Abstract
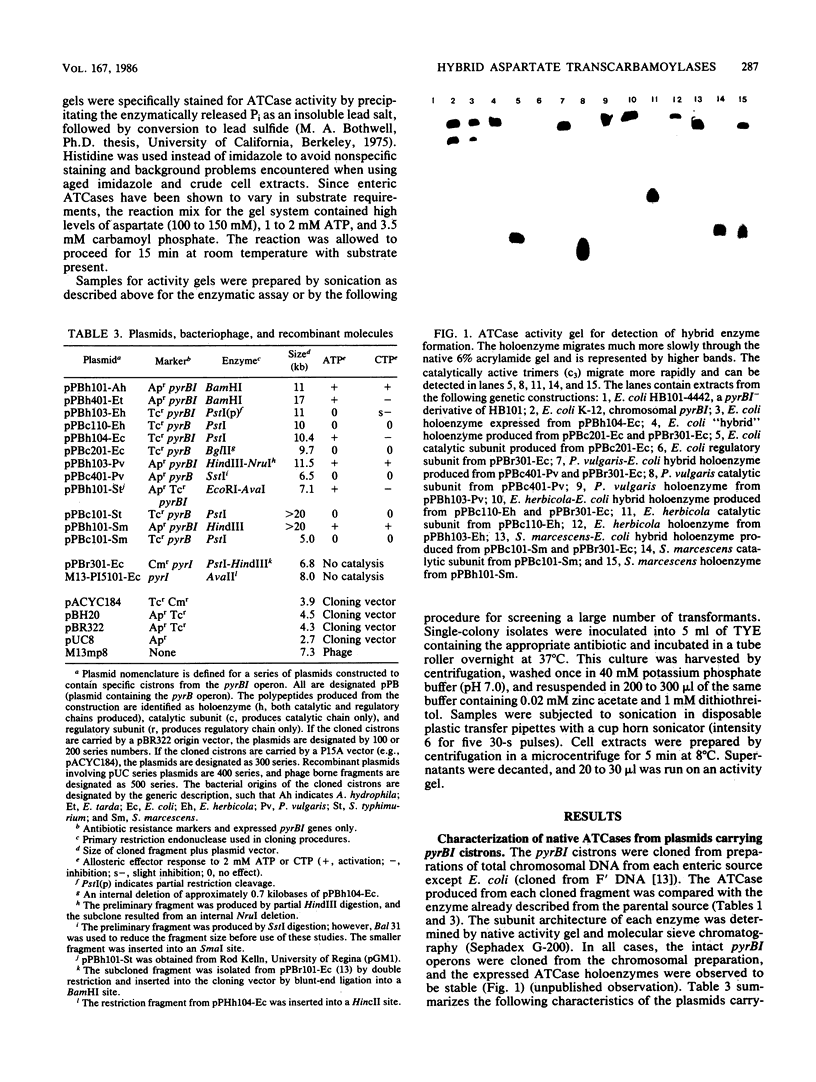
The genes encoding the catalytic (pyrB) and regulatory (pyrI) polypeptides of aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase, EC 2.1.3.2) from several members of the family Enterobacteriaceae appear to be organized as bicistronic operons. The pyrBI gene regions from several enteric sources were cloned into selected plasmid vectors and expressed in Escherichia coli. Subsequently, the catalytic cistrons were subcloned and expressed independently from the regulatory cistrons from several of these sources. The regulatory cistron of E. coli was cloned separately and expressed from lac promoter-operator vectors. By utilizing plasmids from different incompatibility groups, it was possible to express catalytic and regulatory cistrons from different bacterial sources in the same cell. In all cases examined, the regulatory and catalytic polypeptides spontaneously assembled to form stable functional hybrid holoenzymes. This hybrid enzyme formation indicates that the r:c domains of interaction, as well as the dodecameric architecture, are conserved within the Enterobacteriaceae. The catalytic subunits of the hybrid ATCases originated from native enzymes possessing varied responses to allosteric effectors (CTP inhibition, CTP activation, or very slight responses; and ATP activation or no ATP response). However, each of the hybrid ATCases formed with regulatory subunits from E. coli demonstrated ATP activation and CTP inhibition, which suggests that the allosteric control characteristics are determined by the regulatory subunits.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNS K. I., THOMAS C. A., Jr ISOLATION OF HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT DNA FROM HEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:476–490. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. Plasmid detection and sizing in single colony lysates. Science. 1977 Jan 28;195(4276):393–394. doi: 10.1126/science.318764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethell M. R., Jones M. E. Molecular size and feedback-regulation characteristics of bacterial asartate transcarbamulases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Nov;134(2):352–365. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethell M. R., Smith K. E., White J. S., Jones M. E. Carbamyl phosphate: an allosteric substrate for aspartate transcarbamylase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1442–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. A., Schachman H. K. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of the association of catalytic and regulatory subunits of aspartate transcarbamoylase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1962–1970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Lactose genes fused to exogenous promoters in one step using a Mu-lac bacteriophage: in vivo probe for transcriptional control sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4530–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. W. On the mechanism of assembly of the aspartate transcarbamoylase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct;90(2):271–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. W. Subunit interactions in aspartate transcarbamylase. A model for the allosteric mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deonier R. C., Mirels L. Excision of F plasmid sequences by recombination at directly repeated insertion sequence 2 elements: involvement of recA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3965–3969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foltermann K. F., Shanley M. S., Wild J. R. Assembly of the aspartate transcarbamoylase holoenzyme from transcriptionally independent catalytic and regulatory cistrons. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):891–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.891-898.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHART J. C., PARDEE A. B. The enzymology of control by feedback inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Holoubek H. The purification of aspartate transcarbamylase of Escherichia coli and separation of its protein subunits. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2886–2892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Distinct subunits for the regulation and catalytic activity of aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1054–1062. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honzatko R. B., Crawford J. L., Monaco H. L., Ladner J. E., Ewards B. F., Evans D. R., Warren S. G., Wiley D. C., Ladner R. C., Lipscomb W. N. Crystal and molecular structures of native and CTP-liganded aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):219–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. A., Roof W. D., Foltermann K. F., O'Donovan G. A., Bencini D. A., Wild J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the structural gene (pyrB) that encodes the catalytic polypeptide of aspartate transcarbamoylase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2462–2466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Hirose T., Crea R., Riggs A. D., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Boyer H. W. Expression in Escherichia coli of a chemically synthesized gene for the hormone somatostatin. