. Arch Microbiol. 1981 May;129(3):227–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00425256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strongin A. Y., Izotova L. S., Abramov Z. T., Gorodetsky D. I., Ermakova L. M., Baratova L. A., Belyanova L. P., Stepanov V. M. Intracellular serine protease of Bacillus subtilis: sequence homology with extracellular subtilisins. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1401–1411. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1401-1411.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Aoyagi T., Morishima H., Kunimoto S., Matsuzaki M. Chymostatin, a new chymotrypsin inhibitor produced by actinomycetes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Aug;23(8):425–427. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]