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1056–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.412251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. L., Volz K. W., Lipscomb W. N. Structure at 2.9-A resolution of aspartate carbamoyltransferase complexed with the bisubstrate analogue N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1643–1647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makoff A. J., Radford A. Genetics and biochemistry of carbamoyl phosphate biosynthesis and its utilization in the pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):307–328. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.307-328.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco H. L., Crawford J. L., Lipscomb W. N. Three-dimensional structures of aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Escherichia coli and of its complex with cytidine triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5276–5280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navre M., Schachman H. K. Synthesis of aspartate transcarbamoylase in Escherichia coli: transcriptional regulation of the pyrB-pyrI operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1207–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan G. A., Holoubek H., Gerhart J. C. Regulatory properties of intergeneric hybrids of aspartate transcarbamylase. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 30;238(87):264–266. doi: 10.1038/newbio238264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan G. A., Neuhard J. Pyrimidine metabolism in microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Sep;34(3):278–343. doi: 10.1128/br.34.3.278-343.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza C. D., Karels M. J., Navre M., Schachman H. K. Genes encoding Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase: the pyrB-pyrI operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4020–4024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof W. D., Foltermann K. F., Wild J. R. The organization and regulation of the pyrBI operon in E. coli includes a rho-independent attenuator sequence. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(3):391–400. doi: 10.1007/BF00332617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P., Weber K. Localization of the zinc binding site of aspartate transcarbamoylase in the regulatory subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1019–1023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachman H. K. Assembly of aspartate transcarbamoylase in Escherichia coli. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1983;41:199–211. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1983.tb02802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachman H. K., Pauza C. D., Navre M., Karels M. J., Wu L., Yang Y. R. Location of amino acid alterations in mutants of aspartate transcarbamoylase: Structural aspects of interallelic complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):115–119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanley M. S., Foltermann K. F., O'Donovan G. A., Wild J. R. Properties of hybrid aspartate transcarbamoylase formed with native subunits from divergent bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12672–12677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbough C. L., Jr, Hicks K. L., Donahue J. P. Attenuation control of pyrBI operon expression in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):368–372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. New structural model of E. coli aspartate transcarbamylase and the amino-acid sequence of the regulatory polypeptide chain. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1116–1119. doi: 10.1038/2181116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild J. R., Belser W. L., O'Donovan G. A. Unique aspects of the regulation of the aspartate transcarbamylase of Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;128(3):766–775. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.3.766-775.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild J. R., Foltermann K. F., O'Donovan G. A. Regulatory divergence of aspartate transcarbamoylases within the enterobacteriaceae. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 May;201(2):506–517. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild J. R., Foltermann K. F., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. A mutation in the catalytic cistron of aspartate carbamoyltransferase affecting catalysis, regulatory response and holoenzyme assembly. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):373–375. doi: 10.1038/292373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. R., Kirschner M. W., Schachman H. K. Aspartate transcarbamoylase (Escherichia coli): preparation of subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1978;51:35–41. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)51007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]